Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 06, 2023
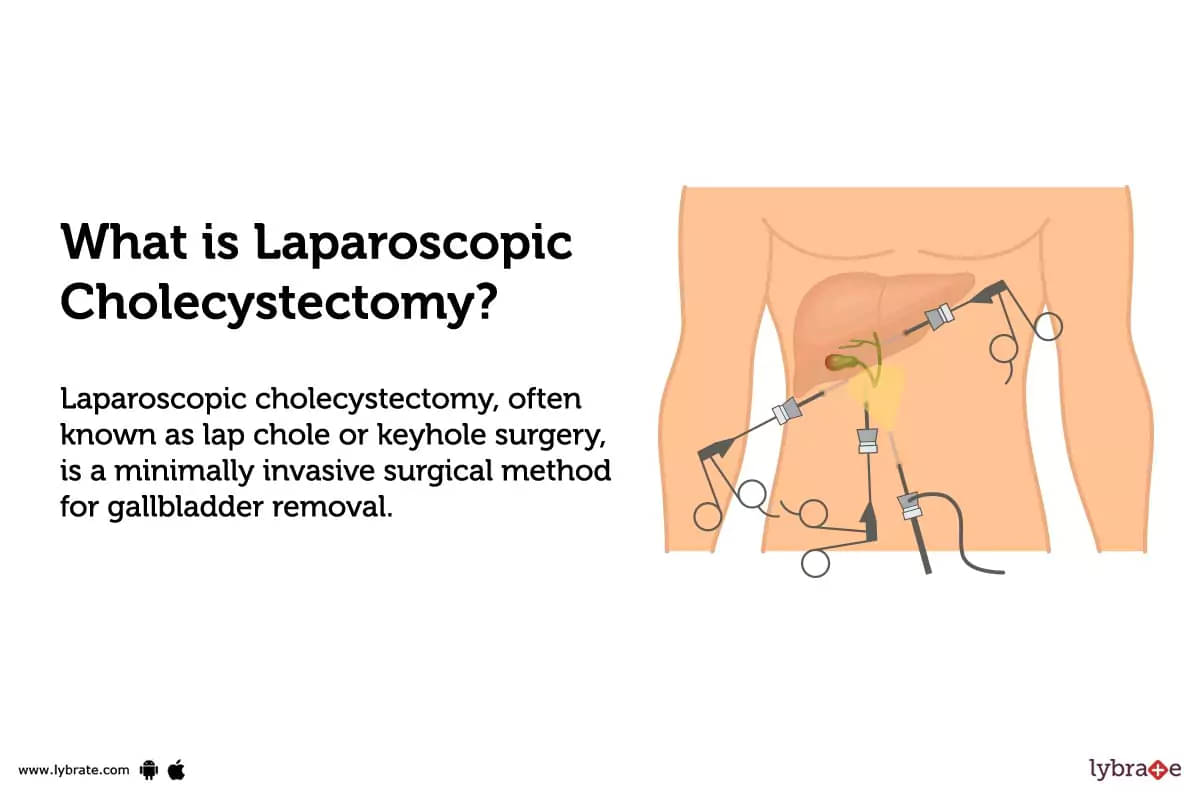
What is Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy?
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy, often known as lap chole or keyhole surgery, is a minimally invasive surgical method for gallbladder removal. Small incisions and sophisticated medical equipment are used in this technique to precisely remove the gallbladder while causing no substantial harm to the surrounding tissues and organs.
Types of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy:
- Single-Incision Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy (SILC): This type of laparoscopic cholecystectomy is performed through a single incision made in the abdomen. The gallbladder is then removed by inserting a laparoscope and other surgical equipment via this incision. This type of surgery is minimally invasive and has been found to be safe and effective for treating gallbladder disease.
- Conventional Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: This particular kind of laparoscopic cholecystectomy requires the patient to have between four and five small incisions made in the abdominal region. In order to remove the gallbladder, a laparoscope and many other surgical equipment will need to be inserted through these incisions. This method is more invasive than SILC, but it has been found to be very successful for treating gallbladder disease.
- Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: This type of laparoscopic cholecystectomy is performed with the help of a robotic device that assists the surgeon during surgery by providing enhanced visualisation, precision, and control over movements within the abdomen during surgery. This method is more complex than conventional or single-incision laparoscopy, but it has been found to be safe and effective for treating gallbladder disease.
- Natural Orifice Translumenal Endoscopic Surgery (NOTES): Natural Orifice Translumenal Endoscopic Surgery (NOTES) is a minimally invasive surgical technique that allows access to the abdominal cavity through natural orifices such as the mouth, rectum, or vagina. During NOTES, a thin endoscope is inserted through the natural orifice and then used to perform the surgical procedure.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy:
This procedure has many benefits such as:
- Shorter Recovery Time: Laparoscopic cholecystectomy often needs a shorter hospital stay and a speedier return to regular activities compared to open surgery.
- Fewer Complications: Laparoscopic cholecystectomy has been shown to have fewer complications than traditional open surgery due to its minimally invasive nature. The risk of infection and wound healing issues are reduced with laparoscopic cholecystectomy, as well as the risk of injury or damage to other organs in the abdominal cavity due to the smaller incisions made during the procedure.
- Less Pain: Because of its minimally invasive nature, laparoscopic cholecystectomy typically causes less postoperative pain than traditional open surgery due to smaller incisions and less tissue trauma caused by the procedure itself.
Why is Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy done?
The procedure is usually done to treat gallstones, which are hard deposits that form in the gallbladder and can cause pain, inflammation, and other symptoms.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is considered the preferred method of treatment for gallstones because it has fewer risks and complications than traditional open surgery.
What are the risks of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy?
- Bleeding: The possibility of bleeding is minimal, although it is possible.
- Injury to nearby organs: During the process, there is a possibility of harming the bile ducts, gallbladder, or other abdominal organs.
- Infection: There is a danger of infection owing to the introduction of bacteria to the surgical site.
- Blood clots: Blood clots can form in the legs or lungs as a result of surgery and may require medical treatment.
- Reactions to anaesthesia: Anesthesia can cause reactions such as nausea, vomiting, and dizziness in some patients.
- Conversion to open surgery: In certain instances, unanticipated difficulties during laparoscopic cholecystectomy may require the physician to switch to open surgery.
How do I prepare for Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy?
- Seek advice: Before having laparoscopic cholecystectomy, it is crucial to consult with your doctor about the surgery.
- Make sure you understand all instructions: You should make sure that you understand all of the pre-operative instructions given to you by your doctor or surgeon before undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. This includes any changes in diet or lifestyle that may be necessary in preparation for the surgery.
- Follow pre-operative instructions: To achieve a favourable result from laparoscopic cholecystectomy, it is essential to adhere to all pre-operative instructions precisely. This may include fasting prior to surgery, avoiding certain medications, and stopping smoking if necessary.
- Arrange for transportation home: After undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy, it is important to arrange for transportation home from the hospital or clinic where you had the procedure done. This is because it may not be safe for you to drive yourself home after having anaesthesia and sedation during surgery.
How is Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy done?
- Several tiny incisions are created in the abdomen during the surgery. A laparoscope (a thin, illuminated tube) is inserted through one of these incisions, enabling the surgeon to see the abdominal cavity on a screen.
- Other surgical devices are put via the other incisions.
- Through one of these small incisions, the gallbladder is detached and removed.
- The rest of the organs are then moved back into place and held there with sutures or staples.
- The wounds are then bandaged after being closed with stitches or surgical glue.
Steps to perform Before the procedure
- Obtain the patient's permission with adequate information.
- Set up an intravenous (IV) line so that fluids and medicines can be given to the patient during the procedure.
- Administer preoperative sedation and analgesia as appropriate for the patient's condition and comfort level.
- Position the patient in a supine position on the operating table with arms tucked at their sides, hips flexed, and head slightly raised on a pillow or bolster to facilitate access to the abdomen by laparoscope insertion ports.
- Apply sterile drapes to cover all exposed parts of the body except for those areas where surgical access is required, such as abdomen or flank area where trocars will be inserted into abdominal cavity through small incisions in skin and fascia layer below it.
- Infiltrate local anaesthetic around trocar sites prior to insertion of trocars into the abdominal cavity to reduce discomfort during the procedure.
Steps to perform During the procedure
- Make a small incision in the abdomen and insert a trocar (a hollow tube) to allow access to the abdominal cavity.
- Insert a camera and other surgical instruments through additional trocars.
- Detach the gallbladder from the liver, the bile ducts, and any other structures that it is attached to by making use of electrocautery or ultrasonic energy equipment.
- Remove the gallbladder by cutting it away from its attachments and placing it in an endoscopic bag for removal from the body through one of the trocars.
- Close any remaining trocar sites with sutures or staples, then close the incision with sutures or staples as well.
Steps to perform After the procedure
- Provide the patient with postoperative instructions, including information about wound care, activity restrictions, and diet.
- Monitor the patient for signs of infection or other complications such as fever, pain, and redness at the incision site.
- Regularly check the patient's vital signs (blood pressure, pulse rate, and temperature) to make sure they are stable after surgery.
- Administer prescribed medications to manage pain or discomfort and prevent infection.
- Educate the patient on how to recognize signs of infection or complications so they can seek medical attention if necessary.
- Follow up with the patient within one week after discharge from hospitalisation to assess their progress and answer any questions they may have about their recovery process or care plan.
How much does Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy cost in India?
The cost of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy in India can vary depending on the hospital, doctor, and other factors.
Generally, the cost of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy in India ranges from around Rs. 25,000 to Rs. 50,000.
What to eat after Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy?
- After having a Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy, it is important to follow a healthy diet that is low in fat and high in fibre.
- Foods to include are lean proteins such as fish, poultry, and beans; whole grains; fruits and vegetables; low-fat dairy products; and healthy fats such as olive oil and nuts.
- Avoiding fried foods, processed foods, red meats, and high-fat dairy products is also recommended.
- It's crucial to keep hydrated during the day by drinking plenty of water.
Is Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy safe?
Yes, laparoscopic cholecystectomy is generally considered safe.
Studies have also shown that laparoscopic cholecystectomy has a lower risk of infection, bleeding, and other complications than open surgery.
Is Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy painful?
- Yes, laparoscopic cholecystectomy can be painful.
- In order to remove the gallbladder, tiny incisions must be made in the abdomen, which may be a source of discomfort.
- Furthermore, the gas used to inflate the abdominal cavity during the treatment may cause pain.
- After the surgery, patients may experience soreness or tenderness at the site of incision for a few days.
How long does it take to recover from Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy?
The recovery time for a laparoscopic cholecystectomy typically takes around two weeks. The majority of individuals are able to return to their regular activities within that time frame.
It is crucial to note, however, that the recovery time varies depending on the person and their general health.
What are the side effects of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy?
The following are some of the most common side effects that might occur after a laparoscopic cholecystectomy:
- Pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Shoulder stiffness.
- Rarely, other more serious complications can occur, such as infection, bleeding or injury to the common bile duct.
- In addition to these physical side effects, some persons suffer psychological changes as a result of the procedure. These may include depression, anxiety, sleeplessness, and difficulties adapting to a new diet and lifestyle.
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Aftercare:
- Observe the guidance provided by your doctor on wound care, medication and level of activity.
- You may be advised to limit your activities for the first few days after surgery, and you should avoid lifting anything heavier than 10 pounds for several weeks.
- Drink lots of fluids, such as water or juice, throughout the day in order to maintain hydration.
- Consume a balanced diet rich in fibre, fruits, vegetables, and lean meats to aid digestion and repair of the wound area(s).
- Avoid strenuous activities such as running or heavy lifting until cleared by your doctor; this typically occurs at least six weeks after surgery in order to allow proper healing time for the incisions made during laparoscopic cholecystectomy surgery.
Conclusion:
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy has been found to be safe and effective, and can provide a quicker recovery time than traditional open surgery. Patients often undergo the operation with little pain or discomfort. The laparoscopic approach allows for better visualisation of the anatomy than open cholecystectomy, which can lead to improved outcomes.
References
- Gallbladder removal - laparoscopic- Medline Plus, Medical Encyclopedia, NIH, U.S. National Library of Medicine [Internet]. medlineplus.gov 2019 [Cited 06 August 2019]. Available from:
- Gallbladder Removal: Laparoscopic Method- American Academy of Family Physicians [Internet]. familydoctor.org 2017 [Cited 06 August 2019]. Available from:
- Cholecystectomy: Surgical Removal of the Gall Bladder- American College of Surgeons, Division of Education [Internet]. facs.org 2015 [Cited 06 August 2019]. Available from:
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find General Surgeon near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors