Know More About Tetralogy Of Fallot!
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a commonest congenital cyanotic heart disease.
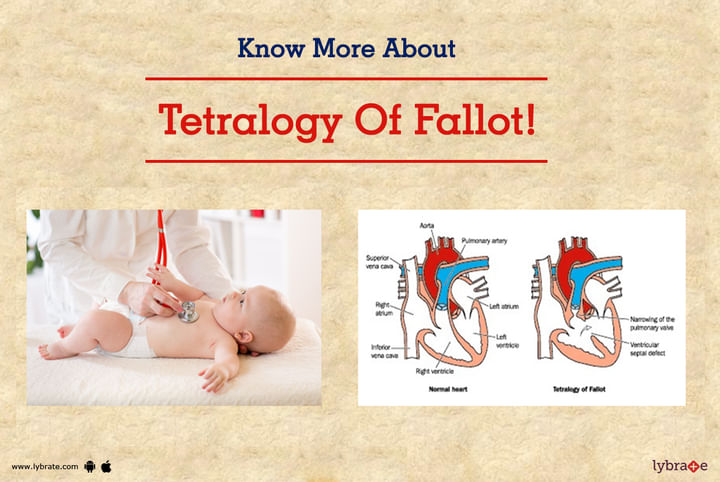
TOF is having a combination of large VSD with severe obstruction of blood flow to the lungs that result in bluish-black discoloration of lips and fingers due to flow of oxygen-deficit blood to the body parts.
The four defects that commonly associated with Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) are –
- Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) – a hole formed in ventricular septum that is situated between two lower chambers of heart known as ventricles
- Pulmonary stenosis – refers to a narrowing of the pulmonary valves and the region below or above it that blocks the flow of blood to the pulmonary artery/lungs from the right-sided ventricle
- Overriding Aorta – the aortic valve becomes enlarged and appears to arise from both the ventricles instead of just the left ventricle
- Right Ventricular Hypertrophy – the walls of the right ventricle becomes thick and hardened as a result of pumping of blood at a high pressure
In few cases, a child with TOF may also suffer from additional defects such as ASD (Atrial Septal Defect), additional VSDs, or abnormalities in the coronary arteries, etc.
What are the symptoms/signs due to TOF?
Symptoms due to TOF depend on how severely there is an obstruction of blood flow to the lungs. The most common sign in children with TOF is cyanosis – a tint of purple or blue on the lips, skin, and fingernails.
Other symptoms/signs to look out for include –
- Irritability
- Clubbing of toes and fingers
- Poor weight gain
- Prolonged crying
- Loss of consciousness in severe cases
- A heart murmur
- Cyanotic spells – the colour of the skin may appear deep blue suddenly after feeding or crying, can be associated with rapid breathing/breathlessness, etc.
Complications of TOF-
If the symptoms go unnoticed and the condition is left untreated, your child may develop the following complications –
- Cyanosis that deteriorates over time
- Tet spells where the level of oxygen in the blood drops drastically
- Dizziness and seizures/loss of consciousness
- Endocarditis – an infection of the lining of your heart
- Irregular heartbeat or arrhythmia
It is essential that you seek immediate treatment for your child. A Paediatric Cardiologist is ideally the person you should refer to.
Diagnosis of TOF-
TOF can be easily diagnosed by doing “Fetal Echocardiogram”. Fetal Echo needs to be done between 18-24 weeks of gestation preferably between 18-20 weeks of gestation.
“Pediatric Echocardiogram” is essential for making the diagnosis. An echocardiogram is a non-invasive test that needs to be done form chest of the child.
Other tests that can be supportive in making the diagnosis are ECG, chest X-ray.
Sometimes CT angio of heart needs to be done for defining the structure of heart when echocardiogram is inconclusive. Occasionally especially in older children or adolescents, Cardiac cath angiography has to be done when CT angio is less desirable.
Treatment for Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
Surgery is the definitive treatment option for managing TOF by open heart surgery.
The two surgical options are –
1. Palliative or Temporary Surgery – The procedure aims for improving the flow of blood to the lungs from a major blood vessel of the heart (Aorta). This is a preferred option when the baby is very blue and is having low weight to undergo complete repair.
This involves creating an artificial channel for the blood to reach the lungs by placing a shunt between a large artery and one of the pulmonary artery (either right or left) that diverges the blood from the aorta to the lungs for blood purification. This is known as BT shunt surgery. Sometimes when the size of pulmonary arteries is very small in size then central shunt needs to be done. This shunt is created between a large vessel of the heart (Aorta) and main vessel of the lung (Main pulmonary artery).
After doing this surgery, the child needs to be followed up at a regular interval till the complete repair is planned.
2. Complete Repair (Intra-cardiac repair of TOF) – Through this procedure, the surgeon enlarges the passage between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery so that blood flows to the lungs improves as well as surgeon closed the hole in heart (VSD) by putting a patch across it. (This abolishes overriding of the aorta as well).
- Hypertrophy of right ventricle decreases gradually over a time period.
Most children do well after complete surgery. Follow-up with Pediatric Cardiologist is required to ensure well being of the child.


+1.svg)
