Is Breast Lump Signal To Breast Cancer?
Most lumps are not cancer, A breast lump is a growth of tissue that develops within your breast. Different types of breast lumps can vary in the way they look and feel. You may perceive a lump as a mass, growth, swelling, thickness, or fullness.
Symptoms and Signs of Breast Lumps
- A distinct lump with definite borders
- A firm, hard area within your breast
- A thickened, slightly more prominent area in your breast that's different from surrounding breast tissue
- Other breast changes, such as redness, dimpling or pitting of the skin
- One breast that's noticeably larger than the other
- Nipple changes, such as a nipple that's pulled inward or spontaneous fluid discharge from your nipple
- Persistent breast pain or tenderness, which might increase during your menstrual period
Sometimes, a breast lump is a sign of breast cancer. That's why you should seek prompt medical evaluation. Fortunately, however, most breast lumps result from Noncancerous (benign) conditions.
Causes of Breast lumps
- Breast cancer.
- Breast cysts — fluid-filled sacs in your breast that are usually benign
- Fibroadenoma— a solid, benign mass most common in young women
- Fibrocystic breast.
- Injury or trauma to the breast
- Intraductal papilloma — a benign, wartlike growth in a milk duct
- Lipoma— a slow-growing, doughy mass that's usually harmless
- Mastitis-— an infection in breast tissue that most commonly affects women who are breast-feeding
- Milk cyst (galactocele) — a milk-filled cyst that's usually harmless
Homeopathic Remedies of Breast Cancer
Well-selected homeopathic remedies are effective for breast lump and cure the condition without further complications
Bryonia alba 1m - Bryonia alba is indicated when breast lump with stitching pain is present. The breast is hard and painful. Pain in breast at menstrual period. The breast pain aggravates during movement.
Calcarea carb 30- An excellent remedy for breast lump. Breasts are hot and swollen. Chronic cystic mastitis. Blunt duct adenosis; best remedy for fibroadenoma. Lump in breast is hard, nodular, and tender to touch in the beginning. Then the pains are reduced and the lump turns to be hard due to calcification. Calcarea acts best when the tumours are calcified. These breasts are swollen and tender before menses. Deficient lactation. The breasts are distended in lymphatic women. The patient complains of profuse sweating around the genitalia with dirty smell. Inflammatory condition of the breast. With breast condition patient has the mental symptoms due to suffering. The patient is anxious, tired, and weak, both mentally and physically.
Calcarea flour 30 - Calcareaflour. It is another top remedy for lump in the breast. Lump in the breast which is hard, movable with clear margins which are sharp in nature, or their edges is sharply defined. Most commonly they are solitary, very rarely multiple. Occurs in young patients usually unmarried. Nodules are in the upper right quadrants. The patient is sad and depressed due to financial conditions. Confused due to melancholic condition of mind. The patient is chilly, and she is very sensitive to cold air, cold wind and cold atmosphere in general. Genitals are sore. Urine is copious and offensive. Pain at the tip of the urethra while urinating and after the act. Pain in back extending to sacrum.
Conium maculatum 30 - Conium maculatum is one of the top remedies for breast lump. Here the mammary glands are hard and sore. A typical carcinoma of the breast, that is, scirrhous adenocarcinoma, which begins in the ducts and ends in the parenchyma. As the stage advances, the cooper's ligament shortens and thus it produces the notch. Sometimes the condition is associated with the inflammation of the breast tissue. The region is hard and nodular, tender to touch. Burning and stinging pains in the breast. The skin over the tumor is adherent. Occasionally there is the discharge of pus from the nipple. The lesion is hard, almost cartilaginous. The edges are distinct, serrated, and irregular; associated with productive fibrosis.
Baryta carb 30 - Baryta carb is very effective for breast lump. Inflammation, insulation, and enlargement are the fundamental pathogeneses of this drug. The mammary gland is enlarged and there is a lump, which is hard. There is very sensitive to touch. The glands which are enlarged are tender with infiltration. The women of the late twenties are affected. These patients present with hard but not serrated mass with a firm rubbery consistency. Their edges are sharply defined. Most commonly the tumours solitary. Or occasionally are multiple. They are differentiated from cancer by smooth rather than irregular lobulations. A bloody discharge from nipple is an indication of this drug. All the glands of the body are very sensitive to cold and they are worse by taking cold. The skin over the gland becomes ulcerated. It is seen that this remedy works better in Paget's disease of nipple which is supposed to be primary carcinoma of the mammary gland.
Bellis perennis 30 - Bellis perennis is prescribed when the lump is caused by a trauma that causes injury to deeper tissues of the breast. The main indication is sore, bruised feeling in breast. Breasts engorged.
Chimaphilia Umbellata 30 - Chimaphilia is indicated for a painful tumor of mammae in women of large breasts. There is sharp pain through the breast.
Hydrastis Canadensis 30 - Hydrastis is prescribed to those patients who have the tendency to indurated glands. Swelling of the mammary glands. Fat necrosis and glandular cell myoblastoma are common in this remedy. Fat necrosis tumor is probably post-traumatic. The patient complains of pain and tenderness. The lesion is fixed to the breast tissue, which sometimes causes dimpling of the overlying skin. Engorged nipples, cracks, and discharges of watery fluid or there is serosanguinous discharge. The patient is weak and emaciated, fainting due to improper assimilation or defective assimilation. All-gone sensation or empty feeling in the stomach, not relieved by eating. Chronic catarrhal condition of the membrane of the stomach. The patient is thirstless. Obstinate constipation, colicky, and crampy pain in the abdomen. The liver is enlarged and tender.
Iodum 30 - This remedy predominantly acts on the enlargement of the mammary glands which may be either neoplastic or malignant. The mucous membranes of the glands and the breast tissue are inflamed. The breast tissues are hypertrophied, enlarged, hard, and nodular. Emaciation of the patient due to malabsorption. The tumours are well differentiated. They have a discrete capsule. Small lesions present leaf-like intracanalicular protrusions and large lesions have cystic space. Inflammation of the lesions, ulceration occasionally, excoriating, and acrid discharge from the nipple or from the lesion. Oedematous swelling of the affected breast.
Lapis Albus 30 - The main action of this remedy is on the glands of the mammary region. These glands have the tendency to turn malignant. Remarkable results are observed in scrofulous condition of the glands. Fibroid tumors, intense burning pains in the parts. The tumors have pliability and a kind of softness rather than hardness. The margins are clear. The glands are elasticity, exactly the reverse of calc. Fluorica.
Phytolacca dec. 30 - Phytolacca is another remedy effective for lump in the breast. Mammae hard an very sensitive. Tumors of the breast with enlargement of axillary glands. When child nurses' pain goes from the nipple all over the body. Irritable breast before and during menses.
Plumbum iodide 30 - Plumbum iodide is another effective remedy for breast lump. There are indurations of breast, especially when a tendency to become inflamed, appears sore and painful. Indurations of great hardness and associated with very dry skin.
Scrophularia nodosa q - Scrophularia has a specific affinity for the breast. It is very useful in the dissipation of breast tumors.
Thyroidinum 1m - An intercurrent remedy
Breast cancer is cancer that forms in the cells of the breasts.
After skin cancer, breast cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in women in the united states. Breast cancer can occur in both men and women, but it's far more common in women.
Substantial support for breast cancer awareness and research funding has helped create advances in the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. Breast cancer survival rates have increased, and the number of deaths associated with this disease is steadily declining, largely due to factors such as earlier detection, a new personalized approach to treatment, and a better understanding of the disease.
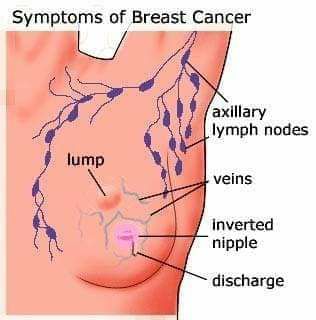
Symptoms of Breast Cancer
- Nipple changes
- Nipple changes
Signs and Symptoms of Breast Cancer
- A breast lump or thickening that feels different from the surrounding tissue
- Change in the size, shape or appearance of a breast
- Changes to the skin over the breast, such as dimpling
- A newly inverted nipple
- Peeling, scaling, crusting or flaking of the pigmented area of skin surrounding the nipple (areola) or breast skin
- Redness or pitting of the skin over your breast, like the skin of an orange
Cause of Breast Cancer
- Doctors know that breast cancer occurs when some breast cells begin to grow abnormally. These cells divide more rapidly than healthy cells do and continue to accumulate, forming a lump or mass. Cells may spread (metastasize) through your breast to your lymph nodes or to other parts of your body.
- Breast cancer most often begins with cells in the milk-producing ducts (invasive ductal carcinoma). Breast cancer may also begin in the glandular tissue called lobules (invasive lobular carcinoma) or in other cells or tissue within the breast.
- Researchers have identified hormonal, lifestyle, and environmental factors that may increase your risk of breast cancer. But it's not clear why some people who have no risk factors develop cancer, yet other people with risk factors never do. It's likely that breast cancer is caused by a complex interaction of your genetic makeup and your environment.
Inherited Breast Cancer
- Doctors estimate that about 5 to 10 percent of breast cancers are linked to gene mutations passed through generations of a family.
- A number of inherited mutated genes that can increase the likelihood of breast cancer have been identified. The most well-known are breast cancer gene 1 (brca1) and breast cancer gene 2 (brca2), both of which significantly increase the risk of both breast and ovarian cancer.
- If you have a strong family history of breast cancer or other cancers, your doctor may recommend a blood test to help identify specific mutations in brca or other genes that are being passed through your family.
- Consider asking your doctor for a referral to a genetic counselor, who can review your family health history. A genetic counselor can also discuss the benefits, risks, and limitations of genetic testing to assist you with shared decision-making.
Risk Factors of Breast Cancer
A breast cancer risk factor is anything that makes it more likely you'll get breast cancer. But having one or even several breast cancer risk factors doesn't necessarily mean you'll develop breast cancer. Many women who develop breast cancer have no known risk factors other than simply being women.
Factors that are associated with an increased risk of breast cancer include:
- Being female. Women are much more likely than men are to develop breast cancer.
- Increasing age. Your risk of breast cancer increases as you age.
- A personal history of breast conditions. If you've had a breast biopsy that found lobular carcinoma in situ (lcis) or atypical hyperplasia of the breast, you have an increased risk of breast cancer.
- A personal history of breast cancer. If you've had breast cancer in one breast, you have an increased risk of developing cancer in the other breast.
- A family history of breast cancer. If your mother, sister or daughter was diagnosed with breast cancer, particularly at a young age, your risk of breast cancer is increased. Still, the majority of people diagnosed with breast cancer have no family history of the disease.
Inherited genes that increase cancer risk. Certain gene mutations that increase the risk of breast cancer can be passed from parents to children. The most well-known gene mutations are referred to as brca1 and brca2. These genes can greatly increase your risk of breast cancer and other cancers, but they don't make cancer inevitable.
Radiation exposure. If you received radiation treatments to your chest as a child or young adult, your risk of breast cancer is increased.
- Being obese increases your risk of breast cancer.
- Beginning your period at a younger age. Beginning your period before age 12 increases your risk of breast cancer.
- Beginning menopause at an older age. If you began menopause at an older age, you're more likely to develop breast cancer.
- Having your first child at an older age. Women who give birth to their first child after age 30 may have an increased risk of breast cancer.
Having never been pregnant
- . Women who have never been pregnant have a greater risk of breast cancer than do women who have had one or more pregnancies.
- Postmenopausal hormone therapy. Women who take hormone therapy breast lump.
Update From Lybrate: Make your sexual life more enhancing and blissful by consuming natural and healthy supplements. Buy these Sexual Wellness Products on Lybrate.


+1.svg)
