Neurons: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Cost, and Side Effects
Last Updated: Jul 01, 2023
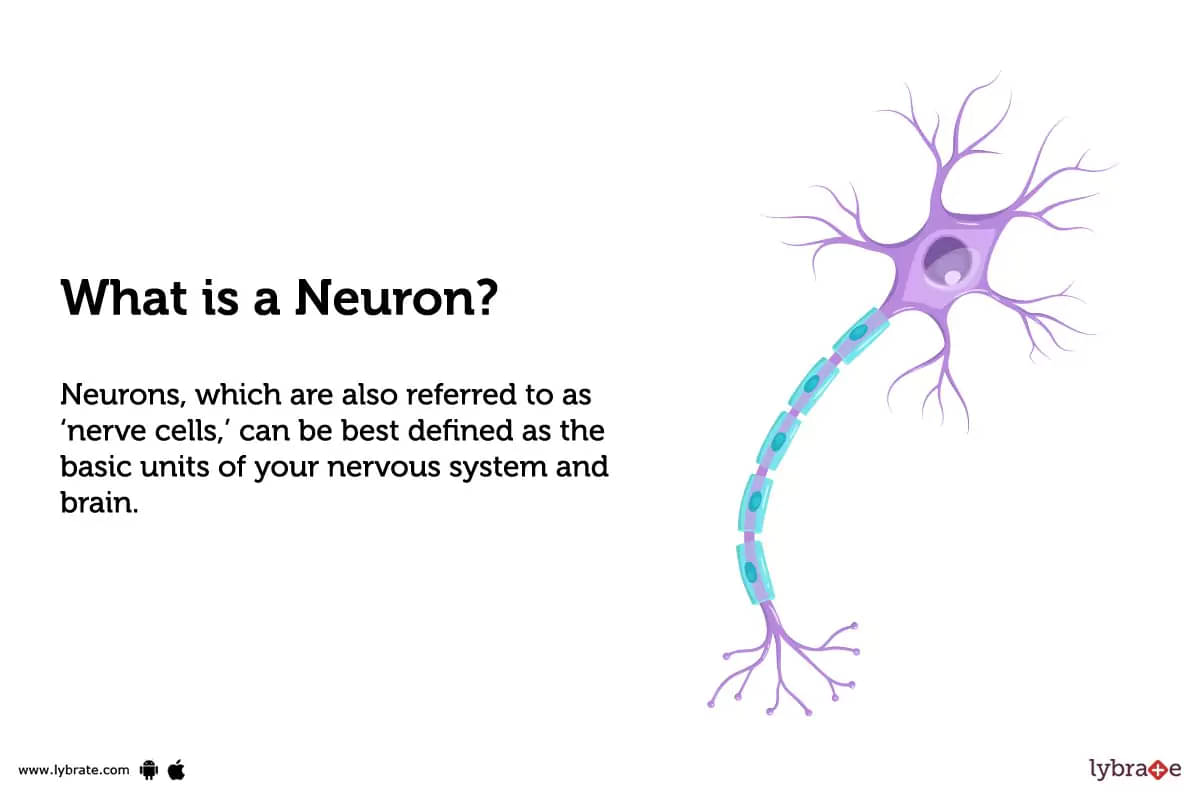
What is a neuron?
Neurons, which are also referred to as 'nerve cells,' can be best defined as the basic units of your nervous system and brain. These cells are naturally designed to receive input from the world around you, send commands to your muscles, and relay electrical signals in between this process. In other words, a neuron is a type of cell that is electrically excitable, and its function is to communicate with all the other cells through synapses, which may be called a point of contact among all the nerve cells in the nervous system. One can also say that neurons are those cells of their nervous system that are responsible for transmitting information to different parts of their body. In fact, these cells are specialized to receive, process, and transmit information.
What are the parts of neurons?
Neurons may come in different structures, shapes, and sizes depending on their role and where they are located. However, almost every type of neuron has three essential parts, which are:
Cell body
The cell body, or soma, is the core section of a nerve cell or neuron that contains important genetic information. The cell body can be called the control center or the headquarters of the nerve cells. It is, in fact, responsible for all of the neuron's functions, such as processing and sending information.
The soma is primarily responsible for providing energy to the neuron in order to drive various activities and for maintaining the neuron's structure. The neuron's soma, similar to that of other cell types, contains a nucleus and other specialized organelles within its somatic membrane, which protects the cell while also allowing it to interact with other cells.
Axon
An axon is a long, thin fiber that extends from the cell body and typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron. The axon hillock is the specific point where an axon is joined to (or meets) the cell body. This junction is important because it's where electrical signals are generated that eventually travel down the axon to the axon terminal.
Apart from that, myelin is a conductor for electrical impulses, and it's a fatty substance that's found around many axons. To understand this better, let us say that myelin is an essential substance that primarily helps axons conduct electrical signals. Most neurons, or nerve cells, have just one main axon.
Dendrites
They look like small, branching roots that come out from the primary cell body. Dendrites function the same way as antennas, in the sense that they receive and interpret signals that other neurons send out. A single neuron (or nerve cell) may have multiple dendrites, which are branch-like structures that receive input from other neurons.
The number of dendrites a neuron has usually depends on what its role is. For instance, purkinje cells are a special kind of nerve cell mainly found in the cerebellum, and they are unique because of their highly developed dendritic trees. Because of this, they are able to receive thousands of signals at once, which allows for a great level of communication within the brain.
What are the types of neurons?
Neurons come in numerous different shapes and sizes, with each one having a unique function and genetic makeup. Just like there are thousands of different species of living organisms on Earth, there are thousands of different types of neurons.
Although there are a great many different types of nerve cells, there are five major ones. Each type combines several elements of the basic neuron shape. Moreover, all five major types of nerve cells are named and explained below:
Multipolar neurons
Multipolar neurons, found in the central nervous system, can be defined as the most common kind of nerve cell. They are distinguished from other types of neurons by their multiple dendrites and a single axon. Multipolar neurons play a key role in communication between different areas of a person's brain and the spinal cord.
Unipolar neurons
They are a type of neuron that is typically only found in invertebrate species. These neurons have just one (or single) axon.
Bipolar neurons
These are neurons that are classified on the basis of having a couple of extensions, or processes, that extend from the cell body. One side has the axon, and the other side has dendrites. Mostly found in the retina of the eye, these types of neurons can also be spotted in those parts of the nervous system that help the function of the ears and nose.
Pyramidal neurons
They are the largest type of nerve cells and can be mostly found in the cortex, the part of the brain that is mainly responsible for conscious thoughts. These neurons have only one axon, but they have several dendrites, which form the shape of a pyramid.
Purkinje neurons
These are basically inhibitory neurons that release neurotransmitters to keep other nerve cells from firing. They get their name from their Purkinje cell bodies, which have multiple dendrites that spread out from the cell body.
What are the functions of neurons?
The primary functions of neurons include processing and transmitting information all across the nervous system. They do this by receiving input from other neurons and then sending output to other neurons. Neurons also have the ability to store information and generate new ideas.
Some other major as well as important functions of nerve cells (or neurons) include:
- Chemical synapse
The action potential of one neuron (at a chemical synapse) influences the activity of another neuron across a gap called a synapse. The action potential is an electrical signal that travels along your axon to a postsynaptic ending, which starts the release of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters work to stimulate the postsynaptic neurons so that they can create an action potential on their own. - Electrical synapse
Electrical synapses are created when two neurons are joined or linked together by means of a gap junction. These gaps are lined with ion channels that allow for the direct transmission of electrical signals. Electrical synapses are much faster than chemical synapses because they don't rely on neurotransmitters to carry the signal from one neuron to another.
Outlook
In simple words, neurons are the cells that the nervous system is made up of, and they have three primary or major parts: the axon, cell body, and dendrites. These parts are primarily responsible for receiving as well as sending electrical and chemical signals.
Although the brain is made up of billions of nerve cells (or neurons), they can be broadly classified into three groups: motor neurons, sensory neurons, and interneurons. These groups are based on the functions of different neurons, with motor neurons responsible for movement, sensory neurons responsible for sensation, and interneurons responsible for communication between different areas of the nervous system.
We still have a lot to learn about neurons and their role in the development of certain brain conditions. That being the case, many research projects and clinical trials are still underway in an attempt to find answers pertaining to the subject of neurons.
We hope you found all the information given in this article worthwhile and beneficial. Keep visiting us for more insights into other interesting topics like this!
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Neurologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors