Radial Artery (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 18, 2023
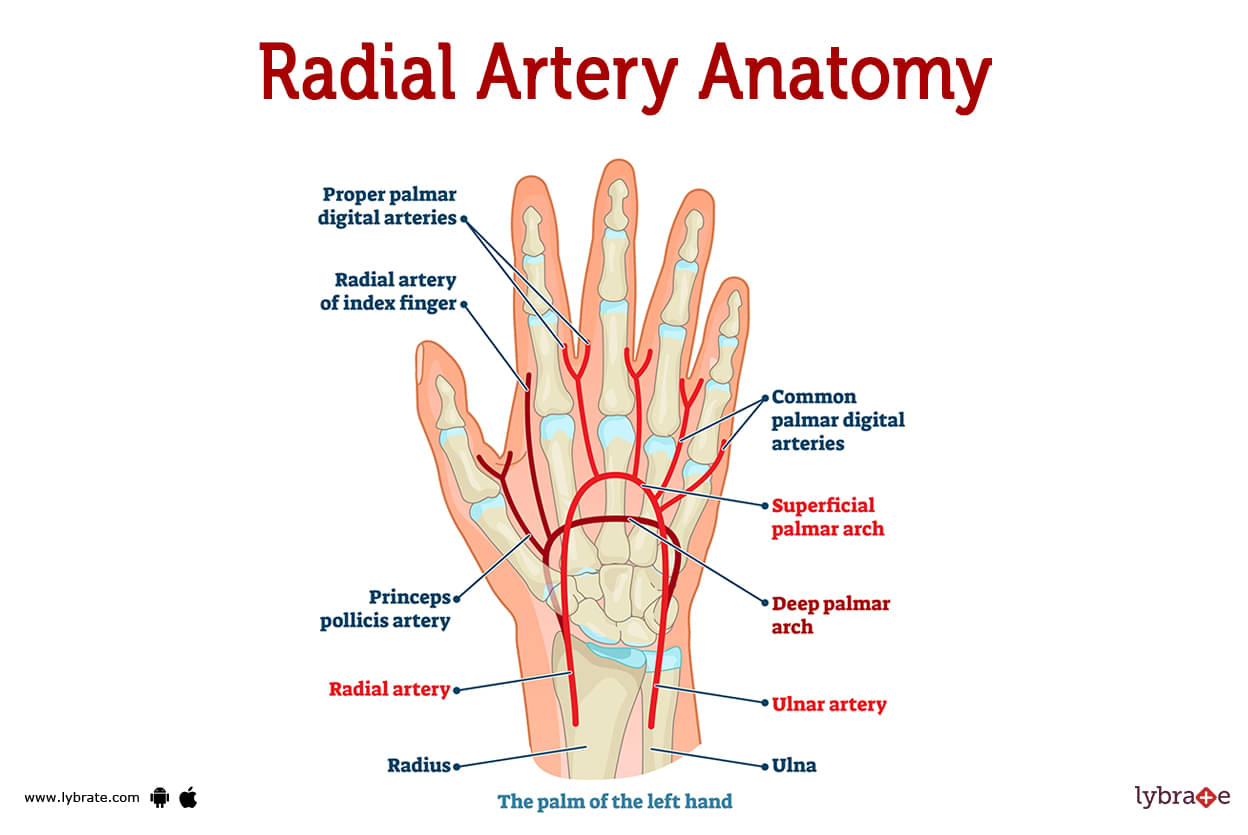
Radial Artery Image
One of the arteries in your arm, the radial artery carries blood to your hand and forearm. Blood is delivered to the body via the arteries. The oxygen has been delivered to this blood.
The hands and fingers receive oxygenated blood from the heart via the radial artery in the forearm. Heart catheterizations, angioplasty, and stenting are all procedures that require access to the radial artery. Additionally, the radial artery can be used in CABG (coronary artery bypass grafting).Among the many arteries and veins that carry blood from the heart to the rest of the body is the radial artery. The radial artery is accessed for cardiac diagnostics and treatment.
Where is the radial artery?
From the elbow all the way down to the thumb, the radial artery is located on the inside aspect of the forearm. The location of the artery can be seen just below the skin's surface. If you look closely inside your wrist, you should be able to spot a blue or purple vein near the artery that supplies blood to your thumb.
What are the radial artery branches?
The brachial artery is the most important blood vessel in the upper arm, and one of its branches is the radial artery. The brachial artery divides into the radial artery and the ulnar artery at the elbow joint. Both of these arteries supply blood to the forearm.
Both the radial and ulnar arteries travel down the forearm and into the hand in a direction that is parallel to each other. They are responsible for delivering blood to the forearm, and also the hands and fingers.
Radial Artery Functions
- The radial artery is a special tube that runs from your heart to your hand. It carries blood all the way from your heart to your fingers to keep them healthy and strong. Sometimes, doctors need to check how fast your heart is beating or how much oxygen is in your blood.
- To do this, they might feel for your radial artery pulse or put a small tube in the artery to take a blood sample. The radial artery is really important because it helps make sure your hand and fingers get all the blood they need to stay healthy.
- To assess your cardiovascular health, there are several tests that can be performed. One way is to check your pulse and heart rate by placing your fingers on the skin above the radial artery and counting the number of heartbeats.
- Another method is to draw a blood sample and measure the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide, known as an arterial blood gas test. To more accurately measure blood pressure, an arterial cannulation may be used. In addition, an arteriovenous (AV) fistula can be utilised for renal dialysis.
Radial Artery Conditions and Disorders
- Radial artery occlusion (RAO): This is a condition in which the radial artery, which is a major blood vessel in the arm, becomes blocked or obstructed.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: It is a disorder that results in numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and fingers when the median nerve, which passes through the wrist, becomes crushed or pinched.
- Cannulation injury of the radial artery: This is a condition that occurs when the radial artery is damaged during the process of inserting a cannula, a small tube used to administer medications or withdraw blood.
- Masson's Hemangioma of Proximal Radial Artery: This is a rare type of benign tumor that occurs in the proximal (upper) portion of the radial artery.
- Glomus tumours: These are rare, benign tumours that occur in the small blood vessels of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the radial artery: This is a rare type of benign tumour that occurs in the radial artery.
- Radial artery aneurysm: This is a bulge or ballooning in the wall of the radial artery.
- Atherosclerosis of radial artery: The radial artery's walls accumulate plaque in this disease, constricting the artery and lowering blood flow.
- Hypoxemia: This is a condition in which the body is not getting enough oxygen.
- Radial artery thrombosis: This is a condition in which a blood clot forms in the radial artery, blocking blood flow.
How do healthcare providers use the radial artery?
Tests and procedures on the heart are often done through the radial artery. These transradial access processes are an alternative to getting to the blood vessel in the groyne through the femoral artery.
Access through the arm may cause less bleeding and less pain than access through the leg. Most of the time, it takes less time to get better after a transradial access procedure.
Radial Artery Tests
- CBC: A complete blood count, often known as a CBC, is a type of blood test that counts the amount of platelets, white blood cells, and red blood cells that are present in the patient's blood. It is frequently used in the process of diagnosing anaemia, infections, and other conditions.
- LDL: LDL, sometimes referred to as low-density lipoprotein, is a kind of cholesterol that is sometimes considered to be 'bad' cholesterol. This is because having high levels of LDL cholesterol has been linked to a higher risk of heart disease.
- HDL: Because of its association with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease, high levels of high-density lipoprotein, or HDL, cholesterol are sometimes referred to as 'good' cholesterol. HDL stands for high-density lipoprotein.
- Allen Test: The Allen test is a diagnostic procedure that evaluates the amount of blood that flows through the radial and ulnar arteries located in the arm. It is frequently used to determine whether or not the radial artery is suitable for cannulation (insertion of a small tube for administering medications or withdrawing blood).
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) test: An arterial blood gas (ABG) test is a blood test that measures the levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH in the blood. It is often used to diagnose and monitor conditions that affect the body's ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and respiratory failure.
Radial Artery Treatments
- Amputation: This is a surgical procedure in which a limb, such as an arm or leg, is removed. Amputation may be necessary in severe cases of radial artery occlusion or injury.
- Radial artery grafts: This is a surgical procedure in which a healthy piece of the radial artery is used to replace a damaged or diseased portion of the radial artery.
- Intra-arterial verapamil: This is a treatment in which the medication verapamil is delivered directly into the radial artery to help widen the artery and improve blood flow.
- Radial Artery Access for Hepatic Chemosaturation: This is a procedure in which the radial artery is used to deliver chemotherapy drugs directly to the liver to treat cancer.
- Surgical excision of the glomus tumour: This is a surgical procedure in which a glomus tumour, a rare benign tumour that occurs in the small blood vessels of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, is removed.
- Angioplasty: This is a procedure in which a balloon catheter is inserted into the radial artery and inflated to widen the artery and improve blood flow.
- Atherectomy: This is a procedure in which plaque is removed from the walls of the radial artery using a special device.
- Stenting: This is a procedure in which a small metal mesh stent is inserted into the radial artery to help hold the artery open and improve blood flow.
- Endarterectomy: This is a procedure in which the inner lining of the radial artery is removed to remove plaque and other debris.
- Bypass surgery: This is a procedure in which a healthy piece of the radial artery is used to bypass a damaged or diseased portion of the artery and restore blood flow.
How can I protect my radial artery?
By maintaining an active lifestyle on the majority of the days of the week, adhering to a diet that is good for the heart, and giving up smoking, you can keep your radial artery and the rest of your circulatory system healthy.
When should I talk to a doctor for radial artery conditions?
If, after a transradial procedure, you have any of the following symptoms, you should get in touch with your doctor as soon as possible:
- Hand or arm numbness.
- A lack of grip and stability when holding objects.
- Loss of hand sensation or strength.
- Sensation in the forearm or hand that is not normal.
Radial Artery Medicines
- Steroids for reducing inflammation of Radial Artery: Some examples of steroids that may be used to reduce inflammation of the radial artery include prednisone and hydrocortisone.
- Analgesics for pain in Radial Artery: Important examples of analgesics that may be used to manage pain in the radial artery include acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen.
- Muscle relaxants for stiffness in Radial Artery: Important examples of muscle relaxants that may be used to treat stiffness in the radial artery include cyclobenzaprine and carisoprodol.
- Antibiotics for infection in Radial Artery: Important examples of antibiotics that may be used to treat infection in the radial artery include penicillins, such as amoxicillin, and cephalosporins, such as cefazolin.
- Nutritional supplements for reducing pain in Radial Artery: Some examples of nutritional supplements that may be used to reduce pain in the radial artery include omega-3 fatty acids and glucosamine.
- Supplements for promotion of growth at the time of fracture of Radial Artery: Important medicines that may be useful for promoting growth at the time of a radial artery fracture include calcium and vitamin D.
- Antivirals for treating infection of Radial Artery: Important medicines that may be useful for treating viral infections of the radial artery include antiviral medications such as acyclovir and valacyclovir.
- Chemotherapeutic medicines for Radial Artery: Important medicines that may be used in chemotherapy to treat conditions affecting the radial artery include cytotoxic drugs such as doxorubicin and cisplatin.
Table of content
Find Vascular Surgeon near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors