Tachycardia - All About It!
Tachycardia
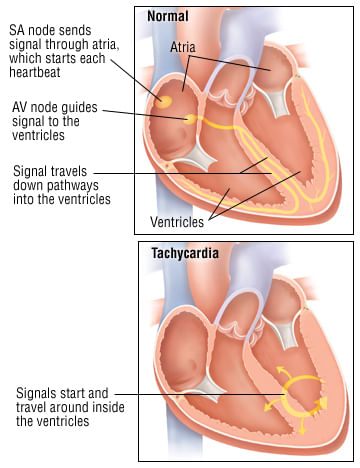
Tachycardia is also known as tachyarrhythmia. It is a common type of heart rhythm disorder. For adults, the normal resting heart rate is between 60 - 100 beats per minute. In tachyarrhythmia, the heart rate is greater than 100 beats per minute. The heart rate generally rises during exercise or when you take a lot of stress. But in case of tachycardia, the heartbeats are faster than normal in the upper or lower chambers or both while at rest. Various treatment options are available including medications and surgery to treat the heart disorder of tachycardia. Sometimes, people are not able to recognise the symptoms of tachycardia. Tachycardia can lead to serious heart problems or complications if not treated properly on time or left untreated. Heart failure, stroke, sudden cardiac arrest, or death can be some of the serious complications of tachycardia. So, if you find out that you are suffering from the symptoms of tachycardia then should visit the doctor at the earliest for a diagnosis.
Symptoms
Due to the fast heartbeat rate, your heart is not able to pump the blood properly to your body. This can lead to various symptoms or signs of tachycardia:
- Pain in the chest
- Fainting
- Lightheadedness
- Rapid pulse rate
- Heart palpitations
- Sudden weakness
Sometimes, people do not experience the symptoms at all. They get to know about it from their doctor after the physical examination or electrocardiogram test.
Causes
Tachycardia happens when something disrupts the normal electrical impulses that control the rate of pumping action of your heart. Many things can cause the problem of tachycardia. Sometimes, it becomes hard to recognise the exact cause of tachycardia. Check out the various causes of tachycardia:
- Drinking too much alcohol and beverages that contain caffeine can lead to the problem of tachycardia.
- Many heart diseases including heart valve disease, heart failure, heart muscle disease, coronary artery disease, tumours, or infections can lead to the tachycardia.
- Congenital heart conditions which are present at the time of birth can lead to tachycardia.
- Sudden stress or hypertension can cause tachycardia.
- Tachycardia can also happen due to smoking, the consumption of cocaine and some other recreational drugs.
- Side effects can happen due to the intake of certain medicines which can result in tachycardia.
- Electrolytes are the mineral-related substances required for conducting electrical impulses. The imbalance of electrolytes can lead to tachycardia.
- Overactive thyroid, high or low blood pressure, fever, anaemia, certain lung diseases and more are some of the other causes of tachycardia.
How is it diagnosed?
As soon as you experience any or some of the symptoms of tachycardia, you should visit the doctor. The doctor will conduct a physical examination in order to diagnose the problem. Your doctor will ask you about your medical history and health habits. You may be asked to get some tests done including:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or ECK): It is a painless test done to diagnose tachycardia. The small sensors (electrodes) are attached to your chest or arms in order to record the electrical activity of your heart. This test helps your doctor to know what type of tachycardia you have and how problems in your heart leading to a fast heart rate. This test provides the information for a limited time period. If your doctor wants more information then he may ask you to use portable ECG devices.
- Holter Monitor: It is a portable ECG device. This device helps to record your heart's activity for around 24 hours. You can easily carry this device in your pocket. It can also be worn on a belt or shoulder strap. If your doctor wants to check the record of your heart activity for a longer period then he may ask you to use this device.
- Event Monitor: It is also a portable electrocardiogram device helps to monitor your heart activity for a few months or weeks. You wear this device for the whole day but it allows you to record the heart activity at the certain times. Whenever you experience the symptoms of fast heart rate, you have to push a button on the device in order to record. There are some monitors that automatically sense your abnormal heart rhythms and start recording your heart's activity. By the help of this, your doctor is able to see the activity of your heart at the time of your symptoms.
- Electrophysiological test: This non-surgical test is done to confirm the diagnosis and to pinpoint the location where the problem is. In this test, a doctor inserts electrodes tipped catheters into your arm, groin or neck and guided through blood vessels to various spots in your heart. Electrophysiologist does this test in the EP lab.
- Stress test: In the stress test, extra stress is given to you in order to check how your heart functions when it works hard. During this test, your doctor may ask you to do exercise may be on a treadmill or stationary bicycle and at the same time, your heart activity would be monitored.
- Tilt-table test: If the electrocardiogram and Holter monitor fail to diagnose the problem then your doctor may perform a tilt-table test. This test helps to monitor the rhythm of the heart, blood pressure, and heart rate.
- Blood tests: Blood tests help to know if thyroid problem or other substances leading to tachycardia.
- Chest X-ray: Chest X-ray is done to check if your heart is enlarged. By the help of this test, the still images of your heart and lungs are taken to check their condition.
Prevention
A healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of tachycardia. The problem of tachycardia can be prevented by making some changes in health habits including:
- You should quit smoking.
- The intake of beverages that contain caffeine should be reduced.
- You should reduce the consumption of alcohol.
- Exercise and weight loss can also reduce the risk of tachycardia.
- Avoid the situations that give you stress.
- Avoid having spicy and fatty food and stick to a healthy diet.
Treatment
The treatment depends on the cause of your tachycardia. It also depends on your age and health record. In tachycardia, the treatment is given to slow down the fast heart rate and minimize the complications that can arise in the future. The following treatment options are available for the people suffering from tachycardia:
Ways to slow down a fast heartbeat:
- Vagal manoeuvres: It is an action performed to slow down your heart rate. Your doctor may ask you to perform this action during an episode of a fast heartbeat. The vagal nerve regulates your heartbeat and vagal manoeuvres affect this nerve. Manoeuvres include coughing, heaving as if you are having a bowel movement and putting an ice pack on the face.
- Medications: If vagal manoeuvres do not show any result then your doctor may give you an injection of an anti-arrhythmic medication for restoring the normal heart rate. Your doctor may also recommend you pill version of an anti-arrhythmic drug.
- Cardioversion: In this, an electric current is given to your heart through electrodes placed on your chest. This helps to restore a normal heart rhythm. This treatment method is used when there is an emergency or vagal manoeuvres and medications do not work with your type of tachycardia.
Ways to prevent episodes of a fast heart rate:
- Catheter ablation: In this, doctor inserts catheters tipped with electrodes into your arm, neck or groin and guide them through the blood vessels to your heart. This method is used when an extra electrical pathway is the cause of increased heart rate.
- Medications: Your doctor may ask you to have anti-arrhythmic medications in pills version regularly to prevent a fast heart rate. Calcium channel blockers and beta blockers are the other types of drugs that may be prescribed by your doctor as an alternative to or in combination with anti-arrhythmic medications.
- Pacemaker: Pacemaker helps in treating some types of tachycardias. A pacemaker is a small device that is implanted under your skin through a surgery. An electrical pulse is emitted by this device whenever it senses an abnormal heartbeat. The electrical pulse helps your heart to resume a normal beat.
- Implantable cardioverter: In this, a device of pager size named implantable cardioverter-defibrillator is implanted in your chest through a surgery. This device helps continuously to monitor your heartbeat, detect an increase in heart rate and deliver calibrated electrical shocks, if required, in order to restore a normal rhythm of the heart. This treatment is recommended if you are having a life-threatening tachycardia.
- Surgery: Doctors recommend surgery when all the other options do not work or when surgery is required to treat another heart disorder. Open-heart surgery is generally done to damage an extra electrical pathway leading to tachycardia. The maze procedure is another type of surgery in which a surgeon makes small cuts in heart tissue.
- Ways to prevent blood clots:
- Blood-thinning medication: Those people who suffer from the heart disorder of tachycardia have a great risk of developing a blood clot. A blood clot can cause a heart attack or stroke. For this purpose, your doctor may prescribe you blood thinners to reduce the risk of developing a blood clot.
Complications
The various complications that are associated with tachycardia are:
- Blood clots: This is one of the common complications of tachycardia. Due to tachycardia, the risk of developing blood clots increase. Blood clots formation can lead to a stroke or heart attack.
- Heart failure: If your condition of tachycardia is not controlled on time then it can make your heart weak. Weak heart increases the chance of heart failure. In heart failure, the heart does not pump the blood properly to all the organs of the body. Due to this, the body of the person can be affected from the left side, right side or both the sides.
- Sudden death: Sometimes, ventricular tachycardia can lead to sudden death.
- Other complications: The other complications of tachycardia are fainting, dizziness, tiredness, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
Myths
Myth #1: If your heart rate is higher than the normal resting heart rate then it means you are stressed out.
In tachycardia, the heart rate is greater than the normal resting rate. It is true that stress can spike your heart rate. But heart rate can also rise due to other causes including fever, anemia, thyroid disease, consumption of alcohol and beverages containing caffeine, smoking and more.
Conclusion
Tachycardia is a heart disorder in which the heart rate is higher than the normal resting heart rate. The normal resting heart rate is between 60 - 100 beats per minute for adults. People who suffer from tachycardia experience the heart rate of greater than 100 beats per minute. Sometimes, people are not able to recognize tachycardia as they do not experience the symptoms at all. Your doctor can help you to diagnose tachycardia through the physical examination and various tests. As soon as you experience any or some of the symptoms of tachycardia, you should reach out to the best doctor. Fever, high or low blood pressure, lung diseases, anemia, consuming alcohol, smoking, drinking beverages having caffeine, thyroid disease and various heart diseases can lead to tachycardia.


+1.svg)
