Poison Ivy Rash!
Poison Ivy Rash Overview:
Poison ivy is basically a plant belonging to the cashew family. It can climb to the poles and trees as well. It can be very harmful to the skin because it contains a specific oil which causes irritation to the skin. When that oil comes in contact with the human skin, it leads to rashes.
Poison Ivy Rash Definition:
Poison Ivy is a condition of skin inflammation. This is one of the examples of contact dermatitis which means that when skin comes in contact with some specific kinds of objects, it gets an allergic reaction. Poison ivy rash is also a type of allergic reaction which is caused when the skin comes in contact with parts of a plant called poison ivy. This plan has a resin which is oily in nature. This resin is called as urushiol and can be found in the leaves, roots and stems of poison sumac, poison oak and poison ivy plants.
Poison ivy plant grows where there is a presence of ample sunlight. It comes in the category of shrub and nurtures on the boundaries of forests. Sometimes, they also have yellowish green flowers and berries which are green in colour, but they possess no thorns. This plant can be distinguished by a bunch of three leaflets, whose colour varies from light green to dark green. The cluster of leaves grows on their own stem which in turn is connected to the vine. It is believed at 85% of the American population is allergic to this plant. Those who do not get any allergic reaction should also stay cautious because depending on the age and number of times the contact has been made; this plant can cause the reaction. It is probably the most dangerous situation when the person smokes the air in which traces of burnt poison ivy are present.
Those people who live in an environment where there are plenty of plants or those who have more exposure to the natural environment are more prone to this allergic reaction. People who work on farms, or do outdoor activities like walking, hiking, trekking, cycling etc., or those people whose profession is to work amongst the plants are more prone, simply because their chances of getting in contact with poison ivy are more. Examples of such professions are as below:
- Botanists
- Gardeners
- Farmers
- People involved in construction work
Poison Ivy Rash Symptoms:
Some of the symptoms of getting poison ivy rash are generic:
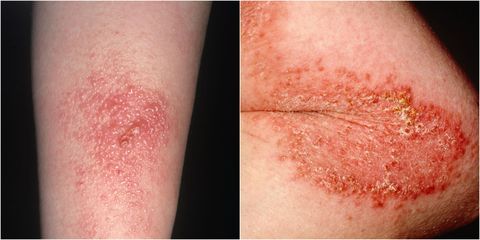
- Redness on the skin which might or might not be accompanied by itching. It could also be a very intense itching.
- Swelling on the area of the skin where the contact was made.
- Blisters and redness on the skin. They could be red bumps or red streaks. Also, there can be oozing from the blisters.
- People also find it very hard to breathe when they breathe the air in which smoke of burning poison ivy is present.
- Hives
- Crusting skin.
When these signs appear, the person should refer to the doctor for medications and some relief. Also, if the conditions get worse, then immediate medical attention should be given. When poison ivy rashes become more serious, following conditions may also occur:
- Problems in breathing. This is generally caused when the smoke of burnt poison sumac, poison oak or poison ivy is inhaled. The respiratory system suffers causing difficulty in breathing normally.
- Trouble in swallowing food or drinking thick liquids.
- Swollen and/or red tongue.
- Multiple rashes on the face or rest of the body.
- Swollen eyelids. The degree of swelling may differ. Some people get so much swelling on the eyelids that their eyes cannot open.
Causes of Poison Ivy Rash:
The primary cause of this allergic reaction is the oily resin. It is very sticky in nature which is why it gets on the skin, clothes, boots, and any gardening equipment or even on pets with furs. If anyone touches the leaves of this plant, or its stem, roots or even berries, then chances are that they will get that allergic reaction. Even if they touch contaminated objects, the substance will get onto their hands and then those hands will touch other parts of the body like the face or even eyes. Therefore, it is necessary to wash hands thoroughly after coming from an area where the presence of poison ivy is even slightly possible. Note that the allergic reaction does not have to be immediate- sometimes it comes up after a few days as well. Urushiol has the capability to penetrate the skin quickly. It leaves red lines on the skin with the help of which one can make out where exactly the plant was touched. This is a unique factor which helps in making sure that the rash is due to poison ivy.
Another cause of getting this rash is by inhaling the smoke coming from burning poison ivy plants (also known as an airborne contact). It could also be the smoke of poison oak or poison sumac. They all contain urushiol and when inhaled, the lungs, eyes, throat and nasal passage gets affected.
Once someone gets a rash because of urushiol, it will not spread on the body. This implies that the rash itself is not transmittable and means that if a person without allergy touches the rash of the person, they won’t get affected unless there is still the presence of the resin on the hands of the allergic person.
How is it diagnosed?
If a doctor suspects the presence of poison ivy rash, they ask about any recent exposure to the natural environment or poison ivy plant in particular. Also, the pattern of rash sometimes helps in recognising the condition. Therefore, a physical examination is the most common way of diagnosing this allergic reaction.
Prevention:
First and foremost, it is important to identify the plant. Anyone will be able to avoid the contact with this plant only once they are able to identify it. When a person is aware that poison ivy plant can be in the location they are going in, then wearing full-length pants along with socks and footwear (or boots) is a must. To avoid contact with palms, gloves should be used. Also, after coming into the dwelling from outdoors, it is important to clean the clothing. The poison ivy might touch the clothes and then it becomes important to avoid touching those clothes by bare hands. Shoes should also be thoroughly cleaned. Keeping the clothes under running water can help. For the shoes, the cleaning instructions should be mentioned on their inside tag. In fact, all other objects like all sorts of garden tools should also be cleaned. Even if there is a slight doubt about being in contact with poison ivy, it is highly suggested that the person should wash their hands with soap and water, followed by a thorough rinse. Using only hand sanitizer might not help but will be better than not washing hands at all.
Also, before going outdoors, use of an over-the-counter cream for the skin is also advisable. Such barrier creams contain bentoquatam which helps in blocking the urushiol oil from making an impact on the skin. It is not just humans, but pets are also sensitive to this plant. Therefore, utmost care should be taken to avoid the pets from getting in contact with this toxin. If there is a chance that the pet might have got in contact with poison ivy, they should be thoroughly cleaned too.
To prevent poison ivy rashes from happening, it is important to avoid the contact even when the person is not currently allergic to this plant. It has been seen that repeated contact can cause an allergic reaction even to those who were not allergic in the first place. The sap of poison ivy is very harmful and if the clothes or pet’s body gets in touch with that sap, it can also be transferred to others.
Another way to prevent this allergy from happening is to completely kill or remove the plants if they are in the backyard. They can be removed by the use of a herbicide or by taking them out of the ground from their roots. While doing that, the person must be extra cautious as the urushiol is present in roots as well. Once it is done, the gloves should also be washed properly, and the hands should be cleaned too. It is important to note that after removing poison ivy, they should not be burnt because that smoke can cause allergies to everyone around. It is best to check the disposal methods as advised by the local council so that others can also be safe when this is done.
Treatment of Poison Ivy Rash:
Many times, there is no treatment a required for poison ivy. It can go away in 2-3 weeks of time by itself. Depending upon the condition of the person who has got this rash, the treatment can vary. Sometimes, the chances of the rash healing by itself are there but still, people might feel uneasy because of a symptom and they might want a treatment for it. Below are some of the treatments that provide some relief when a poison ivy rash happens on the skin:
- If the contact with the plant has been made within an hour, then showering with cool water can help. Using the soap and cool water will help in removing the presence of the resin from the body and can prevent the rash from happening or growing any further.
- If there is any specific body part which is itching or getting red, it can be soaked in cool water or accompanied by an oatmeal cleansing. Note that the water temperature should be cool only. Hot water will make the skin condition even worse.
- If the skin is too itchy and a burning sensation is there, then over-the-counter drugs like hydrocortisone or calamine creams help in giving some relief to the itchy skin.
- The doctor might also prescribe some anti-allergy or anti-histamine drugs like Benadryl, Allegra, and Zyrtec. It should be noted that such kind of drugs also cause sleepiness so they should be taken when the person can sleep as well. Taking them during work time might not be helpful because the body will feel even more tired. Many of them are also available over the counter also.
- Sometimes doctors also prescribe corticosteroids that are to be taken in the oral form. When the condition is more severe, these might be injected to ensure that the reaction does not grow any further. It is for the medical practitioner to decide the dosage of these corticosteroids and should not be taken without consultation and prescription.
- In case the rash causes some infection, then antibiotics are given.
Normally, cold compress also helps soothing down the itchiness and burning sensation. The cold compress should be made by soaking a washcloth in the cold water, which is the safest option. Care should be taken not to use ice on the skin directly.
Complications:
The rash caused by the poison ivy, poison sumac or poison oak can get infectious if it is not treated properly. If the person scratches the rash, then chances of the bacteria getting under the fingernails increases which have a high chance of causing more infection. It is also to be noted that scratching will not spread the allergy more, but it can cause a different type of infection or prevent the skin from healing quickly. It is important to seek medical help in case the blister starts oozing out the liquid.
Myths:
Probably the most common myth is that the rash is contagious. It is not true. The rash in itself is not contagious, but if the traces of urushiol are still present on the skin, then it might spread to the other person as well. Some people might also believe that dead plants will not cause any allergic reaction. But in reality, they can cause the reaction so it is best to stay away from those plants and avoid even a minute contact with them.


+1.svg)
