Vagotomy: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 04, 2023
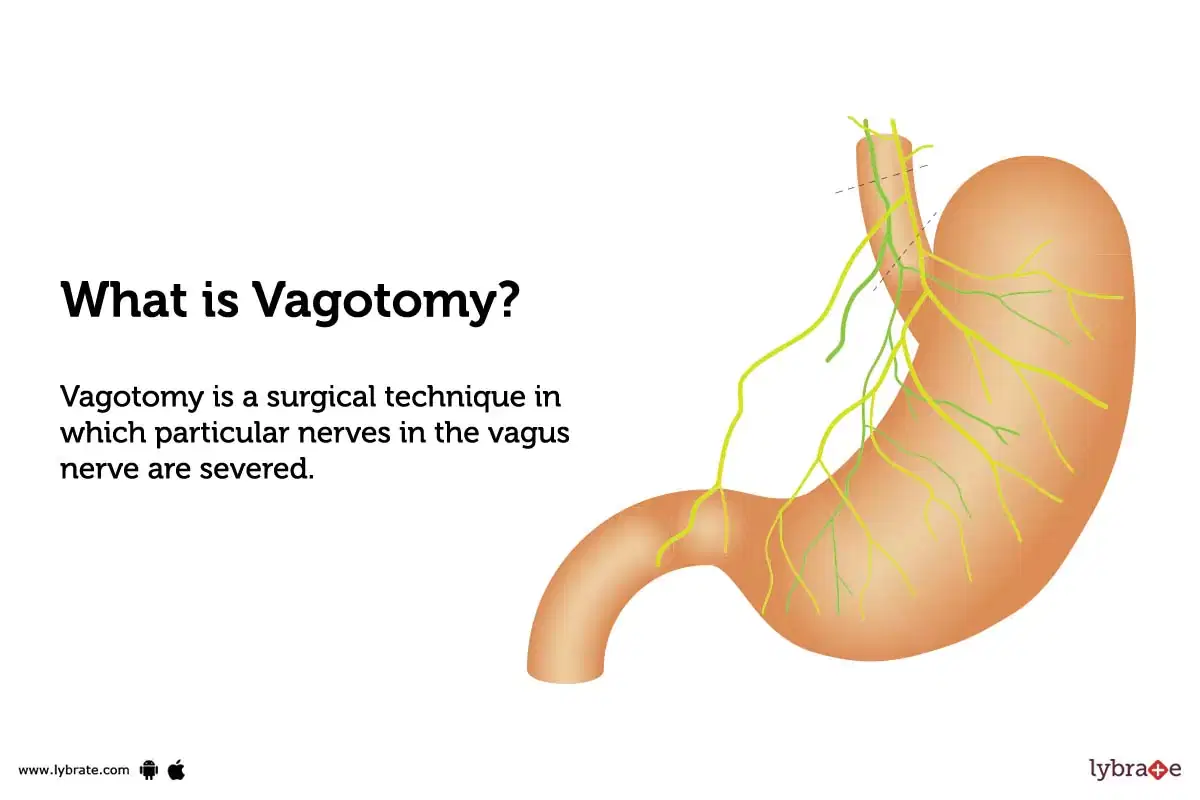
What is Vagotomy?
Vagotomy is a surgical technique in which particular nerves in the vagus nerve are severed. The vagus nerve is responsible for controlling the digestive system, and cutting certain branches of this nerve can help reduce or eliminate symptoms associated with conditions like acid reflux and ulcers.
The procedure is usually done through laparoscopy, meaning small incisions are made in the abdomen to access the area around the stomach. Depending on the severity of symptoms, either a partial or full vagotomy may be performed.
Types of Vagotomy
- Truncal Vagotomy: This is the most commonly used type of vagotomy and involves cutting or removing the main trunk of the vagus nerve. This procedure is often used to treat peptic ulcers caused by an overproduction of stomach acid.
- Selective Vagotomy: This type of vagotomy involves cutting or removing only a few branches of the vagus nerve, rather than its entire trunk. It is often used to treat ulcers that have not responded to previous therapies.
- Highly Selective Vagotomy: This type of vagotomy is similar to selective vagotomy, but it involves cutting or removing even fewer branches of the vagus nerve. It is usually recommended for patients who have had recurrent ulcers or those who cannot tolerate truncal or selective vagotomies due to medical conditions such as diabetes or heart disease.
- Parietal Cell Vagotomy: This type of surgery involves cutting or removing only a portion of the parietal cells in the stomach wall that produce hydrochloric acid (HCl). It can be used to reduce acid production in patients with peptic ulcer disease and other gastrointestinal disorders involving excessive HCl production in the stomach lining.
Benefits of Vagotomy
- The main benefit of vagotomy is that it can provide relief from GERD symptoms such as heartburn, chest pain, and nausea.
- It may also decrease the likelihood of GERD problems like esophageal strictures and Barrett's oesophagus.
- Vagotomy can help prevent peptic ulcers by reducing acid production in the stomach.
- It may also help improve digestion by increasing stomach emptying time and reducing bloating and gas.
Why is Vagotomy done?
Vagotomy is often used to treat digestive disorders like stomach ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and gastroparesis.
By cutting the vagus nerve, it reduces or eliminates the amount of acid produced by the stomach, which can help reduce symptoms associated with these conditions.
What are the risks of Vagotomy?
The most common risks associated with vagotomy include:
- Bleeding or infection at the surgical site.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Poor digestion or difficulty absorbing nutrients.
- Damage to adjacent organs, like the intestines or stomach.
- Nerve damage resulting in numbness or tingling in the face or neck.
- Abdominal pain and bloating due to changes in digestive function.
- Perforation of the stomach wall during surgery.
How do I prepare for Vagotomy?
- Before having a vagotomy, it is vital to consult with your doctor and ensure that you know all of the risks and advantages.
- Your doctor will likely recommend that you stop taking any medications that can thin your blood or increase the risk of bleeding, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and aspirin.
- Additionally, you should inform your doctor of any allergies or health issues that may influence your procedure.
- Additionally, your physician may ask you to avoid food and drinks for at least 8 hours prior to the treatment.
- You'll need to have someone else take you home from the hospital following surgery since you won't be able to drive safely under the influence of anaesthesia.
- It is important to discuss with your doctor any questions or concerns you may have about vagotomy before undergoing the procedure so that he or she can better explain what will happen during and after surgery.
How Vagotomy is done?
The surgery is performed either by an open abdominal incision or laparoscopically, which involves making minor incisions and inserting equipment through them.
During a vagotomy, the surgeon will isolate the vagus nerve—the nerve that carries signals from the brain to the digestive system—and then cut it or block it with an electrode.
This stops signals from reaching the stomach, reducing its ability to produce acid.
In some cases, only a portion of the nerve will be cut or blocked—a partial vagotomy—while in others all of it will be severed—a complete vagotomy.
Afterward, the patient may need to take medication for several weeks to help control any remaining acid production.
Steps to perform Before the procedure
- Obtain informed consent from the patient.
- Perform a physical examination and obtain any necessary laboratory tests or imaging studies to evaluate the patient’s condition.
- Discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with the patient, including potential complications and alternative treatments for their condition.
- Administer preoperative medications, if necessary, to reduce anxiety or manage pain levels during the procedure.
- Place an intravenous (IV) line for administration of fluids and medications during surgery, if needed.
- Provide fasting instructions to the patient prior to their scheduled surgery date; typically this means no food or drink after midnight on the day before surgery is performed.
- Ensure that all necessary equipment is available in the operating room prior to beginning the procedure, including an endoscope and any specialized instruments required for performing a vagotomy (such as a scalpel).
Steps to perform During the procedure
- The patient is placed under general anesthesia and made comfortable.
- To get access to the stomach, an incision in the abdomen is created.
- The vagus nerve is recognized and separated from surrounding tissue.
- The vagus nerve is then cut or ablated to sever its connection to the stomach wall and reduce acid production in the stomach.
- Sutures or staples are used to seal the incision, and the treatment is finished.
Steps of perform After the procedure
- Assess the patient's vital signs and degree of discomfort.
- As suggested by the doctor, provide antibiotics and other drugs.
- Encourage the patient to walk and move around after surgery, as this will help to reduce swelling, improve blood circulation, and help with pain management.
- Monitor for any signs of infection or complications from surgery, such as fever, nausea, vomiting, or excessive bleeding.
- Follow up with the doctor for regular check-ups after surgery to ensure that healing is progressing properly and any potential complications are being addressed in a timely manner.
- Educate the patient on proper wound care instructions to prevent infection and promote healing of the surgical site(s).
How much does Vagotomy cost in India?
In India, the cost of vagotomy varies on the kind of operation and the facility where it is conducted.
Generally, the cost can range from around Rs. 10,000 to Rs. 1,50,000.
What to eat after Vagotomy?
After having a vagotomy, it is essential to consume a well-balanced diet.
Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats should all be included in this diet.Water consumption throughout the day is essential for maintaining proper hydration.
Is Vagotomy safe?
Yes, a vagotomy is regarded to be a relatively risk-free treatment with just a small chance of experiencing any consequences.
The most common risks associated with vagotomy are bleeding, infection, and damage to nearby organs or nerves.
However, these risks are rare and the overall complication rate is low.
Is Vagotomy painful?
While vagotomy can be an effective treatment option, it may cause some pain and discomfort during and after the procedure.
The extent of the individual's discomfort is also influenced by the particular vagotomy procedure that is done.
The majority of patients do not feel any pain during surgery since general anaesthetic is often administered before the process.
After surgery, some people may experience mild to moderate pain in their abdomen or chest area that can last for several days or weeks.
How long does it take to recover from Vagotomy?
Most patients are able to resume normal tasks within a few days following surgery.
However, complete healing might take a few weeks.
What are the side effects of Vagotomy?
The most frequent vagotomy side effects are stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and bloating.
Other potential negative effects include increased gas, constipation, and trouble urinating or defecating.
In some cases, scarring may occur at the site of the surgery.
Vagotomy Aftercare
The following are some tips for aftercare following a vagotomy:
- Take all medicines exactly as advised by your physician.
- Avoid eating spicy or acidic foods for several weeks after surgery as this can irritate your stomach and cause discomfort or pain.
- Drink lots of liquids to keep hydrated and enable your body to flush out impurities.
- Avoid strenuous activities for at least two weeks after surgery so that you don't strain your abdominal muscles or put undue stress on your internal organs while they heal from surgery.
- Make sure you get plenty of rest so that your body can heal properly and quickly from the procedure itself as well as any potential complications associated with it such as infection or bleeding in the abdominal area.
- Follow up with your doctor regularly to make sure everything is healing properly and there are no signs of infection or other complications associated with the procedure itself or its aftermaths such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, etc..
Conclusion
Vagotomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting the vagus nerve, which is responsible for controlling the digestive system. The procedure is used to treat certain digestive disorders, such as stomach ulcers and reflux disease.
It can also be used in some cases to reduce the risk of gastric cancer. While it has been shown to be effective in treating these conditions, there are potential risks associated with the procedure, such as infection and bleeding. Before determining if this operation is suitable for you, you should explore all of the risks and advantages with your doctor.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Neurosurgeon near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors