Treatment of Edema!
Treatment of Edema
Homeopathic Treatment of Edema
Acupuncture & Acupressure Treatment of Edema
Psychotherapy Treatment of Edema
Conventional / Allopathic Treatment of Edema
Surgical Treatment of Edema
Dietary & Herbal Treatment of Edema
Other Treatment of Edema
What is Edema
Symptoms of Edema
Causes of Edema
Risk factors of Edema
Complications of Edema
Lab Investigations and Diagnosis of Edema
Precautions & Prevention of Edema
Treatment of Edema
Homeopathic Treatment of Edema
Homeopathic Treatment of Edema reduces swelling especially in legs and ankle. It is also helpful when puffy swelling develops below the eyes or in the extremities. Homeopathy improves the root cause of swelling thus prevents it developing further. Some of the homeopathic remedies for treatment of edema are:
Apis mellifica
Calcarea carbonica
Graphites
Ledum palustre
Kali carbonicum
Pulsatilla
Acupuncture and Acupressure Treatment of Edema
Acupuncture improves energy flow, removes blocks and relieves edema. It cures underlying blockage of energy channels to stop edema from occurring.
Psychotherapy and Hypnotherapy Treatment of Edema
Psychotherapy and hypnotherapy can help in stress relief. They can help in better coping and early relief.
Conventional / Allopathic Treatment of Edema
Allopathic Treatment of Edema involves the use of drugs that help your body expel excess fluid in the form of urine. One of the most common diuretics is furosemide (Lasix).
Dietary & Herbal Treatment of Edema
Reduce your sodium intake
Eat foods high in vitamin B such as dark leafy greens, oatmeal, lima beans, and asparagus.
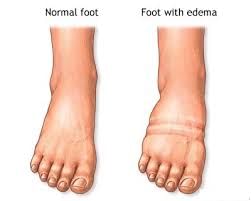
What is Edema?
Edema is swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in your body’s tissues. It usually occurs in the feet, ankles and legs, but it can involve your entire body.
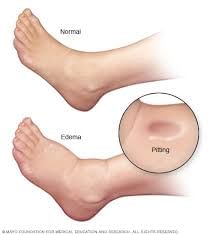
Symptoms of Edema
Swelling of the tissue directly under your skin
Stretched skin
Skin that retains a dimple after being pressed for several seconds
Increased abdominal size
Causes of Edema
Sitting or staying in one position for too long
Eating too much salty food
Kidney disease
Liver disease
Premenstrual signs and symptoms
Weak or damaged leg veins
Pregnancy
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Estrogens
Congestive heart failure
Cirrhosis
Risk factors of Edema
Taking certain medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, estrogens, calcium channel blockers and diabetes medications
Complications of Edema
Difficulty in walking
Decreased blood circulation
Decreased elasticity of arteries, veins, joints and muscles
Painful swelling
Stiffness
Stretched skin,
infection in the swollen area
Scarring between layers of tissue
Increased risk of skin ulcers
Diagnosis of Edema
Diagnosis of Edema involves the following tests:
Physical exam and medical history
X-rays and ultrasound exams
Blood tests or urine analysis
Precautions & Prevention of Edema
Prevention of edema can be achieved by the treatment.


+1.svg)
