Aortic Stenosis - All You Must Know About It!
If the blood flow between left ventricle and aorta is obstructed, it is known as Aortic Stenosis.
Aortic stenosis can occur in newborn, infants, children and adolescents. It is more common among boys than in girls.
Mild cases of this disorder do not need treatment. However, if a child has a severe case of aortic stenosis, then it requires treatment.
Aortic stenosis: Causes-
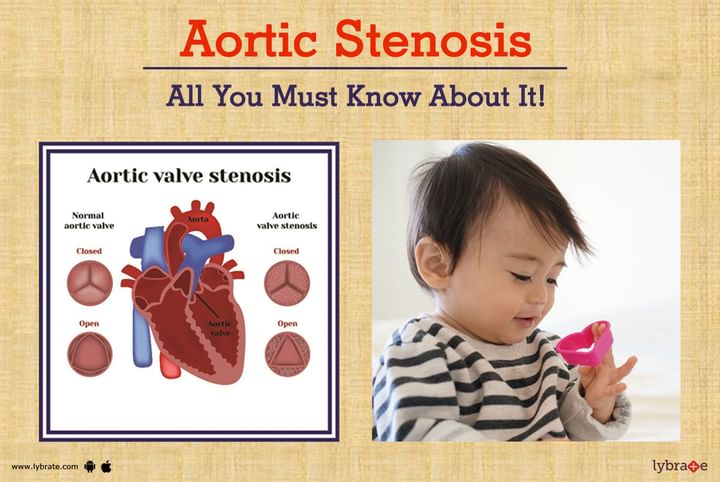
- Blockage in the valve, mainly in the form of bicuspid valve stenosis (Aortic valve stenosis)
- Muscular/fibrinous obstruction beneath the aortic valve (Subaortic stenosis)
- Narrowing above the aortic valve in aorta itself (Supravalvular aortic stenosis)
Aortic valves regulate blood flow to the body parts. When aortic valve opens, it allows blood to go forward then it closed down so that blood will not come back to left ventricle.
However, if there is a problem with the aortic valve, it cannot open entirely and that restricts the passage of blood. The heart has to work extra hard to ensure that the entire volume of blood flow through the faulty valve.
Sometimes babies are born with deformed aortic valve in the form of bicuspid aortic valve that is prone for obstruction as compared to normal trileaflet aortic valve.
Aortic Stenosis: Symptoms-
- Symptoms due to aortic stenos is depends on age of the child and its severity.
- If occurs in newborn babies, it is generally severe in intensity and babies are generally in shock like state due to low cardiac output.
- Infants are generally tired easily during feeding.
- Children show signs of easy fatigue, chest pain, loss of consciousness and in late stages with shortness of breath.
Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis-
- Pre-natal testing like a fetal echocardiogram can reveal aortic stenosis if moderate to severe in intensity. That is why as soon as the baby is born, treatment is initiated.
- Even if the child was not born with a problematic valve, this condition can arise a few years later.
- For diagnosing this disease pediatric echocardiogram by pediatric cardiologist needs to be done from the chest of the child
Treatment of Aortic Stenosis-
If aortic stenosis is mild to moderate in intensity then we need to do follow-up of the child at regular intervals.
However, in severe aortic stenosis, treatment needs to be done
In valvular aortic stenosis, treatment of choice is by doing ballooning of aortic valve (Balloon aortic valvuloplasty, BAV) in any age group.
- Balloon Aortic Valvuloplasty - This is not open-heart surgery. It is done in cardiac cath lab under fluoroscopic guidance by using vessels in thigh. We cross the valve with wire and catheters and we inflate a balloon across the stenosed aortic valve.
- Open heart surgery: In subvalvular and supravalvular aortic stenosis, treatment is by open heart surgery.
- Valve Replacement - An artificial valve or a donor valve is surgically attached at aortic valve location when valve is not amenable for ballooning. It is generally done in adolescent or adult patients.
Parents need to be alert and attentive to any physical discomfort that their child is suffering because that could be a symptom of aortic stenosis. The right treatment at the right time is necessary whenever required.


+1.svg)
