Tonsils (Human Anatomy): Image, Definition, Location, and Problems
Last Updated: Apr 08, 2023
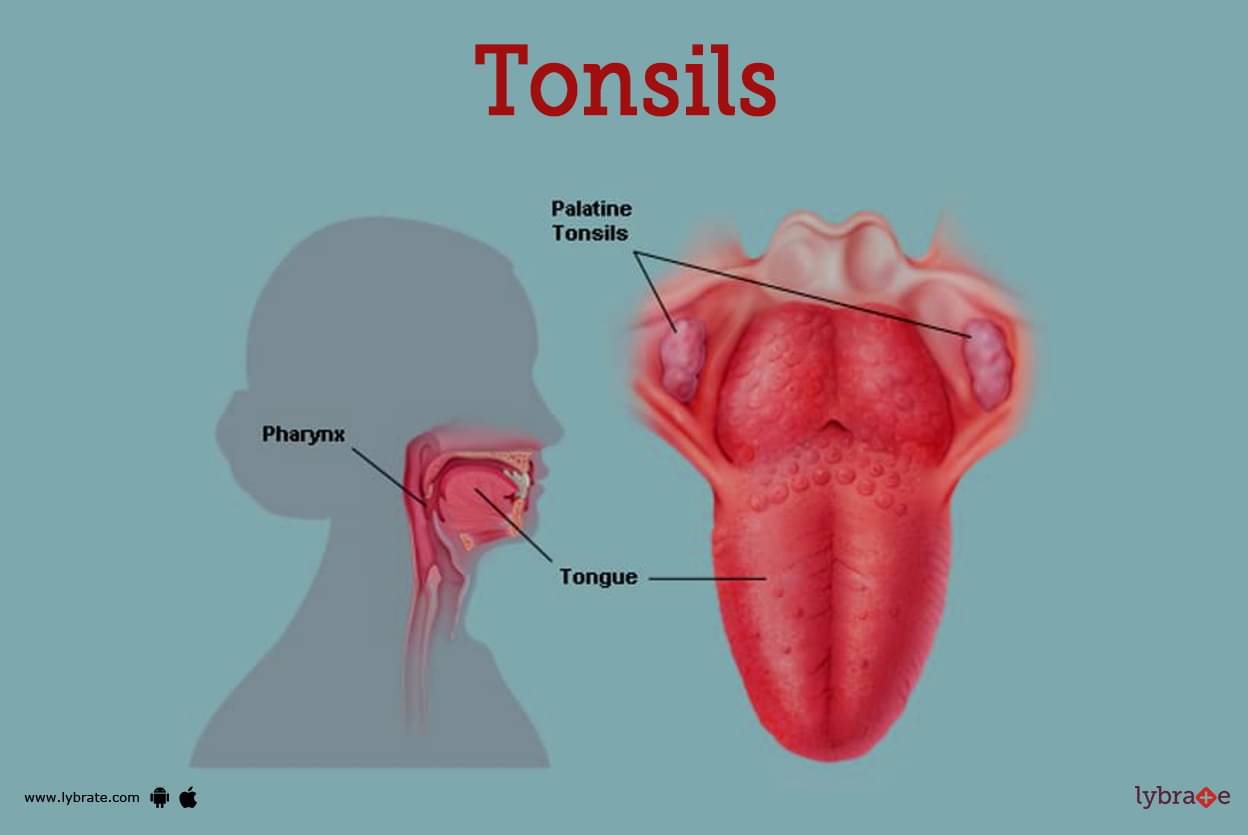
Tonsils Image
Tonsils, and more specifically palatine tonsils, are the mass of a pair of soft tissues that are located in the region of the throat that is near to the pharynx. Tonsils are responsible for producing mucus that helps protect the pharynx from infection. The tonsils, in addition to other regions of the body, may be found in the throat. Both tonsils are made up of the same kind of tissue, which is also found in lymph nodes.
They are guarded by the pink mucosa that coats the inside of the mouth, which also serves as their protective barrier. Crypts are the term given to the little pits that may be seen in the mucosa layer of each tonsil. Crypts can be present in certain tonsils but not in others.
Tonsils functions
They are part of the body's immune system and have several important functions, including:-
- Protecting against infection: The tonsils contain lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell that helps to fight infection. They help to protect the body against bacteria and viruses that enter through the mouth and throat.
- Filtering out harmful substances: The tonsils help to filter out harmful substances that may enter the body through the mouth and throat, such as bacteria and viruses.
- Producing antibodies: The tonsils produce antibodies, which are proteins that help to defend the body against infections.
- Reducing the spread of infection: The tonsils help to reduce the spread of infections by trapping and destroying bacteria and viruses before they can enter the rest of the body.
- Regulating the immune system: The tonsils play a role in regulating the immune system, helping to balance the body's response to infection and inflammation.
The tonsils are a part of the lymphatic system, much like the thymus and the other lymph nodes in the body. When it comes to fighting off infections, the immune system receives assistance from the lymphatic system.
In some cases, tonsils may be removed surgically if they are chronically infected or causing other problems, such as sleep apnea. While the tonsils are not essential for overall health, their removal can lead to a slightly increased risk of throat infections. The removal of the tonsils does not, however, result in an increased risk of infection.
Tonsils Conditions
- Rheumatic fever: Rheumatic fever is a very unusual condition, although it is a possibility in the event that strep throat is not promptly treated. Rheumatic fever is another possible outcome of failing to finish the prescribed course of medicines for an infection. Rheumatic fever affects children more often than it does adults, however people of all ages may be affected by it. If the condition is not adequately treated in a timely manner, it may cause irreparable damage to the heart and even lead to death.
- Viral tonsitilits: When a person is infected with a virus of any kind, such as influenza, rhinovirus, rotavirus, etc., he or she runs the risk of developing an acute or chronic form of tonsillitis, in which the tonsils become swollen and lumpy, and the person feels pain when their tonsils are palpated lightly or when they are talking.
- Bacterial Tonsillitis: When a person has an infection from bacterial inflammation, such as streptococcus or pneumococcus, his or her tonsils become infected. This causes the tonsils to expand and causes pain when the jaw is moved.
- Acute tonsillitis: Both the painful swelling of the throat and the soreness of the throat may be traced back to an infection brought on by bacteria or a virus. Tonsillitis often presents with a covering of exudate that may be either grey or white in colour.
- Chronic tonsillitis: Chronic tonsillitis is the outcome of an infection of the tonsils that has lasted for a lengthy period of time and is often brought on by recurring episodes of acute tonsillitis. Acute tonsillitis may bring on chronic tonsillitis in certain cases.
- Peritonsillar abscess: In the case of peritonsillar abscess, the infection causes the formation of a pouch or pocket that becomes filled with pus and is positioned near to the tonsil. This further presses the tonsil toward the opposite side of the infectional region. Because it might lead to more issues if it is not treated right away, it has to be drained as soon as possible.
- Acute mononucleosis: Epstein-Barr virus is the causative agent in the majority of cases of acute mononucleosis. Under these circumstances, the infection produces considerable enlargement of the tonsils, as well as fever, a sore throat, exhaustion, and rashes, all of which are easy to notice.
- Strep throat: Strep, which literally translates to 'strep throat,' is an illness that is caused by a bacterium that affects both the tonsils and the throat. Strep is referred to as 'strep' in the medical community. Other symptoms that may be present include a fever and achy muscles in the neck, in addition to a sore throat (in majority of cases).
- Enlarged (hypertrophic) tonsils: Tonsillitis is already a challenging illness, but when it has advanced to a more severe level, the anguish that it produces becomes terrible. The presence of large tonsils may create a decrease in the size of the airway, which can make it more likely that a person would have symptoms such as snoring and/or sleep apnea.
- Tonsilloliths or tonsil stones: It is possible that the buildup of debris in the tonsils that calcifies into tonsilloliths is to blame for the production of stones. These stones are also known as tonsilloliths. In order to prevent any more infections from taking place, it is necessary to treat it with medication in order to eradicate it.
Tonsils Tests
- Throat (pharynx) swab: The tonsils and the back of the throat are rubbed by a professional with a cotton swab, and then the expert sends the sample (which is present on the swab) to a laboratory for analysis. It is carried out in order to determine whether or if the infection was brought on by bacteria, such as Streptococcus.
- Monospot test: Antibodies are produced by a person's body in response to an illness, whether it be caused by bacteria or a virus. Antibodies help the body fight against infections. Because of this, a test of the blood can be helpful in the search for the antibodies in question. The presence of these antibodies either implies or proves that the person in question is experiencing symptoms that are caused by mononucleosis.
- Epstein-Barr virus antibodies: If the monospot test comes out negative, there is another test that may help determine whether or not mononucleosis is present. This test searches for antibodies in the blood that are directed against the Epstein-barr virus.
- Rash: strep throat infection may cause a person to develop signs of a rash when they are afflicted with the infection.
Tonsils Treatments
- Abscess drainage: Because the infection may create further complications if it is allowed to go untreated for a significant amount of time, the abscess will need to be drained. The majority of the time, a needle is used to puncture a tiny hole in the abscess, and the pus that gathers within is subsequently drained out of the abscess. The patient is able to recuperate more fully as a result of this.
- Tonsillectomy: Surgery is the only therapeutic option that is left when the tonsils are excessively large and have been there for a substantial length of time, or when there is recurring infection. During surgery, the tonsils are removed in the presence of an expert professional.
- Salt water gargling: Warm salt water can help soothe a sore throat and the pain that comes with tonsillitis. It can also reduce swelling and pain, and it may even help fight infections.
- Humidifier: If the air is dry or if you have tonsillitis and your mouth is dry, a humidifier can help ease your sore throat. Dry air can irritate the throat, and humidifiers can help relieve pain in the throat and tonsils by adding moisture back into the air.
Tonsils Medicines
- Broad Spectrum Antibiotics for tonsiltis: Your dentist may recommend antibiotics to help treat an infection if you have gum disease or a tooth problem that has spread to your jaw or other teeth. The antibiotic is available as a mouthwash, gel, tablet, capsule, or oral tablet. During surgical operations, topical antibiotic ointment may also be given to the gums or teeth.
- Specific Oral Antibiotics for tonsilitis: Antibiotics like Erythromycin , and combinations of penicillin and amoxicillin are known to be useful for treating oral infections.
- Analgesics for tonsiltis: Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs use for relevance of paint at the time of tooth infection or toothache are useful as they are not habit forming and have lesser side effects some of the examples of analgesics are Ibuprofen, diclofenac sodium, naproxen etc
- Antifungals for tonsillitis: Drugs for the treatment of oral candidiasis like micro-statin clotrimazole etc are also used and topical solutions of neomycin are also known.
- Antiseptics for tonsiliths: Oral cleaning solutions of antiseptic are known to be used by people regularly for prevention of fungal and bacterial infections which kills germs and reduces the chances of infections like chlorhexidine gluconate, and milder solutions are chloroxylenol.
- Anaesthetics for peritonsillar abscess: Topical anaesthetics which come in forms of oral ointments, sprays and liquids can relieve the pain and deterioration of the surface lining of the mouth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How to cure tonsillitis in 4 hours?
What causes tonsil stones?
How to cure tonsils fast?
How to remove tonsil stones?
What are tonsil stones?
How to cure tonsils permanently?
How to prevent tonsil stones?
Where are tonsils located?
Table of content
Find ENT Specialist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors