What is Androgenic Alopecia?
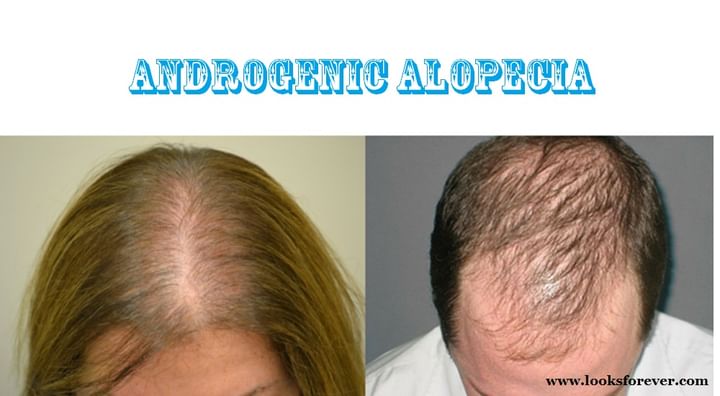
Androgenic alopecia is a typical type of hair loss in both men and women. In men, this condition is also called as, Male Pattern Baldness. Hair is lost in an all around characterized pattern, starting above both temples. After some time, the hairline recedes to frame a characteristic "M" shape. Hair additionally thins at the crown (close to the top of the head), regularly advancing to partial or Complete Baldness.
The pattern of Hair Loss in women contrasts from male pattern baldness. In women, the hair winds up plainly more slender everywhere throughout the head, and the hairline does not recede. Androgenic Alopecia in women occasionally prompts add up to total baldness.
Androgenic alopecia in men has been, related with a many other medicinal conditions including coronary illness and growth of the prostate. Moreover, Prostate Cancer, Disorder of Insulin Resistance, (for example, diabetes and Obesity), and High Blood Pressure (hypertension) have been identified with Androgenic Alopecia. In women, this type of hair loss is, related with an expanded risk of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). PCOS is, portrayed by a hormonal imbalance that can prompt sporadic Menstruation, Acne, Abundance hair somewhere else on the body (Hirsutism), and Weight Gain.
Androgenic Alopecia is an incessant reason for hair loss in both men and women. This type of hair loss influences an expected 50 million men and 30 million women in the United States. Androgenic Alopecia can begin in teenage also and risk increments with age; more than 50 percent of men over age 50 have some level of hair loss. In women, hair loss is no doubt after menopause.
Causes of Androgenic Alopecia
Change in Genetics
An assortment of hereditary and natural components likely, assume a part in causing Androgenic Alopecia. In spite of the fact that scientists are contemplating risk considers that may add to this condition, a large portion of these elements stay obscure. Scientists have discovered that this type of hair loss is, identified with hormones called Androgens, especially an Androgen called Dihydrotestosterone. Androgens are critical for ordinary male sexual development before birth and during puberty. Androgens likewise have other critical functions in both males and females, for example, controlling Hair Growth and Sex Drive.
Hair Growth initiates under the skin in structures called Follicles. Each strand of hair typically develops for 2 to 6 years, goes into a resting stage for many months, and afterward drops out. The cycle begins once again when the follicle starts growing another hair. Increased levels of Androgens in hair follicles can prompt a shorter cycle of hair growth and the growth of shorter and thinner strands of hair. Moreover,
To replace strands, which are shed off there is a deferral in the growth of new hair.
In spite of the fact that Researchers speculate that several Genes play a part in Androgenic Alopecia, varieties in just a single Gene, Androgen Receptor, have been affirmed in Scientific Studies. The Androgen Receptor Gene gives directions to making a protein called an Androgen Receptor. Androgen Receptors enable the body to react fittingly to Dihydrotestosterone and different Androgens. Studies propose that varieties in the Androgen Receptor Gene prompt expanded action of Androgen Receptors in hair follicles. It stays misty, nevertheless, how these hereditary changes increment the risk of Hair Loss in Men and Women with Androgenic Alopecia.
Researchers keep on investigating the association between Androgenic Alopecia and other medical conditions, for example, Heart Disease and Prostate Cancer in men and Polycystic Ovary disorder in Women. They trust that some of these disorders might be, related with elevated Androgen Levels, which may assist to describe why they have a tendency to happen with Androgen related Hair Loss. Other hormonal, natural, and hereditary components that have not been, recognized likewise might be included.
Inheritance Pattern
The Inheritance Pattern of Androgenic Alopecia is hazy in light of the fact that numerous hereditary and natural components are probably going to be included. This condition tends to cluster in families, in any case, and having a nearby relative with patterned hair loss has all the earmark of being a risk calculate for developing the condition.
Symptom
Notwithstanding Male Pattern Baldness, Androgenic Alopecia in men has been, related with a few other therapeutic conditions including Coronary Heart Illness and augmentation of the Prostate. Moreover, Prostate Cancer, Disorders of Insulin Resistance, (for example, Diabetes and Obesity), and High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) have been identified with Androgenic Alopecia in men. In women, Androgenic Alopecia is, related with an expanded risk of Polycystic Ovary Disorder (PCOS) which is, described by a hormonal imbalance that can prompt sporadic Menstruation, Acne, Excess body hair (Hirsutism), and Weight Gain.
The Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) gives the accompanying list of components that have been, reported in individuals with this condition. A significant part of the data in the HPO originates from Orphanet, a European uncommon disease database. On the off chance that accessible, the rundown incorporates an unpleasant gauge of how regular a component is (its recurrence). Frequencies depend on a particular study and may not be illustrative of all studies.
Diagnosis
Genetic Testing
What is Genetic Testing?
Genetic testing is a sort of therapeutic test that distinguishes changes in chromosomes, genes, or proteins. The consequences of a genetic test can affirm or preclude a speculated genetic condition or help decide a person’s chance of creating or passing on a genetic disorder. More than 1,000 genetic tests are at present used and more are being, developed.
Various techniques can be, utilized for Genetic Testing:
-
Molecular Genetic Tests (or Gene Tests) ponder single genes or short lengths of DNA to distinguish varieties or transformations that prompt a Genetic disorder.
- Chromosomal Genetic Tests analyze entire chromosomes or long lengths of DNA to check whether there are expansive Genetic changes, for example, an additional copy of a chromosome, that cause a genetic condition.
- Biochemical Genetic Tests contemplate the sum or action level of proteins; variations from the norm in either can demonstrate changes to the DNA that outcome in a Genetic Disorder.
Genetic testing is intentional. Since, testing has benefits and in addition restrictions and risks, the choice about whether to be tested is an individual and complex one. A Geneticist or Genetic Counselor can help by giving data about the advantages and disadvantages of the test and examining the social and enthusiastic parts of testing.
Treatment
Each patient is exceptional and just the Doctor can assess and decide the Best Treatment.
Surgical Treatment of Androgenic Alopecia has great restorative outcomes. The principle issue is covering the Bald area with Donor Plugs (or follicles) adequate in number to be powerful. Micrografting produces a more Natural appearance than the old method of Transplanting Plugs.
It is critical for the patients with Androgenic Alopecia to be assessed for treatable reasons for "Telogen Effluvium" (diffuse Hair Shedding, frequently beginning abruptly) like anemia or hypothyroidism, particularly in patients who had a quick advance of their illness or a sudden begin of the sickness.
Different Names of Androgenic Alopecia
Androgenic Alopecia
Female Pattern Baldness
Male Pattern Alopecia


+1.svg)
