Giant Hives: What Are The Causes Behind?
Allergic reactions are the body’s way of responding to foreign substances. The body recognizes these substances (be it food, pollens, insect bites, etc.) as antigens and produces antibodies. These antibodies can cause various reactions depending on the severity of the allergen, be it skin rash, hives, or angioedema. In severe cases, there could be swelling of the tongue and the respiratory tract, leading to choking of the airways.
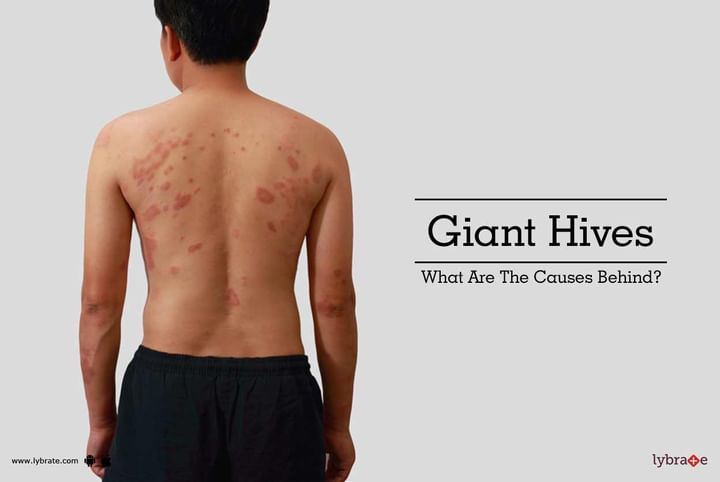
Literally, angioedema means swelling of the blood vessels. These are located in the underlying layers of the skin and their swelling can lead to formation of giant hives, which can be extremely itchy, reddish, and oval or circular in shape. The affected area is usually warm and painful to touch.
Causes
Angioedema is caused due to the following:
-
Food allergies including eggs, peanuts, shellfish, milk, tree nuts, chocolates, etc.
-
Insect bites or stings
-
Pollen, latex, animal dander, poison ivy, and other common allergens
-
Medications like aspirin, penicillin, ibuprofen, and some blood pressure medicines
-
In response to blood transfusions
-
Auto-immune disorders like lupus
-
Conditions like leukemia and thyroid disorders
-
Infections like hepatitis, cytomegalovirus infections, Epstein-Barr infections, etc.
-
Weather conditions like extremes of cold, heat, or pressure
-
Extreme emotional stress
-
Genetic angioedema, passed on from parents to children, which could last forever
While hives usually develop without any warning, the following condition puts a person at risk of developing angioedema.
-
Predisposition to allergic reactions (highly active immune system)
-
Previous history of allergies
-
Genetic history of allergies or angioedema
Most angioedema cases are limited to the skin and hives, but there could be severe cases leading to respiratory distress.
Diagnosis
If it is the first instance of hives, the doctor would ask detailed questions about similar occurrence in the past. They would also check if there are similar hives on other parts of the body like the back, which you may have missed. If required, this examination is followed by allergy testing and blood testing. The allergy testing will help identify if you are allergic to some of the common things which cause allergy. The blood test will look for your eosinophil count, which is usually high in people prone to allergies. C1 esterase inhibitor test and complement particles also can be checked, if there is suspicion of genetic angioedema.
Treatment
This would depend on the severity of symptoms
- In case of angioedema, admission in hospital may be needed.
- Tracheostomy may also become essential to save patients life.
- Vigorous therapy with intravenous medications like steroid, antihistamines and others may be needed.
- Under medical treatment, antihistamines like cetirizine and loratadine are prescribed. However, severe cases may require steroids like prednisolone.
Prevention
Once you know what caused it, avoid exposure to these substances and further attacks can be prevented. If you wish to discuss about any specific problem, you can consult a Dermatologist.


+1.svg)
