DVT: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Feb 18, 2023
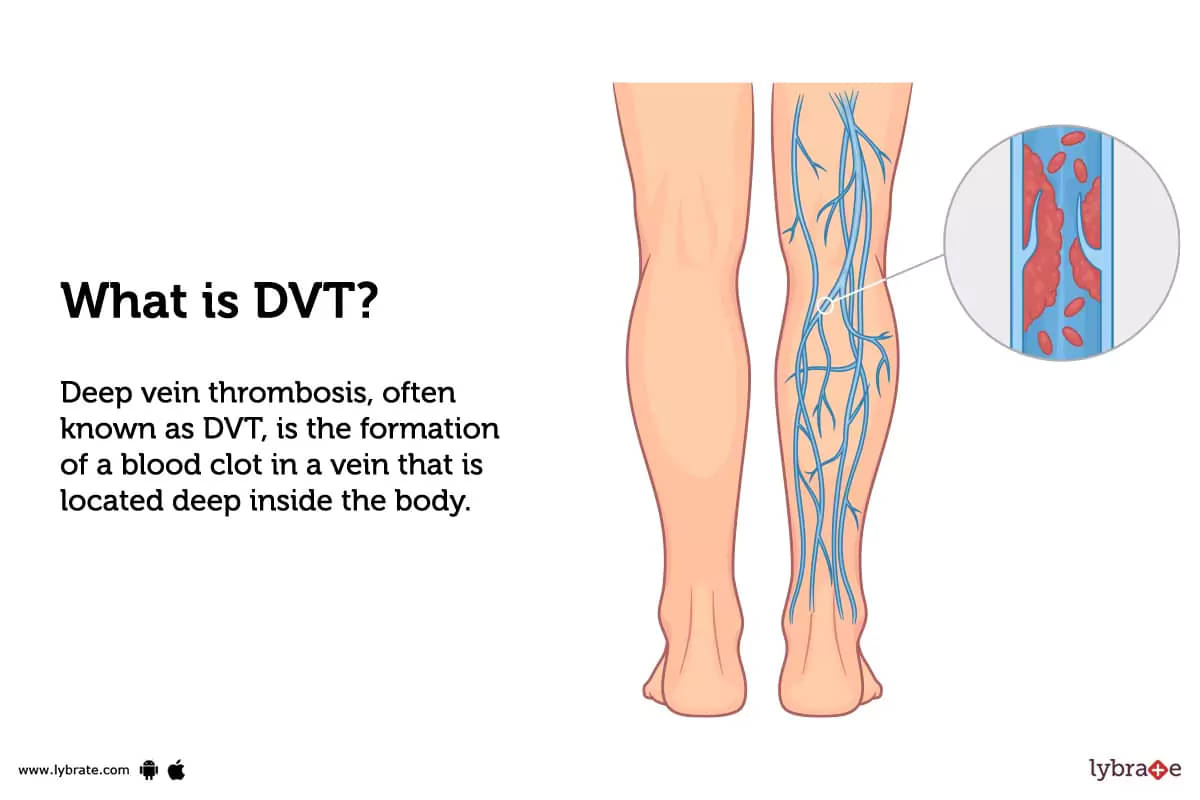
What is DVT?
Deep vein thrombosis, often known as DVT, is the formation of a blood clot in a vein that is located deep inside the body. It usually occurs in the lower leg or thigh and can be serious if it breaks loose and travels to the lungs.
Types of DVT
There are two main types of DVT:
- Unprovoked DVT: This type of DVT occurs without an obvious cause. It can happen after long periods of sitting, such as on long flights or car rides, and may be caused by certain medical conditions such as cancer or heart failure.
- Provoked DVT: This type of DVT is usually caused by an injury to the veins or an underlying medical condition such as a blood-clotting disorder, pregnancy, surgery, trauma, obesity or smoking.
What causes DVT?
Common causes of DVT include:
- Prolonged immobility: Long durations of sitting or laying down might raise the risk of getting DVT.
- Injury to the veins: Trauma or surgery to the veins can cause clotting and lead to DVT.
- Certain medical conditions: Medical conditions such as cancer, heart failure, and obesity can increase risk.
- Medications: Certain blood thinning medications may increase the risk of developing a clot.
- Hormone use: Hormone use (such as estrogen) may increase risk for some people.
What are the symptoms of DVT?
- Pain and tenderness in one leg (usually calf)
- Swelling of the affected leg
- Warmth or redness in the clot area
- Discoloration of the skin (bluish-red or purple)
- Increased pain with movement or pressure
How can you prevent DVT?
- Engage in frequent physical exercise and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Avoid prolonged periods of sitting and get up and walk about often.
- Wear compression stockings, particularly for lengthy journeys or flights.
- To improve circulation, consume lots of fluids and a balanced diet rich in fibre and vitamins C and E.
- If you are taking birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy, talk to your doctor about the risks associated with it and other preventive measures that can be taken.
- If you have a family history of DVT, discuss it with your doctor who may suggest taking anticoagulants or other medications to prevent clotting before travelling long distances or having surgery.
DVT - Diagnosis and Tests
These tests are often used to identify DVT:
- Doppler Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to create images of the veins and can detect clots in the deep veins. It is non-invasive and painless.
- Venography: This test uses a special dye injected into the vein to show up on X-rays and reveal any blockages in the veins or clotting. It requires an intravenous line and can be slightly painful.
- D-dimer Test: This blood test examines the amounts of a protein that is secreted in the body when a clot develops, suggesting that a person may have DVT. It is not always accurate, but it may help rule out other illnesses with comparable symptoms.
- CT Scan: This imaging test uses X-rays to take detailed pictures of the veins and may be used if other tests cannot confirm a diagnosis of DVT or if there are complications with the clotting.
What are possible complications of DVT?
- Pulmonary embolism: A life-threatening condition where a clot travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow.
- Post-thrombotic syndrome: Chronic pain, swelling, and skin discoloration in the afflicted region.
- Recurrent DVT: The risk of another DVT increases after the initial episode.Chronic venous insufficiency: Vein deterioration over time that may lead to leg ulcers and other problems.
Home Remedies for DVT?
- Take herbs like ginger, turmeric, and garlic to boost circulation and reduce inflammation.
- Massage your feet and legs with warm oil every day to improve blood flow in the area around the DVT site.
- Apply warm compresses over the affected area for 15–20 minutes each day to help reduce swelling and pain caused by DVT.
- Soak your feet in a warm Epsom salt bath for 15–20 minutes each day to reduce inflammation and pain caused by DVT.
What to eat in DVT disease ?
The following foods are recommended for a DVT diet:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables, particularly spinach and kale.
- Whole grains such as brown rice, oats, and quinoa.
- Lean proteins, including fish, poultry, eggs, legumes and nuts
- Healthy fats such as olive oil, and avocado.
- Low-fat dairy products.
- Herbs and spices for flavor.
- Fiber-rich foods that may help improve regularity.
- Water to stay hydrated.
What not to eat in DVT?
- High-fat foods: Foods high in fat, such as bacon, sausages, red meat and processed meats, can increase the risk of a DVT.
- Refined carbohydrates: Foods such as white bread and pasta can cause inflammation and raise the risk of DVT.
- Salt: Eating too much salt increases blood pressure and may increase the risk of developing a DVT.
- Alcohol: Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol can increase the risk of developing a DVT by increasing blood pressure and causing dehydration.
- Caffeine: Too much caffeine can intervene with normal blood clotting mechanisms which could lead to an increased risk of a DVT.
DVT Treatment
- Elevate the affected limb: Raise the affected limb on pillows or blankets to reduce swelling and pain.
- Exercise: Move the affected extremity to keep the blood flowing and help reduce clotting.
- Medications: Anticoagulants such as heparin and warfarin can be used to prevent further clots from forming, while antiplatelet drugs like aspirin can help thin the blood and reduce risk of clotting.
- Thrombolysis: This procedure involves using a catheter to deliver a medication directly into a clot, which helps dissolve it more quickly than other treatments alone can do so.
Which doctor to consult for DVT?
To diagnose and treat DVT, it is necessary to consult a healthcare professionals such as a doctor or vascular specialist.
Which are the best medicines for DVT ?
Anticoagulant medications are the mainstay of treatment for DVT, and help to prevent further clotting. Examples include heparin, warfarin, apixaban and rivaroxaban.
- Nsaid: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may also be used in some cases to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Steroid for DVT: Steroids may be used to treat deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a type of blood clot in the veins. Steroids work by reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system, which can help reduce pain and swelling in the affected area.
How long does it take to recover from DVT?
Depending on the particular situation and the degree of the clot, the recovery period from DVT might be anywhere from a few weeks and several months.
With proper medical care and treatment, most people with DVT are able to make a full recovery within 6–12 weeks.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
The effects of DVT treatment can be permanent depending on the severity of the condition and the type of treatment received.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- After treatment for deep vein thrombosis (DVT), it is important to follow the doctor’s instructions and take preventive measures to help reduce the risk of future DVT.
- These post-treatment guidelines include taking prescribed anticoagulants (blood thinners) as directed, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking.
- Compression stockings should also be worn to help prevent swelling and improve blood circulation in the affected area.
- Regular follow-up with a doctor is also recommended so that any changes in health or symptoms can be quickly addressed.
What is the cost of DVT treatments in India?
The cost of DVT treatment in India can range from anywhere between ₹10,000 to ₹50,000 or more.
What are side-effects of DVT treatments?
- Pain and swelling near the affected area: This is a common side effect of DVT treatments, as it can cause discomfort and inflammation in the affected area.
- Bleeding complications: DVT treatments can increase the risk of bleeding, which can be serious or even life-threatening.
- Infection: DVT treatments may put patients at increased risk for developing infections due to weakened blood vessels or puncture wounds caused by needles used during treatment.
- Blood clots: New blood clots may develop as a result of DVT treatment, which might be problematic if they spread to the lungs or other vital organs.
- Skin reactions: Some patients may experience skin reactions such as rashes, itching, or irritation where IV lines are placed during treatment.
DVT - Outlook/ Prognosis
If you are experiencing any problems relating to DVT, you should see a doctor right away because they can cause complications such as 'Pulmonary embolism, Post-thrombotic syndrome, Deep vein thrombosis, Leg ulcers, and so on' in which the treatment course can span from a few months to years depending on the severity of the condition.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Vascular Surgeon near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors