3 Symptoms Of Hives
Hives or urticaria is an outbreak of reddish swollen bumps around the skin surface, formed mainly due to the body’s response to particular allergens. Generally, the infectious bumps are of varied shapes and sizes and last for about 5-6 weeks. Although not a serious medical condition, hives can cause tremendous discomfort to the concerned person and affect his/her daily activities. Hives can be cured with a prescribed dosage of antihistamines or oral corticosteroids.
Causes of hives
Although the exact reason behind their formation is still unknown, researchers suggest that this disorder occurs as a response to involuntary histamine release by the skin blood vessels (that in turn, causes a leakage of blood plasma). Some other factors that can be responsible are:
- Hives can occur due to insect or parasite bites.
- Hives can also result as a side effect of painkillers such as codeine and other anti- inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen or ACE inhibitors.
- Excessive exposure to sunlight or high levels of stress (leading to high cortisol levels in the body) can also result in hives.
- Intense scratching around the same spot can also result to hive formation.
- Excessive alcohol intake can render you even more vulnerable to this disease.
- Excessive intake of foods such as eggs, fish, nuts, chocolate and berries might also cause hives. Additionally, excessive consumption of certain food preservatives can also trigger the release of histamine.
- Suffering from serious underlying medical conditions such as cancer, hepatitis or thyroid disorders can make you prone to chronic cases of hives (which might last for more than 6 weeks).
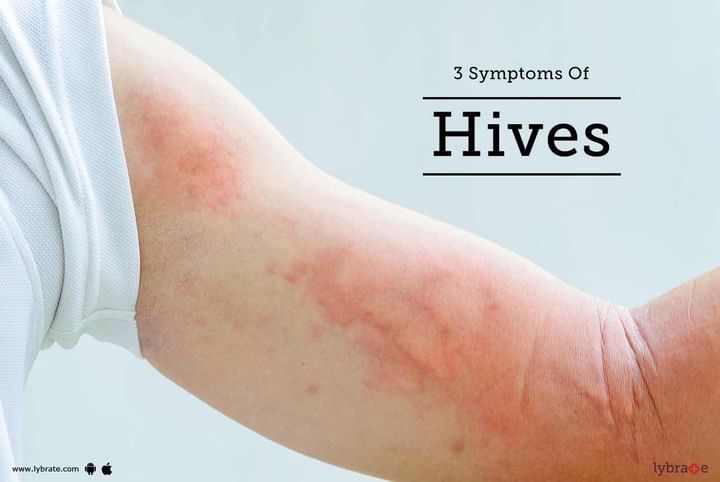
Symptoms of hives
The symptoms of hives include, but are not limited to:
- Appearances of several reddish welts around the face or arms which might cause a severe itchy sensation.
- Painful and abnormal swelling around the mouth
- You might also feel tightness in your chest along with recurring bouts of dizziness.
If not treated promptly after diagnosis, hives might result in life-threatening allergic reactions, such as Anaphylaxis (narrowing down of the bronchial tubes, thus causing significant breathing trouble) and auto-immune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis.


+1.svg)
