Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 04, 2023
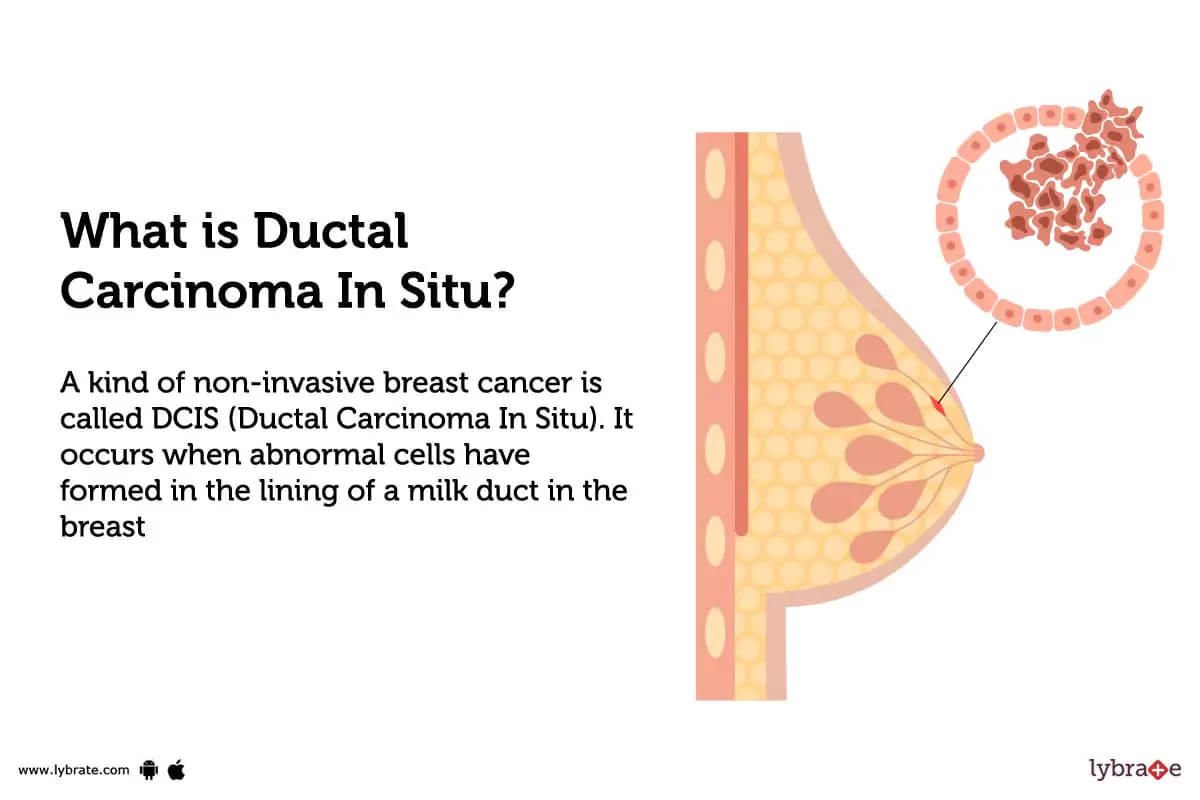
What is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ?
A kind of non-invasive breast cancer is called DCIS (Ductal Carcinoma In Situ). It occurs when abnormal cells have formed in the lining of a milk duct in the breast, but have not spread outside of the duct. DCIS is considered to be a precancerous condition and if left untreated, it can progress to an invasive form of breast cancer.
Types of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
There are three main types of DCIS: comedo, micropapillary and cribriform.
- Comedo: This type of DCIS appears as white or greyish patches on mammograms and consists mostly of non-invasive cells that have not spread outside the ducts. This type is often associated with calcifications, which can be seen on mammograms and ultrasound images.
- Micropapillary: This type has clusters of cells that look like tiny papillae (small bumps) under a microscope, but they do not usually spread outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue.
- Cribriform: This type has cells that look like small holes or pores under a microscope and may have some small areas where there are clusters of cells that look like tiny papillae (small bumps). Cribriform DCIS can sometimes spread outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue, but this does not always happen.
What Causes Ductal Carcinoma In Situ?
The exact cause of DCIS is unknown, however certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing it, such as age and family history of breast cancer.
Other risk factors include a personal history of breast biopsy or radiation therapy to the chest area, as well as lifestyle choices such as diet and alcohol consumption.
Research suggests that certain genetic mutations can also play a role in the development of DCIS, although these mutations are rare and not all cases are linked to them.
What are the symptoms of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ?
DCIS is often detected during a screening mammography and does not produce any symptoms.
However, if DCIS advances, it may produce changes in the form or size of the breast, as well as changes in the skin, like dimpling or redness.DCIS may also induce nipple discharge or pain in the afflicted region in rare circumstances.
How can you Prevent Ductal Carcinoma In Situ?
- Smoking and heavy alcohol usage should be avoided.
- Eat a lot of fruits and veggies in your diet.
- Reduce the amount of time you spend in the sun by using sunscreen and wearing protective gear when you are outside.
- Get regular screening tests for breast cancer starting at age 40 or earlier if recommended by your doctor.
- Discuss the risks and benefits of hormone therapy with your doctor if you are considering it for menopausal symptoms or other conditions related to hormones such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ - Diagnosis and Tests
- Mammography: Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS) is typically detected through mammography and appears as small, calcified clusters or masses on the mammogram.
- Biopsy: A biopsy is often performed to diagnose DCIS, which entails the removal of a tiny tissue sample from the afflicted region. A pathologist next examines the sample under a microscope to identify whether cancer cells exist and, if so, what kind they are.
- MRI: An MRI can provide detailed images of the breast tissue, allowing doctors to accurately diagnose DCIS and determine its size, shape, and location.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging can be used to diagnose DCIS by looking for abnormal growths or masses in the breast tissue. Ultrasound can also help identify potential areas of concern that may need to be biopsied for further testing. Additionally, ultrasound imaging may be utilised to track the size and shape changes of DCIS lesions over time.
What are possible complications of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ?
- Increased risk of developing invasive breast cancer: If untreated, DCIS, which is a precancerous disease, can result in the growth of invasive breast cancer.
- Risk of recurrence: Even after successful treatment for DCIS, there is a chance that the condition could recur in the same or other area of the breast.
- Anxiety and depression: A diagnosis of DCIS can cause significant psychological distress for some people, leading to anxiety and depression.
- Impact on quality of life: People with DCIS may experience changes in their quality of life due to fear and anxiety associated with their diagnosis or treatment side effects.
Home Remedies for Ductal Carcinoma In Situ?
- Drink a mixture of turmeric, ginger and honey to help reduce inflammation and boost immunity.
- To alleviate stress and enhance general health, combine ashwagandha powder with warm milk.
- Consume a variety of fruits and vegetables to get antioxidants that may aid in the battle against cancer cells.
- Drink green tea regularly to help protect against cancer-causing agents in the body.
- Take triphala powder with warm water every night before bedtime to cleanse the body of toxins and promote healthy digestion.
- Consume amalaki fruit or its juice for its anti-cancer properties as well as its ability to boost immunity levels in the body.
What to eat in Ductal Carcinoma In Situ?
- Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats may minimise the chance of recurrence and enhance overall health.
- Some specific foods that may help to reduce the risk of recurrence in those with DCIS include:
- the cruciferous family of vegetables, which includes broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, kale, and cabbage.
- Foods high in antioxidants such as berries, apples and citrus fruits
- Omega-3 fatty acids may be found in flaxseeds, walnuts, and tuna.
- Lean proteins such as chicken breast, greek yoghourt.
- Healthy fats from avocados, olive oil or nuts like almonds or walnuts.
What not to eat in Ductal Carcinoma In Situ?
- Avoid processed, fried and sugary foods: Processed, fried and sugary foods can increase inflammation in the body and have been linked to an increased risk of developing cancer.
- Reduce your intake of red meat: Eating too much red meat has been linked to an increased risk of developing numerous cancers, including breast cancer.
- Avoid alcohol: Alcohol should be avoided by persons with Ductal Carcinoma In Situ since it has been related to an increased risk of breast cancer (DCIS).
- Limit consumption of saturated fats: Eating too many saturated fats can increase inflammation in the body and contribute to weight gain, which increases the risk of developing certain cancers like DCIS.
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Treatment
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy is a promising treatment option for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS).The goal of immunotherapy is to use the immune system of the patient to locate and eliminate malignant cells.
- Lumpectomy: A lumpectomy, in which the tumour and some surrounding tissue are removed, is the standard surgical therapy for DCIS.
- Mastectomy: The removal of the whole breast is called a mastectomy, and it is a more thorough operation. This kind of therapy may be suggested if the tumour is very big or if several tumours are found.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy is usually recommended for patients who have had a lumpectomy, as it can help reduce the risk of recurrence by killing any remaining cancer cells in the breast tissue.
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: If the tumour has spread to surrounding lymph nodes, a sentinel lymph node biopsy may be done to assess if further therapy is required.
- Axillary Lymph Node Dissection: If the sentinel lymph node biopsy finds cancer cells in the axillary lymph nodes, an axillary lymph node dissection may be carried out to eliminate any leftover malignant tissue.
Which doctor to consult for Ductal Carcinoma In Situ?
If you've been identified with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), you should visit a breast cancer expert immediately.A breast cancer specialist is typically an oncologist, a surgeon, or a radiation oncologist who has specialised training and experience in treating breast cancer.
Which are the best medications for Ductal Carcinoma In Situ?
- Hormonal Therapy: Hormonal therapy, also known as endocrine therapy, is a type of treatment that uses medications to block the effects of hormones on certain types of breast cancer cells. Tamoxifen, anastrozole, and letrozole are the most often used drugs for hormonal treatment.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may be prescribed before or after surgery in certain circumstances to lower the chance of recurrence.The type of chemotherapy used will depend on the individual case and may include drugs such as doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, or paclitaxel.
- Targeted Therapies: Drugs that target specific molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells, such as HER2/neu inhibitors or mTOR inhibitors.
How long does it take to recover from Ductal Carcinoma In Situ?
Recovery from Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS) depends on the type of treatment used. Surgery recovery often takes several weeks and can be uncomfortable and swollen.
Radiation therapy typically takes four to six weeks, with some patients needing additional treatments for more advanced cases.
Hormonal therapy may be employed in certain circumstances and might take several months to show benefits
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
The treatment of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is generally successful in removing the abnormal cells from the affected area. However, there is no guarantee that the condition will not recur, as DCIS can be difficult to completely remove or eradicate.
What are Post-treatment guidelines?
- Get regular check-ups: After treatment for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), it is important to follow up with your doctor on a regular basis. This involves undergoing physical examinations, mammography, and other testing that your doctor may advise.
- Notice signs: It is also important to be aware of any changes in the breasts or areas around the breasts that may indicate a recurrence of DCIS or another form of cancer. It is crucial to call your doctor as soon as any unusual symptoms appear.
- Lifestyle changes: Lifestyle changes can also help reduce the risk of recurrence and improve overall health after treatment for DCIS. Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, limiting alcohol consumption, and not smoking are all recommended lifestyle modifications that can help reduce the risk of cancer recurrence and improve overall health.
- Take medications regularly: It is important to take any medications prescribed by your doctor regularly in order to ensure that the treatment is effective. Depending on the type of medication prescribed, it may be necessary to take them once a day or more often. It is also important to follow your doctor’s instructions for taking the medication and not stop taking it without talking to your doctor first.
What is the Cost of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Treatments in India?
Depending on the type of therapy selected, Ductal Carcinoma In Situ therapies in India may cost differently. Generally, the cost includes the doctor's fee, hospital charges, laboratory tests, and medication.
The cost of surgery can range from Rs. 25000 to Rs. 50000, while radiation therapy can cost between Rs. 5000 to Rs. 10000 per session. Chemotherapy may also be recommended in some cases and can range from Rs. 5000 to Rs 15000 per cycle depending on the drugs used.
What are side-effects of Ductal Carcinoma In Situ treatments?
Conclusion
If you are suffering from any complications relating to ductal carcinoma in situ then you should consult a doctor nearby as they can cause complications like Increased risk of developing invasive breast cancer, anxiety, and depression, etc. in which treatment course can range from a few months to years depending on the severity of the situation.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Oncologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors