Psoriasis - How To Treat Them?
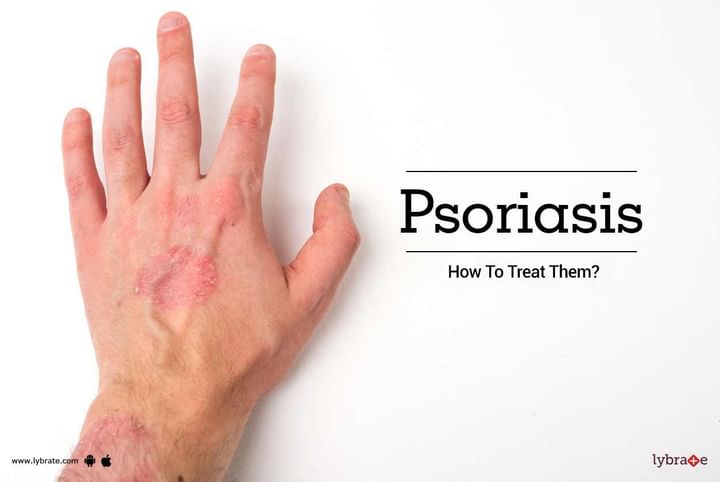
Psoriasis is a disorder which is characterized by the rapid multiplication of skin cells on the skin’s surface. These extra skin cells develop into silvery scales, which are often dry and itchy. It may also lead to the formation of painful red patches on the skin. This disorder might produce symptoms, which flare up and reduce periodically. There is no cure for psoriasis; treatments, however, can make the symptoms manageable.
Symptoms
The symptoms of psoriasis include red patches on the skin and scaly and dry skin. The red patches might be itchy and one might often experience a burning sensation around the area. The joints in your body may also become stiff and swollen.
Causes
The exact cause of psoriasis has not been ascertained. The accepted theory is that psoriasis occurs when the immune system attacks healthy skin cells. There is a type of white blood cell called the ‘T cell’, whose function is to combat harmful virus or bacteria in the body. With Psoriasis or any other autoimmune disorder, these T cells start attacking the healthy (skin) cells.
Overactive ‘T Cells’ may trigger other responses in the body, thus, leading to excess production of skin cells and white blood cells. The excess cells move to the skin surface and end up causing the red painful patches.
Treatment options to manage psoriasis
Although there’s no cure for psoriasis as such, the symptoms can be controlled. The treatment options for psoriasis are:
1. Topical treatments: Topical treatments involve the application of creams and lotions. They have been mentioned below:
I. Corticosteroids: Corticosteroid creams or lotions reduce the excess skin cell production, thus, reducing inflammation. They are generally not used as a long term treatment as they cause skin thinning.
II. Vitamin D analogues: A synthetic form of Vitamin D, it helps in slowing down skin cell growth.
III. Salicylic acid: This treatment is used to reduce scaling on the skin, caused due to psoriasis. It is usually administered along with other medications.
2. Light therapy: Light therapy involves using sunlight or artificial light to reduce inflammation and scaling. It helps in reducing the activity of T cells in the body.
3. Oral medications
In case of severe symptoms, oral medications are prescribed. Medications such methotrexate helps in reducing the excess production of skin cells. Cyclosporine is a drug that is used to suppress the erroneous immune system response.

+1.svg)
