Eczema In Children - What Should You Know?
Eczema in Children:
-Also known by the term 'atopic dermatitis', eczema is more prevalent in infants and children. This article discusses the possible causes of eczema in children.
-Eczema is one of the most bothersome and chronic disorders of the skin. Atopic eczema is the type commonly observed in children, while contact eczema is more prevalent in adults.
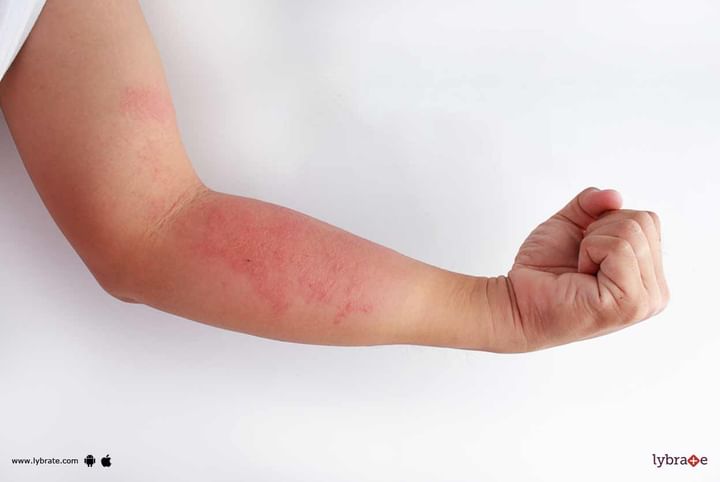
-The arms, and the region behind the knees, are the commonly affected sites. However, any part of the body may be affected.
Symptoms
-The classic symptoms include the appearance of red-brown bumps or patches on the affected area.
-This may be accompanied with itching, which gets severe at night. When these bumps or patches are scratched, they may leak and crust over.
-Other symptoms which indicate the onset of eczema include cracked skin, that may become thick and have a scaly appearance.
-These symptoms occur both in children and adults. Symptoms specific to children include crusting or oozing rash on the face and scalp.
Causes
-Eczema is believe that some malfunction in the immune system when accompanied with dry, irritated skin, could be a contributing factor in the onset of this condition in children and adults.
-Although experts are not sure about the exact causes of eczema, they have been able to determine triggers that can worsen the symptoms of this condition.
These may include:
-Stress (in adults)
-Perspiration
-Exposure to changing temperature
-Low humidity levels
-Use of soaps, detergents, etc.
-Smoke
-Certain foods
-Certain man-made fabrics
Types of Eczema:
Atopic Eczema:
The most common of all types, atopic eczema is also known as infantile eczema. This form generally affects people who are extremely sensitive to allergens in their environment such as pollens, dust, animals skin or hair, and certain foods. Many experts believe, that children suffering from this condition may be genetically predisposed to get eczema from parents or family members who have history of hay fever, asthma, or other allergies. Atopic eczema is characterized by an extremely itchy red patch on the skin, that may sometimes swell, and develop into fissures that may crack and ooze out clear fluid or even blood. The infected skin seems to be crusty and scaled.
Hand Eczema:
This is a chronic form of eczema that only infects the hand. Hand eczema, also known as hyperlinear palms is caused due to constant hand washing with harsh soaps, detergents, or contact with strong chemicals like bleach, etc. Eczema on hands develops shiny red blisters and lesions that are quite painful. People who have this form of eczema find it difficult to perform their daily activities, as there are many chances of aggravating the eczema blisters.
Varicose Eczema:
Varicose eczema affects the skin on lower legs, and is caused by poor blood circulation. It commonly affects older people mostly on the shins and ankles. This condition predominantly affects people suffering with varicose veins. Varicose eczema should not be left untreated for long time, as they develop into stubborn ulcers that don't heal easily. Large varicose eczema tends to turn sore, and develop deep in the skin, which upon cracking leaves the skin vulnerable to other types of skin infections.
Contact Eczema:
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin is exposed to irritants, resulting in an allergic reaction. It either occurs or aggravates only when the skin comes in contact with a specific substance, else it largely remains dormant. Chemicals or even natural oils present in cosmetics, deodorants, skin cream and lotions, shampoos, body soaps, fragrances or deodorants, cleaning products may cause allergic reactions. This allergy commonly affects people who spends many hours working in the soil. Certain medications also can cause contact eczema. People can develop this form of eczema while consuming foods that contain certain herbs, or chocolate or caffeine.
Nummular eczema:
Adults are more prone to develop nummular eczema. Its name has been derived from the Latin word nummus, which means coin. This type produces coin shaped patches of infected skin (hence the name), mainly on the legs, arms or chest. It usually occurs in adults.
Seborrheic Eczema:
Seborrheic Eczema first develops on the face or neck around the nose and at the scalp line. In infants, it is termed as cradle cap, while in adults it is known as dandruff. This eczema causes extremely greasy pink or yellow patches, which are often covered by scales.
Dyshidrotic Eczema:
Commonly known as pompholyx or vesicular eczema, dyshidrotic eczema mostly affects the hands and the feet. It is characterized by small itchy blistering bumps, that cause an extreme burning or itching sensation.
Discoid eczema:
Discoid eczema occurs as round red scaly patches of blisters, usually affecting the arms and legs.They become itchy and can ooze fluid, causing the infection to spread.
Treatment:
-Eczema treatment in children or in adults for that matter, attempts to reduce the inflammation and itching, as well as prevent future flare-ups.
-Apart from medication, some patients may be recommended to expose their skin to controlled amounts of natural sunlight.
-This process is known as light therapy. In case of infants, parents are advised to keep their babies away from skin irritants, and extreme temperatures.
-Using baby bath oils, lotions or creams helps to keep the skin hydrated, thus avoiding dry skin. If these measures do not provide relief, babies may be given oral antihistamines by the doctor.
- They help in reducing the itching, and encourage drowsiness which helps at bedtime.
- Apart from the above treatment options, parents can help their children recover with the help of a few self-care measures.
- These may include avoiding triggers, helping them to avoid scratching, giving them warm baths, choosing appropriate baby soaps, and using cool compresses (as it helps in reducing scratching). Using humidifiers and making your kids wear loose, smooth-textured cotton clothing, are some other effective ways to cope with the condition.
- Children must be educated about the importance of drinking plenty of water, and keeping their skin moisturized.


+1.svg)
