Athlete s Foot - Know More About Its Causes!
Athlete’s Foot
Athlete’s foot is a commonly occurring infection of the skin which is caused by fungus. The medical name of this condition is known as tinea pedis. It is a fungal infection which primarily affects the skin on the feet. It is a contagious condition. It might also spread to the toenails and the hands. The disease is named as athlete’s foot because it mostly affects athletes. This is not a serious condition but sometimes it can be hard to cure.
Any condition that causes inflammation of the skin and affects the skin between the toes and the sole of the foot is generally referred to as athlete’s foot. The condition presents itself as scaly, red and raw looking eruptions and sometimes it might also be oozing with small blisters. It can affect both athletes and non-athletes alike. It is caused fungal infections but there might be other causes also which can be distinguished through proper testing.
There are different kinds of fungi that might be responsible for causing athlete’s foot. Exposure to these fungi can happen at many places which include swimming pools, gyms, communal showers, locker rooms, nail salons and from contaminated clothing from an affected person. It is a contagious disease and can spread from contact from affected individual to non-affected individual. Majority of the people contract this disease by walking barefoot at the place where someone suffering from athlete’s foot has also walked barefoot. Some people can be more at risk than others for the disease while others might be resistant to the condition. This condition is also known by the name ‘Jungle Rot’. This is usually used by the members of the armed services serving in tropical climates.
Infections caused by different fungi are spread by moisture and warmth. It is believed that the condition of athlete’s foot was less prevalent before the advent of enclosed shoes. It was thought to be a rare condition and became more prevalent in the 1900s as more and more health clubs and shoes became popular. If an individual contracts this disease once, it does not guarantee resistance from subsequently occurring infections.
Globally, this condition occurs in about 15% of the population. Males are more likely to develop this disease than females. Older children and younger adults are more often affected. This condition is treatable by the use of over the counter antifungal medicines. Prescription medicines are also available.
What does athlete’s foot look like?
Athlete’s foot caused by fungal infections leads to rashes on one or both the feet and can also affect the hands. Marks or rashes on two feet and one hand is a common characteristic of the presentation of athlete’s foot especially in men. Fungal athlete’s foot can also cause ringworm of the groin which is mostly seen in men or can cause ringworm on the hands. The fungal infections on the hands are known as tinea manuum. All areas affected by fungal infection should be treated simultaneously to decrease the risk of re-infection.
Risk factors of Athlete’s foot-
Some risk factors for developing athlete’s foot include walking barefoot in areas like communal showers, indoor swimming pools, locker rooms etc. which can lead to increased exposure to pathogenic fungi which are the cause of athlete’s foot. Individuals with the problem of excessive sweating or other sources of excessive moisture is also a common risk factor. Wearing occlusive footwear like trainers and socks can also prove to be a factor. People suffering from diabetes are also more prone to the disease. Pedicures when done in unhygienic environments can cause significant risk. Wearing the same socks and shoes for long periods can also lead to the development of athlete’s foot. Men are more at risk than women for this condition.
Athlete’s foot Symptoms-
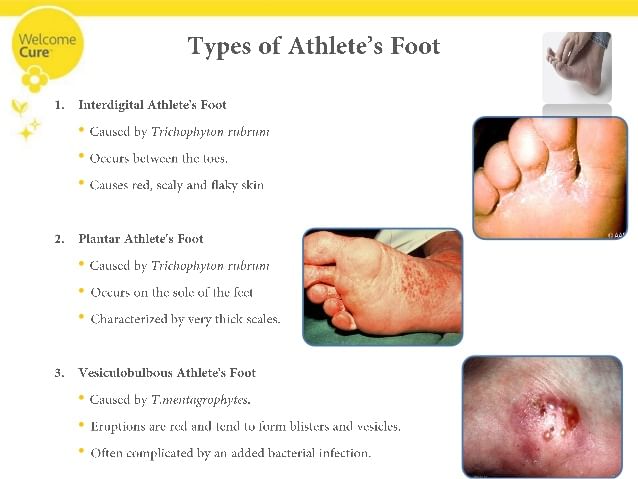
- Athlete’s foot can be demarcated into 4 categories namely, Plantar with plantar referring to the sole of the foot, interdigital athlete’s foot which means between the toes, acute ulcerative tinea pedis that leads to the development of lesions with scaly borders and vesiculobullous athlete’s foot which causes fluid filled lesions.
- When interdigital athlete’s foot is caused by Trichophyton rubrum, the condition might be symptomless or may show signs such as itching, appearance of red or ulcerative skin between the toes which might or might not be itchy. An acute type of ulcerative interdigital athlete’s foot which is caused by T. mentagrophytes shows signs such as pain, erosion and fissures on skin, skin maceration, crusting of the skin and odor because of secondary bacterial infection.
- Plantar’s athlete’s foot caused by T. rubrum shows signs such as appearance of redness on the sole of the foot which is often covered by fine, flaky scales. In case of vesiculobullous athlete’s foot is generally very rare and is caused by T. mentagrophytes and shows signs of itchy blisters on the soles of the foot.
- General symptoms of the disease include itching, burning and stinging sensation between the toes, itchy blisters on the feet, dryness of the skin on the soles and the sides of the feet, discoloration of the toenails, raw skin on the feet, itching, stinging or burning sensation on the soles of the feet, pulling away of toenails from the nail bed, cracking and peeling of the skin generally between toes and on the soles of the feet, thick or crumby toenails etc.
Causes of Athlete’s foot-
Athlete’s foot is a form of dermatophytosis which refers to fungal infection of the skin which is generally caused by dermatophytes, fungus living in the layers of the skin and digesting keratin. These fungi which are parasitic in nature thrive in human hosts. The fungus that is related to the development of ring worm and jock itch is associated with causing athlete’s foot. Moisture providing places like damp socks and shoes provide a favorable condition for the fungi to grow. Exposure to the fungus is mostly through direct contact with a person infected by the disease or through coming in contact with places contaminated by the fungus. Showers, indoor swimming pool decks, locker rooms would be the most likely places to contract this disease.
Diagnosis of Athlete’s foot-
The most reliable and the best way to diagnose athlete’s foot is to recognize it’s causes and symptoms. Fungal athlete’s foot is very easy and straight forward to diagnose and treat. Getting the fungus removed from the foot is a very easy and cost-efficient process. The patient should immediately see a doctor if their rashes look infected and they have diabetes, the rash has changed into ulcers or sores that leak liquid or if the infection has spread to their groin or hands. If the rash just won’t go away or the symptoms get worse the doctors might suggest a biopsy. A skin lesion potassium hydroxide (KOH) exam is a very common test conducted by the doctors for athlete’s foot. A skin lesion is an unusual change on the skin’s surface. The doctors might order a KOH exam if they suspect fungus to be the reason for the skin lesion. The doctors will use a slide of glass or some other instrument to scrape off a bit of the skin from the patient’s lesion. The scraped skin is then mixed in with potassium hydroxide. Potassium hydroxide will destroy the healthy skin leaving behind only the fungus for the doctors to examine. The test is very simple and straightforward and has no risks to it.
Athlete’s foot Treatment-
It is advised to get athlete’s foot treated as soon as a person notices any symptoms. Athlete’s foot can be treated by medications, home remedies or therapies. The treatment for the foot infection are as follows:
Over the counter medications
Many medications for the foot infection are available to treat fungal and non-fungal athlete’s foot. Medications such as miconazole (Desenex), clotrimazole (Lotrimin AF), terbinafine (Lamisil AT), tolnaftate (Tinactin), butenafine (Lotrimin Ultra) are available without any prescription of the doctor. Although, it is really hard to determine which one of these medications is the most effective. These medications are also available for purchase online over the internet.
Prescription medications-
Advanced or severe cases of athlete’s foot may require some oral anti-fungal pills such as prescription strength terbinafine. These medications are prescribed by consultation of doctors to restrict the spread of the infection. The drugs such as topical prescription strength miconazole and clotrimazole, oral anti-fungal medications such as fluconazole (Diflucan) and itraconazole (Sporanox) are also prescribed by the doctors. Lab tests to check for liver diseases will be done before the doctors prescribe these oral anti-fungal medications. Topical steroids are suggested for inflammatory infection to reduce the pain caused by the infection. Oral anti-biotics are suggested if raw skin and blisters are the reason for the bacterial infection. Topical steroids are not to be used in cases of fungal athlete’s foot as they help the fungus in spreading further by suppressing the immune system of the body. Topical steroid creams are more useful in treating non-fungal or non-infectious athlete’s foot. During pregnancy it is suggested that the patient should avoid anti-fungal pills because of possible harm to the fetus or other side effects that may take place.
Home Remedies-
Use of tea tree oil has been proven really helpful in treating athlete’s foot in recent years. But, it is suggested that the individual first confirms with their doctor that the use of tea tree oil won’t affect their skin as tea tree oil causes dermatitis in some cases. There are also other home remedies for treatment of athlete’s foot such as soaking your foot in dilute vinegar or use of dilute vinegar spray (four parts water and one-part household white vinegar), soaking the foot in diluted Clorox or taking a dilute Clorox bath (approximately one-fourth cup of Clorox household bleach in a tub of water). Other unconfirmed remedies also include use of Epsom salts and Vicks vapor rub.
Complications Related to Athlete’s foot-
Athlete’s foot can cause complications in some cases. Minor complications include allergic infection due to fungus, blistering on the feet and hands. The fungal infection can also return even after being treated. More severe complications make take place in case of secondary bacterial infection. These complications include foot getting swollen, hot and painful, fever, drainage and pus. The infection might even spread further to other parts of the body if not treated in the early stages. Fungal nail infection (Onychomycosis) is also highly possible to take place because of the athlete’s foot. Groin infection (tinea cruris) and Body skin fungus (tinea corporis) may as well take place. Individuals with diseases that affect the immune system such as HIV/AIDS, cancer and diabetes will be prone to many kinds of infections. Athlete’s foot fungal infections with diabetes may cause severe ulcers on the body of the patient. Bacterial infection may cause cellulitis or inflammation of the skin of the patient. Use of topical steroid creams weakens the patient’s immune system which can result in other infection to take place.
Prevention of Athlete’s foot-
There are many things an individual can do to avoid athlete’s foot such as maintaining proper hygiene and washing your feet with water and soap and drying them off properly every day. The area between the toes should be cleaned and dried off thoroughly.
- Use anti-fungal powder for your feet every day.
- Disinfecting your shoes by using disinfectant sprays and wipes. Do not share your towels, socks and shoes with others as this might result in spread of the infection. Wear sock and footwear made of breathable fibers and material that also wicks away the moisture from your feet.
- Change your socks and shoes whenever your feet start to sweat. staying bare foot or in footwear like slippers is suggested at home to air out your feet and remove the moisture. Moisture helps the spread of fungus, to prevent athlete’s foot keep your feet clean and moisture free. Change between two or more different pair of shoes every other day to let each pair dry out between uses.
- Make sure family members with athlete’s foot are treated to avoid the spread of the infection to other family members.


+1.svg)
