Heart (Anatomy): Diagram, Functions, Diseases, Treatments
Last Updated: Apr 05, 2023
Heart Image
Heart is a muscular organ located in the thoracic cavity behind and to the left of the sternum. It plays an important role which is the pumping of blood throughout the body. It form a vast network of arteries and capillaries forming the cardiovascular system.
Chambers Of Heart
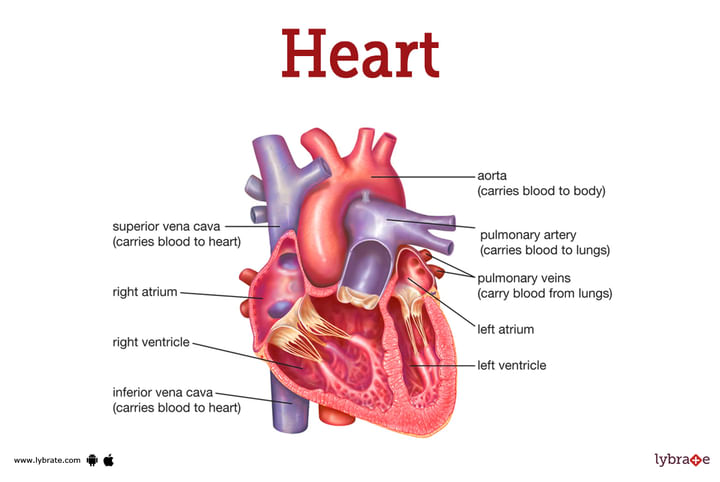
The right and the left sections of the heart having lower and higher amounts of oxygen-containing blood separated, each consisting of an atrium and a ventricle. So, there are two atriums and two ventricles, making four chambers of the heart.
Right Atrium: The vena cava, divided into two parts, delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium from the superior and inferior regions of the heart.
Right Ventricle: The right ventricle, comparatively smaller in size than the left, pumps deoxygenated blood to the pulmonary artery, which further transcends into the lungs.
Left Atrium: The blood oxygenated by the lungs is transported through the pulmonary veins into the atria of the left, which is then transcended into the left ventricle, which is larger as compared to the right.
Left Ventricle: The oxygenated blood is pumped to the large artery called the aorta. The left ventricle, having a larger size, also has a higher partial pressure than all of the other regions of the heart.
Valve Of Heart: The valves are the passages that help regulate the blood volume into the different chambers of the heart.They are of two types, i.e., the atrioventricular valves and the semilunar valves.
Tricuspid Valve: In the space shared by the right atrium and the ventricle, the three-flap valve is called a tricuspid valve.
Mitral Valve: In between the left atrium and ventricle is a two-flap valve called the mitral valve.
Aortic Valve: It opens when pressure is increased by the left ventricle and blood is pumped from the ventricle to the aorta.
Pulmonary Valve: It opens when the pressure is raised in the right ventricle and blood is pumped to the pulmonary arteries.
Heart Functions
The heart maintains constant blood flow throughout the body, which helps replenish oxygen.
The heart circulates nutrients among various cells of the body.
One of the main functions of the heart is to pump blood.
It also ensures proper blood pressure throughout the body. There are two types of circulation.
The pulmonary circulation is responsible for the transportation of deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs and the transportation of oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Systemic circulation is essential for the transport of oxygenated blood from the heart to every other region of the body.
Aside from this, a basic form of circulation known as coronary circulation is also crucial for maintaining the nutrient and oxygen supply of the heart.
Heart Diseases
Coronary Artery Disease: In CAD, the arteries that fulfill the myocardium's nutritional needs get clogged because of the accumulation of cholesterol plaques. When arteries are narrowed, they are more likely to get clogged, which can lead to a complete blockage and a heart attack.
Stable Angina Pectoris: It is the localized chest pain that increases with exertion is caused by the clogging of coronary arteries, which reduces the higher oxygen supply received by the heart in times of strenuous activity.
Unstable Angina Pectoris: The chest pain that worsens with rest and symptomatically radiates to the arm can precede dysrhythmia, myocardial infarction, and heart block.
Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack) : It is a condition which is caused by complete clogging and necrosis of the myocardial tissue.
Arrhythmia (Dysrhythmia): In this situation, Non-rhythmic contraction and relaxation are caused by faulty electrical impulses in the heart, which can be acute or chronic.
Congestive Heart Failure: In this disease, the electro myogenic system of the heart weakens or gets stiff because of ineffective pumping of blood throughout the body, causing breathlessness and pedal edema.
Cardiomyopathy: In this heart disease, the heart's ventricles become irregularly enlarged or stiffened due to clogging of myogenic cells in the heart, which reduces the stroke volume.
Myocarditis: In this situation, the myogenic cells of the heart face inflammation, which is caused by strenuous work or a viral infection.
Pericarditis: The disorder in which the outermost covering of the heart is inflamed, which can be caused by viral infection, fluid retention, and autoimmune disorders.
Pericardial Effusion: This disease causes the fluid retention caused by pericarditis, kidney disorders, infection, or cardiomyopathy in between the pericardium and myocardium.
Atrial Fibrillation: In this situation Due to anomaly in the sinoatrial node, the evolution of an abrupt electrical impulse causes an irregular heartbeat.
Pulmonary Embolism: It is a disorder which is caused by the transportation of a blood clot from the heart to the lungs and clogging of the alveolar system, which disrupts the oxygen and carbon dioxide exchanging capability of the lungs.
Valvular Disorders: It is a type of disease which occurs when there is Inflammation of chordae tendineae and different cusps of valves, causing stenosis and necrosis in the valves of the heart.
Endocarditis: When the endocardium gets inflamed due to infection or coagulation of the myocardium, causing serious complications. Due to stretching of chordae tendineae, the mitral valve is prolapsed forward and backward when contraction of the ventricle occurs.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA): It is a communication disorder causing an anomaly forming a passage between the descending aorta and the pulmonary artery, found occasionally in children who were born at high altitudes and also have mothers affected by rubella disease.
Mitral Stenosis: It is caused mainly due to recurrent rheumatic fever, which causes calcification and stiffness of the mitral valve.
Aortic Stenosis (AS): Most commonly due to degenerative calcification of a congenitally bicuspid valve and also chronic deterioration and calcification of a trileaflet valve, exertional dyspnea, angina, and syncope are cardinal symptoms; they occur late, after years of obstruction and reduced area of the aortic valve..
Cardiac Tamponade: In this disorder, the pericardial fluid fills up, causing increased pressure in cardiac chambers, causing a decrease in stroke volume and ultimately a decrease in cardiac output, which is a life-threatening scenario.
Heart Failure (Hf): It is caused when there is any anomaly in anatomical features of the heart, which results in clinical features like breathlessness and fatigue, causing swelling around the legs and hands, decreasing the chances of survival, so it is important to find out acute symptoms of heart failure.
Cor Pulmonale: Enlargement of the right ventricle or altered function is caused by primary lung disease which leads to hypertrophy of the right ventricle and eventually loss of function. This disorder is also caused by chronic cases of pulmonary hypertension.
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD): It is one of the most common forms of congenital disorder found at birth but is diagnosed also during childhood. the symptoms of this disorder occur in the aspect of the size of the defect and resistance provided by the walls of the heart
Heart Tests
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): It is a primary test done for the evaluation of the cardiac activity. The graphical representation showing the electrical activity of the heart is a useful diagnostic tool for a wide variety of heart diseases.
Echocardiogram: For proper visualization of the cardiac anomalies, echo is the standard diagnostic tool. Echocardiography allows for direct visualization of any issues that may exist with the pumping capabilities of the heart muscle and the heart valves.
Cardiac Stress Test: It involves using a device or cardiac stimulant drugs that force the heart to function at its peak. This could help identify patients who have coronary artery disease.
Cardiac Catheterization: A catheter is inserted into the blood vessels after being put into the main artery in the groin. A doctor can then examine X-ray scans of the coronary vessels to see if there are any blockages and do stenting or other operations.
Holter Monitor: A portable cardiac monitor can be worn when an arrhythmia is suspected. It is a specific device to constantly monitor cardiac activity.
Event Monitor: When an infrequent arrhythmia is suspected, the doctor advises an event monitor, a portable cardiac monitor worn by the patient. Then the stimulation activity is recorded in the event of cardiac arrhythmia, and the disorder can be diagnosed appropriately.
Heart Treatments
Angioplasty or PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty): It is a type of cardiac surgery in which catheterization of a major artery is done, and in the blocked coronary arteries small balloon is inflated, and the stent is provided, which keeps the artery unobstructed.
Coronary Artery Stenting: In this cardiac surgery, a metal wire standing is done inside the blocked coronary artery, which increases the flow of blood, relieving conditions like angina pectoris.
Thrombolysis: Specific thrombolytic drugs are given to the patient through intravenous injection, which can dissolve the clot, which creates cardiac complications. It also has a lot of side effects, which is why stenting is preferred over thrombolysis.
AED (Automated External Defibrillator): In the event of cardiac arrest, an AED is used to assess the heart's rhythm and can stimulate the heart by an artificial electrical impulse.
ICD (Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator): In cases of severe arrhythmia, A surgically implantable cardioverter defibrillator is used to monitor cardiac activity and input electrical impulses whenever necessary.
Pacemaker: For maintaining the normal rhythm of the heart, patients with cardiac rhythm disorders like arrhythmia, tachycardia Bradycardia, bundle branch block, etc., are advised to use a pacemaker.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: Its advantages include Lower rate of recurrent angina and also Ability to achieve complete revascularization but it is also having Risk of a repeat cardiac event and also higher risk of Morbidity and mortality because of major surgery
Heart Medicines
Lipid-Lowering Agents: Drugs like Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin, belonging to the class of statins, are helpful in reducing cholesterol for people having a high risk of atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis.
Diuretics: This class of drugs reduces the fluid load in the bloodstream excreting out water promoting urination and fluid loss which also reduces any other cardiovascular event. Some of the regularly used diuretics are Diuretics, Furosemide, Torsemide, Bumetanide, Hydrochlorothiazide, Metolazone etc.
Beta-Blockers: They also reduce the strain on the heart reducing heart rate also preventing various situations like heart failure and arrhythmias. Some of the common salts used by cardiologists are Carvedilol, Bisoprolol, and Metoprolol succinate.
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACE Inhibitors): They cause the relaxation of larger and smaller blood vessels which decreases the fluid load and helps the heart maintain stroke volume. Some of the commonly used ACE inhibitors are Captopril Enalapril Lisinopril Ramipril Trandolapril.
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers: they cause disruption of Angel tendon metabolism controlling blood pressure and also maintaining cardiac output some of the medication salts used by expert physicians only are Valsartan Candesartan Losartan
Aspirin: It is the first line of the drug to prevent the formation of blood clots which also reduces the risk of a heart attack.
Clopidogrel (Plavix): Loading a dose of Clopidogrel reduces the formation of clots. This drug prevents the coagulation of platelets and the combination of them. It is also considered an important drug at the time of any cardiovascular event.
Antiarrhythmic Medications: The medicine which helps in reducing the heart rate and helps in maintaining its electromyogenic activity. They are also helpful in preventing arrhythmia, and heart block.
Table of content
Find Cardiologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors