12 diet & exercise tips for prostate health
What is Prostate Dysfunction?
Prostate dysfunction, also known as prostate disease, is a general term referring to any abnormality or disorder in the prostate gland which can affect both men and women. Prostate diseases may be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Prostate dysfunction affects the physical and mental health of an individual due to its involvement in urination, ejaculation, sexual pleasure and other important bodily functions.
What are the signs and symptoms of Prostate Dysfunction?
Depending on the underlying cause, the symptoms of prostate dysfunction might vary, but they can include the following:
- Difficulty starting or maintaining urination.
- A weak flow of urine.
- Urinating more frequently, particularly at night.
- Burning or pain during urination.
- There was blood in either the pee or the sperm.
- Discomfort and stiffness in the buttocks, hips, or upper thighs may be present.
- Painful ejaculation
- Difficulty achieving an orgasm.
What are possible complications of Prostate Dysfunction?
Prostate dysfunction can affect the urinary system, reproductive system, and general health. Complications of prostate dysfunction can include:
- Urinary incontinence: Prostate enlargement or blockages in the urethra caused by prostate dysfunction can make it difficult to completely empty the bladder. As a result, men may experience urinary incontinence or leaking urine unintentionally.
- Urinary retention: Urinary retention is the condition in which a person is unable to completely empty their bladder. It is possible for it to create a strong urge to urinate frequently as well as trouble completely emptying the bladder, which can lead to pain and discomfort.
- Anejaculation: Prostate enlargement or blockages caused by prostate dysfunction can inhibit semen from being fully released during ejaculation. This is known as anejaculation and it can be associated with painful orgasms or even inability to achieve orgasm.
- Infertility: Some cases of prostate malfunctioning have been linked to infertility in men due to the inability to produce adequate amounts of healthy sperm that’s necessary for fertilisation.
- Sexual Dysfunction: Erectile dysfunction (ED) is one of the more common complications associated with prostate diseases such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). ED refers to difficulty maintaining an erection sufficient for intercourse despite adequate stimulation from a partner. Additionally, low libido (reduced sexual desire) has been observed in patients with diagnoses such as BPH and prostatitis, which are two types of chronic prostatitis that refers to inflammation of the male reproductive organ-the prostate gland.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Depending on severity, some individuals experiencing problems related to their prostate may need surgeries that require catheters or other devices inserted through their urethra—a potential entry point into the body for bacteria causing UTIs such as E Coli and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa if precautions aren’t taken properly after surgery.
12 diet & exercise tips for prostate health
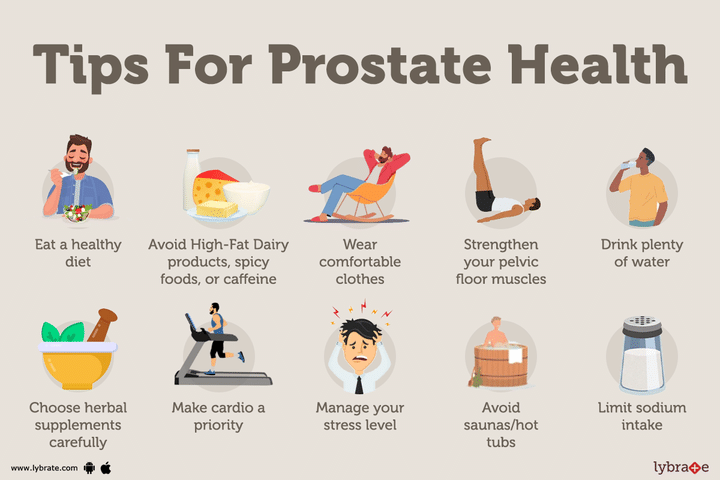
- Eat a healthy diet: Consume a diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Incorporate plenty of fiber in your diet which can help improve prostate health.
- Avoid some foods: The following foods should be avoided:
- Foods such as high-fat dairy products, processed meats and red meat which have been linked to an increased risk of prostate dysfunction issues such as enlargement and cancer risk.
- Avoid spicy foods as they may irritate the bladder or colon which can be problematic for those with prostate problems.
- Limit or avoid caffeine, alcohol and sugary beverages as they can increase inflammation in the prostate gland.
- Wear comfortable clothes: Wear loose fitting clothing around the waist area especially when doing exercise activities so you don’t trap any excessive heat near your groin region where the Prostate Gland is located.
- Strengthen Your Pelvic Floor Muscles: These muscles help control your bladder and improve erectile function in men with prostate issues. Consider adding pelvic floor exercises (such as Kegels) to your workout routine for additional prostate benefits. These can be performed during any seated position- no equipment necessary!
- Drink plenty of water: Maintaining a healthy level of hydration in the body is critical to one's overall health, including the health of the prostate. Consume a lot of water to keep your urine clear and to assist your body in eliminating toxins through the urinary tract.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Alcohol can irritate the bladder, which may lead to prostate problems over time if consumed regularly in large amounts.
- Choose herbal supplements carefully: Some herbal supplements such as saw palmetto have been used to reduce symptoms of enlarged prostate, but should be taken only after consulting with a medical professional.
- Make Cardio a Priority: A consistent cardio routine improves overall prostate health, reducing the risk of developing an enlarged prostate or even cancer. Aim for 30 minutes of aerobic activity 4-5 times per week, such as brisk walking, running, or cycling. This helps keep your heart healthy while also promoting optimal function of the glands within the reproductive system.
- Stress reduction techniques: Managing stress levels through relaxation techniques such as yoga and meditation helps promote overall well-being that includes improved prostate health.
- Get plenty of sleep: Sleep helps the body repair itself, both mentally and physically, so make sure you’re getting enough rest each night to give your body its opportunity for repair work.
- Avoid saunas/hot tubs or continually sitting with crossed legs as these may heat up the area around your groin leading to irritation to your prostate gland.
- Limit sodium intake: Reduce your sodium intake as it can increase the risk of prostate dysfunction.
In the event that the strategies described above are unsuccessful in alleviating your symptoms, you may be required to undergo surgical procedures.
What are the surgical treatments for Prostate Dysfunction?
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): This procedure involves the removal of prostate tissue using an endoscope that is inserted through the urethra.
- Prostate Adenomectomy: This is a surgical procedure for removing noncancerous benign tumors from the prostate gland.
- Open Prostatectomy: This invasive procedure involves removing part or all of the prostate gland through an incision in the abdomen or lower back.
- Laparoscopic Prostatectomy: A minimally invasive, keyhole surgery that is performed by making small incisions in the abdominal wall and using a thin, lighted tube (laparoscope) to examine and remove diseased tissue from inside the prostate.
- Cryotherapy: This treatment option uses extreme cold to freeze and destroy tumors in the prostate gland, often with just one treatment session.
- High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU): HIFU uses sound waves to destroy cancerous cells within the prostate gland while avoiding damaging healthy surrounding tissue.
Best doctors to consult for Prostate Dysfunction
It is recommended that men with suspected prostate dysfunction consult a urologist.
- Urologist: A urologist specializes in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases that affect the male and female urinary tract system, including prostate disorders.
- Prostate Oncologist: A prostate oncologist is a physician who specializes in treating cancerous conditions of the prostate.
- Oncological Surgeon: An oncological surgeon is a doctor who specializes in performing surgeries for cancer-related disorders, including surgeries for prostate cancer.
- Radiation Oncologist: A radiation oncologist is a doctor who specializes in treating cancers with radiation therapy. This type of doctor may be involved with treatments that involve radiation for prostate cancers as well.
- Integrative Medicine Doctor: An integrative medicine doctor focuses on combining different elements of health care, such as nutrition and lifestyle changes, to treat disease or symptoms related to them.


+1.svg)
