Silent Thyroiditis - What Are The Signs Of It?
The thyroid is a small gland that controls metabolism and growth. Silent thyroiditis is a common autoimmune disorder that affects the thyroid gland. It causes an inflammation of the thyroid gland and is characterized by mild symptoms of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. It is known as Silent thyroiditis because this condition is not painful in any way. Silent thyroiditis is also known as lymphocytic thyroiditis or subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis.The cause of this condition is unknown and hence it is not possible to prevent it. This is one of the least common disorders to affect the thyroid gland. However, middle aged women are at the highest risk of suffering from this condition. Other risk factors include a family history of thyroid disorders, certain autoimmune diseases, removal of the adrenal gland or treatment for cancer.
Some of the symptoms of silent thyroiditis are:
- Fatigue
- Increased sensitivity to heat and cold
- Erratic bowel movements
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Increased appetite
- Palpitations
- Irritability and nervousness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Excessive sweating
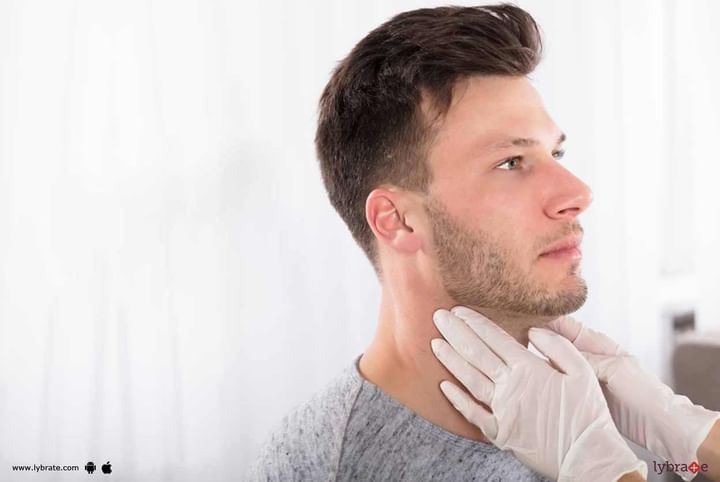
If you notice such symptoms, you must consult a doctor. To determine a silent thyroiditis diagnosis, a thorough physical examination and a few tests are required. The physical examination focuses on the size of the thyroid gland, heart rate and presence of tumors if any. A blood test will also be required to check thyroid hormone levels such as T3, T4 and TSH levels. Your doctor may also ask for an ultrasound of the thyroid gland and an imaging test to determine iodine radioactive uptake.
Silent thyroiditis has a good prognosis and patients usually recover within one year. The acute phase typically lasts only three months. Most patients do not require any form of treatment for this condition but regular checkups are advised to keep track of the disease. In rare cases, medical treatment may be required. For example, if the patient complains of increased heart palpitations or excessive sweating, beta blockers may be prescribed to lower the heart rate. The patient is advised to get plenty of rest and avoid any stressful situations.
In some cases, silent thyroiditis may lead to permanent hypothyroidism. In such cases, medication may be prescribed to normalize the thyroid hormone levels. In some cases, thyroid hormone replacement therapy may also be advised. Surgery and radioactive iodine treatment are not required to treat silent thyroiditis.


+1.svg)
