Gangrene - All You Must Know About It!
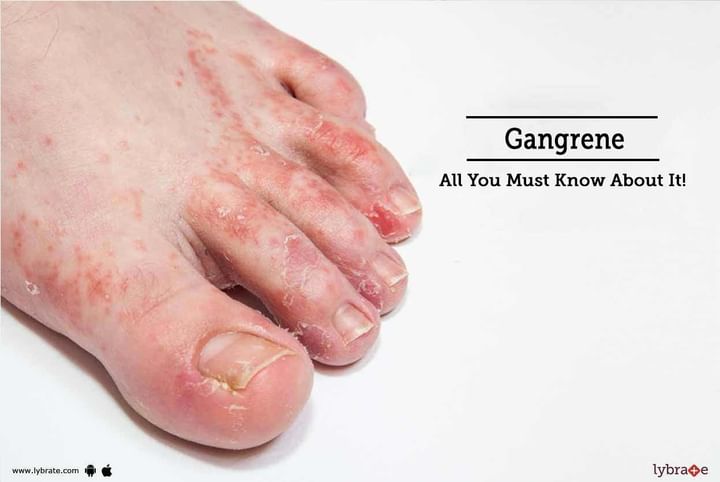
Gangrene is an extremely serious condition in which there is an acute shortage of oxygenated blood to the tissue in the body resulting in tissue necrosis or death. Most of the times, it is seen that Gangrene affects the extremities externally, like feet or hands, but it might also affect the body internally and severely damaging the internal organs.
Types of Gangrene-
There are majorly two broad categories of Gangrene: Wet and Dry.
-
Wet Gangrene: In this type of fatal Gangrene, there is swelling of the skin along with the appearance of blisters, often accompanied by the formation of pus. It is associated with injuries in diabetic patients. Sometimes, Dry Gangrene deteriorates and manifests itself into Wet Gangrene. This type spreads more quickly from the affected area to other parts of the body due to infection.
-
Dry Gangrene: Also referred to as mummification, it develops slowly and is often associated with chronic diabetes. Skin becomes shriveled, dry and dark in color, and it feels cold to touch due to tissue death. Moreover, it is also associated with injuries in diabetic patients, with vascular diseases, and with Raynaud’s Disease. Usually, it does not get infected, but if it does, it gets converted into the more dangerous Wet form.
Symptoms-
Symptoms of Gangrene include-
-
Discoloration of the skin leading to its darker and shinier appearance accompanied by shedding of the skin
-
The appearance of a swollen, pus-filled blister in case of Wet type
-
Pain in the affected area leading to loss of sensation or numbness and subsequently leading to an inability to move the affected part
-
Cold when touched
-
Loss of pulse
Diagnosis-
A physical examination for diagnosing Gangrene is often followed by tests of tissue, blood, and discharge for getting to know the type of infection. In case of extreme severity, especially when internal organs are involved or if Gangrene seems to be deep-seated, X-Ray, CT scans, and MRIs might be recommended for ascertaining the extent of the disease.
Treatment-
Since Gangrene is associated with tissue necrosis, the only available approach to treatment is the removal of the dead tissue.
-
Also referred to as debridement, surgical removal of the dead tissue prevents infection from spreading. Sometimes, amputation (severing the affected part) might also be required.
-
Maggot Therapy is another method which is sometimes followed. Maggots from the larvae of fly bred in sterile conditions in the laboratory are placed on the affected area. They consume for food the dead and infected tissue without causing any harm to healthy tissue.
-
Intravenous antibiotics help in preventing infection from spreading.
-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy involves an increase in pressure and oxygen supply to the affected tissue for its healing and to curb infection.
Take Away-
Gangrene, or tissue death, is a life-threatening condition which can be treated through surgery, Maggot therapy, intravenous antibiotics or Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy.


+1.svg)
