Elbow (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Injuries, and More
Last Updated: Feb 25, 2023
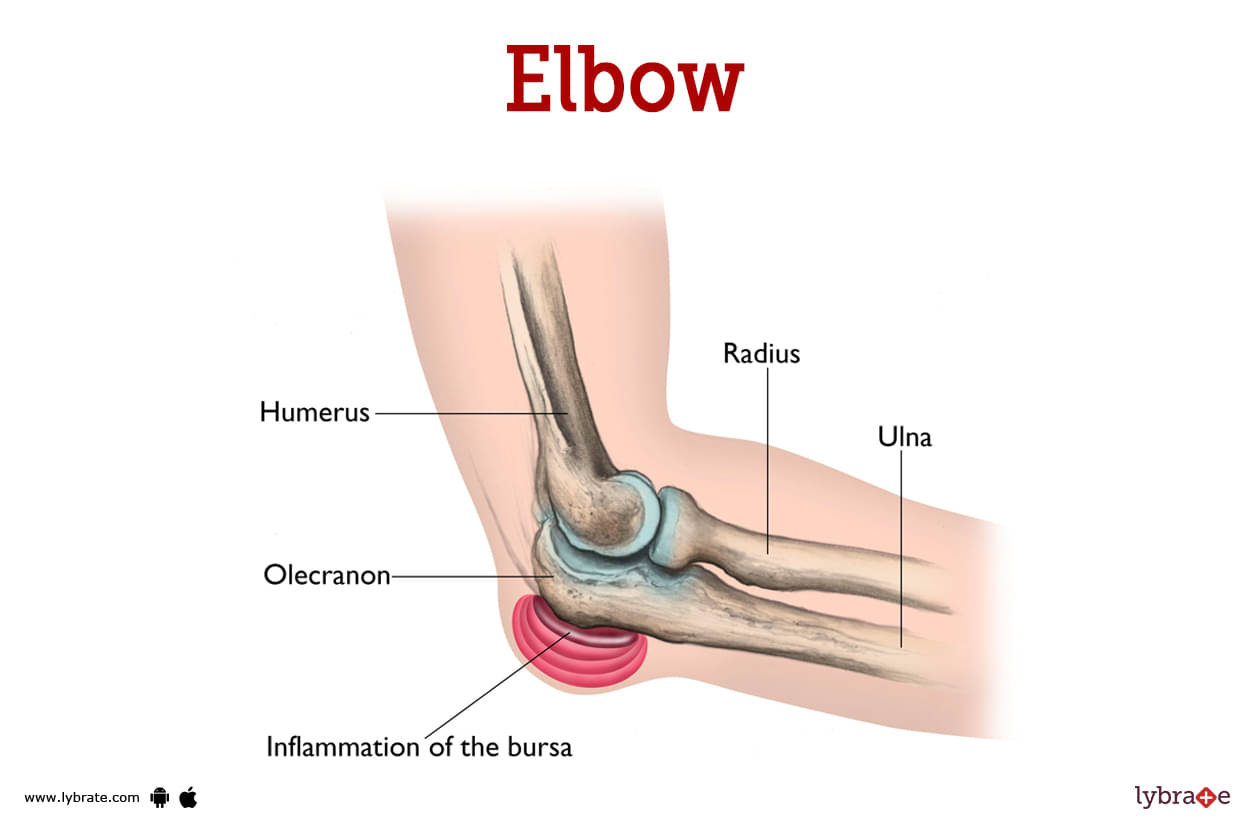
Elbow Image
The elbow joint is a synovial joint in the upper limb that connects the arm and the forearm. It is a three-bone joint composed of the humerus of the arm and the radius and ulna of the forearm.
The elbow joint is structurally classified as a synovial joint. Because the joint has two articulations, it is structurally classified as a compound joint. Synovial joints, also known as diarthroses, are mobile joints. At these joints, a layer of hyaline cartilage separates the articular surfaces of the bones. A highly viscous synovial fluid acts as a lubricant at these joints, allowing for smooth movement.
The joint is surrounded by a fibrous capsule, and the inside is lined with a synovial membrane. Synovial joints can be put into more groups based on what they do. The elbow joint is a hinge joint, which means it can only move in one direction.
The hinge-like features that are distinctive of the elbow are due to the presence of two joints known as the humeroulnar and the humeroradial joints. The concave surfaces of the trochlear notch on the ulna and the head of the radius compete with the rounded surfaces of the trochlea and capitulum of the humerus to determine the direction of rotation.
Function of Elbow joint
Its main functions are:
- Flexion and extension: The elbow joint allows the arm to move in two main directions: flexion (bending) and extension (straightening). This movement is important for activities such as lifting and reaching.
- Pronation and supination: The elbow joint also allows for pronation and supination of the forearm. Pronation is the rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces downward, while supination is the rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces upward. This movement is important for activities such as turning a doorknob or holding a cup.
- Stabilization: The elbow joint helps to stabilize the arm during movement by providing a rigid connection between the upper arm and forearm bones.
- Serves as a connector: Serves as a connector between the radius and the ulna. Transfers to the ulna the compression forces that are applied to the radius by the hand. Following that, the ulna is responsible for transmitting these forces to the humerus.
- Weight bearing: The elbow joint also bears weight and helps in the movement of the upper limb.
Overall, the elbow joint is a critical joint that allows for a wide range of movements in the arm and forearm, including flexion and extension, pronation and supination, and stabilization of the upper limb. It is also a weight-bearing joint.
Conditions of Elbow
- Tennis elbow: Tennis elbow is a reasonably common overuse injury that can affect any part of the forearm. This condition can be brought on by either repeated hand and forearm motions over time or an injury to those areas. There is a risk of injury to the tendons that attach the extensor supinator muscles (which twist and extend the forearm) to the olecranon process (commonly known as 'the elbow') due to the frequency with which these movements are performed. The lateral forearm is often the site of the originating pain. Additionally, weakness, numbness, and stiffness are fairly common, as is sensitivity upon contact.
- Golfer’s elbow: In many ways, golfer's elbow is the same as tennis elbow, though it is much less common. It's caused by doing the same thing over and over again, like in a golf swing, and it wears on the body. One more thing that can set this off is trauma. When the wrist is pronated and flexed forward, the tendons at the medial epicondyle of the elbow are inflamed (the forearm is rotated). Pain, stiffness, a lack of sensation, and weakness may occur on the inside of the elbow and travel down the forearm and into the fingers.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Joint inflammation caused by rheumatoid factors, sometimes called: Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, degenerative joint disease. In addition to being most common at the radioulnar joint in the wrist, where it is extremely widespread, the wrist is also where it is most abundant. There will be pain, stiffness, and anomalies as a result of this. While there is no shortage of options for dealing with rheumatoid arthritis, experts can't seem to agree on the best way to do it. Some of the most often used treatments for rheumatoid arthritis include wrist splints, operations, physical and occupational therapy, and antirheumatic drugs.
- Cubital tunnel syndrome: An inflammation and irritation of the ulnar nerve causes cubital tunnel syndrome. Ulnar neuropathy is the more prevalent name for this issue. This is especially common in the area surrounding the elbow, where the ulnar nerve is most vulnerable to damage. The ulnar nerve passes through the 'funny bone' near the top of the elbow. This region can become inflamed either immediately following a traumatic incident or later on as a result of persistent, repeated stress. Bone deformities and athletics are other common precipitating factors for this illness. Aside from pain, patients frequently experience tingling, numbness, and paralysis.Effusion within the elbow joint's cavity causes a posterior distention of the joint. This is because the joint capsule and the overlying fascia are both relatively thin towards the back. While the elbow is bent at a right angle, a needle is inserted posterolaterally, just above the head of the radius, to aspirate the joint.
- Elbow dislocations: Fractures of the coronoid process are a typical complication of posterior elbow dislocations. Elbow dislocations can go either way. Most cases of dislocated hand occur when the patient falls onto their outstretched hand. The olecranon's triangular attachment to the humeral epicondyles is no longer present. Keep in mind that when your elbow is flexed normally, a right triangle is formed by your humeral epicondyles and the end of your olecranon process.
- Nursemaid's elbow: Subluxation of the head of the radius is the root cause of pulling elbow, also known as nursemaid's elbow. This disease can develop in children as young as three years old if they are subjected to a rapid stimulus that causes the forearm to go into a pronated position. The elbow is kept slightly flexed and pronated throughout the process, and the head of the radius is liberated from the annular ligament.Attempting a supinate position of the forearm will result in extreme discomfort. The reduction can be performed with little effort by supinating and extending the elbow and then applying direct pressure posteriorly on the head of the radius.
- Student's elbow: Student's elbow is characterised by a painful, circular swelling above the olecranon that might vary in size. This issue arises from inflammation of the subcutaneous olecranon bursa, which sits over the subcutaneous triangle on the back of the olecranon process.
- Tendonitis: Tendonitis is the medical word for inflammation of the tendons, which are the tissues that connect muscles to bones. A painful ailment, tendinitis can be brought on by either overuse (repetitive motion) or a sudden event. Tendonitis is characterised by localised pain, edoema, and limited motion at the affected tendon.
- Bursitis: Bursitis is an excruciating inflammation of the bursae, the fluid-filled sacs that act as shock absorbers for bones, tendons, and muscles. Bursitis is a painful condition that can severely restrict your mobility. Direct damage, infection, or another ailment are just a few of the many potential causes of elbow bursitis. Symptoms including swelling, discomfort, or limited mobility often accompany pain.
- pitcher's elbow: Little league pitchers often suffer from an ailment known as 'pitcher's elbow.'Children and teenagers who engage in sports like baseball pitching that need a recurrent throwing action sometimes suffer from overuse ailments like little league elbow, also known as pitcher's elbow or medial apophysitis. A painful ailment characterised by swelling and limited mobility.
- Cubital tunnel syndrome: Cubital tunnel syndrome is caused by irritation or compression of the ulnar nerve; this ailment is also known as ulnar neuropathy. The groove on the inside aspect of the elbow is the path taken by the ulnar nerve (in the area commonly referred to as the funny bone). The symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome include aching, tingling, and muscle weakness.
- Osteochondritis dissecans: Osteochondritis dissecans is a disorder that occurs in children and adolescents when a piece of bone or cartilage inside a joint is cut off from its blood supply. Sometimes this causes a piece of cartilage and the thin layer of bone just beneath it to break off and fall into the joint space. Joint pain, swelling (edoema), and decreased mobility are typical manifestations of this condition.
- Fractures: Pain (which is exacerbated by movement or pressure), edoema (swelling), bruising, and loss of function are all symptoms of a fracture. Open fractures, in which the broken piece of bone protrudes through the skin, can make the surrounding tissue look skewed or misshapen. The case is even stronger for more serious fractures.
- Arthritis: Arthritis, commonly known as osteoarthritis, is a condition that occurs when cartilage in a joint deteriorates. Although there are several types of arthritis (osteoarthritis being the most frequent), rheumatoid, psoriatic, septic, post-traumatic, and lupus arthritis are all relatively uncommon. Fever and chills are a rare symptom of arthritis, but it is one of many. Arthritis can also cause swelling, soreness, severe pain, stiffness, and other symptoms.
- Inflamed bone spurs: As the name implies, bone spurs are bony projections that form on the surface of a bone. Bone spurs often form on a bone because of osteoarthritis. Bone spurs often don't cause any pain or other symptoms, but they can irritate or even tear the tissue or tendon they're attached to. Corns or calluses may form over time to provide additional protection for the skin around the bone spur.
- Ruptured biceps tendon: If the tendon that connects the biceps muscle to the radius is subjected to too much strain and ruptures, it will cause pain and a noticeable bulge in the arm. The most typical cause of this disorder is a sudden injury sustained while attempting to withstand a big weight by bending at the elbow. Both elbow flexion and forearm rotation become impaired as a result of this injury.
- Ligament tear: The most common type of ligament tear is the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) tear, which is commonly found in baseball pitchers and other athletes that participate in repeated overarm movement. A UCL rupture can be caused by repetitive motion or by the natural breakdown of the ligaments in the elbow. Damage to the UCL can range from mild inflammation to a total tear. This is an illustration of the later type.
Test of elbow
- Palpation: Using one's fingers or hands to feel for anomalies, as part of a physical examination. The doctor will physically feel an organ or part of your body to assess its size, shape, consistency, texture, location, and tenderness. Palpation, or the use of one's hands to feel for abnormalities, is one technique that can be employed during a physical examination.
- X-rays: It is also called X-radiation, are a type of electromagnetic radiation with a high enough frequency to penetrate most materials. In comparison to X-radiation, X-rays are quite rare. The wavelength of most X-rays ranges from around 10 picometers to about 10 nanometers. This is the range of energies from 145 electron volts to 124 keV and frequencies from 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz.
- Magnetic resonance imaging: It is abbreviated as 'M.R.i.' for simplicity) is a radiology-approved imaging technique used to capture pictures of internal human structures and functions. MRI scanners use high magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to create images of the body's internal organs.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce a sonogram, or image, of internal organs, tissues, and other anatomical structures in the human body. Contrary to x-rays, ultrasounds do not employ any form of radiation.
- Elbow flexion test: The elbow flexion test is used to assess a patient's range of motion and determine whether or not they have cubital tunnel syndrome. The patient is coached to forcefully maintain full elbow flexion with the wrists fully extended for three to five minutes. 184. If the patient's symptoms can be replicated in the lab, the test is termed positive.
- The Tinel's Symbol: When a doctor taps a patient's skin over a nerve, the patient may experience a tingling or 'pins and needles' sensation known as Tinel's sign. Tinel's sign can be used to identify a variety of diseases and disorders. If a person experiences Tinel's sign when tapping, it could mean that a nerve in the area is being compressed or has been injured.
- physical examination: When trying to diagnose ulnar nerve compression, a doctor will first ask about your symptoms, then review your health history, and finally perform a physical examination of your arm, elbow, and hand. Your doctor may also perform a physical exam on your arm to look for signs of numbness, sensation loss, and nerve irritation or damage.
- Computerized tomography (CT): It scans employ a sequence of X-ray pictures taken at different angles to build cross-sectional pictures (slices) of your bones, blood arteries, and soft tissues. These pictures can help doctors diagnose diseases including cancer and heart problems. The images obtained from a CT scan are more detailed than those from a regular X-ray.
- Electromyography: The procedures of electromyography (EMG) are as follows: A diagnostic procedure, electromyography (EMG) examines the health of a patient's muscles and the nerve cells that are responsible for controlling those muscles (motor neurons). Problems with nerve function, muscle function, or the transfer of nerve signals to muscles can all be gleaned from the results of an electromyography.
- Biopsies of bursa fluid: Biopsies of bursa fluid revealed the following: A synovial biopsy is a biopsy taken from the synovial membrane that lines a joint. The term 'synovial membrane' is used to describe this sort of tissue. A joint lining tissue sample, or synovial tissue sample, is obtained during a synovial biopsy. In addition to aiding in the diagnosis of gout, this test can be used to detect bacterial infections and other infections.
Treatment
- Injections: Your physician may recommend that you have an injection of platelet-rich plasma, Botox, or another type of irritant (prolotherapy) into the tendon that is causing you pain. A technique known as dry needling, in which the injured tendon is pierced multiple times with a needle, may also be beneficial.
- Ultrasonic tenotomy: During an ultrasound-guided ultrasonic tenotomy, your doctor will insert a special needle through your skin and into the portion of the tendon that is damaged. This procedure is performed under ultrasound guidance. The needle is subjected to rapid vibration by ultrasonic energy, which causes the injured tissue to liquefy and become easier to remove using suction.
- Ice: For 15 minutes, three to four times a day, apply ice or a cold pack to the affected area.
- Rest: Relax and stay away from any activities that make the discomfort in your elbow worse.
- Bracing of elbow: The elbow brace or support is a simple and effective product that will help in relieving pain, tendonitis, sprains, strains, joint discomforts, and fatigue. Braces or supports for the elbow are also known as elbow supports.
- Arthroscopic surgery: In order to cure damaged cartilage, remove loose tissue from the body, and restore torn ligaments, practitioners will often opt for this particular type of surgery. During this procedure, a tiny incision is first created, then a fibre optic camera is placed into the joint, and finally the procedure itself is carried out.
- Surgery for a partial elbow replacement: In this procedure, the surgeon will replace the part of the elbow that is the most damaged with plastic or metal components. In most cases, this is accomplished by making a very little incision. The knee's injured tissues will mend more quickly as a result of this procedure.
- Total elbow replacement surgery: During total elbow replacement surgery, the damaged bone is entirely replaced with an artificial joint made of metal, alloy, or plastic. This type of surgery is performed on the elbow.
- Compression: Compression is a technique in which a bandage is put around the knee in the area where inflammation has taken place. This assists in achieving the correct alignment. Contributes to a speedier recovery. Another benefit is that it reduces inflammation.
- Heat: Patients may have some short-term alleviation from their symptoms if heat packs are applied to the irritated area of the elbow.
Medicine
- Treatments for hurting bodies: You could try over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB) or naproxen (Aleve) (Aleve).
- For inflammation in the elbow: Here, the corticosteroid injection is administered into the elbow joint. As a result, the inflammation in the elbow is alleviated. Some forms of arthritis may also respond favourably to this treatment. However, there are circumstances where it would be useful.
- Hyaluronic acid treatment: Hyaluronic acid treatment aids in elbow motion by replacing lost fluid with a thick fluid that is similar to the fluid already present in the tissue. An injection of hyaluronic acid is made into the elbow. It also helps with the discomfort associated with the elbow joint. In certain cases, it might last for an entire year.
- Platelet-rich plasma: PRP, or platelet-rich plasma, is a form of plasma that has been concentrated to increase its concentration of growth factors for injection. When injected into the elbow joint, it helps reduce inflammation and promotes healing of damaged tissue. Evidence suggests that P.R.P. can help those with osteoarthritis, too.
- For treatment of bacterial infection: One family of drugs used by doctors to treat bacterial infections is antibiotics. These drugs are excellent in eliminating bacterial infections. Common antibiotics like amoxicillin are used to treat bacterial infections and prevent them from spreading.
- For Deformities of elbow joint: Darunavir, atazanavir, and ritonavir are examples of antiviral drugs used to treat viral illnesses and the resulting abnormalities. Deformities of the elbow joint are sometimes treated with ritonavir.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What diseases are associated with elbow pain?
What are five common injuries of the elbow?
What are the common conditions of the elbow?
What causes elbow inflammation?
What is elbow bursitis?
How do I know if my elbow pain is serious?
Table of content
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors