Arm Muscles (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 18, 2023
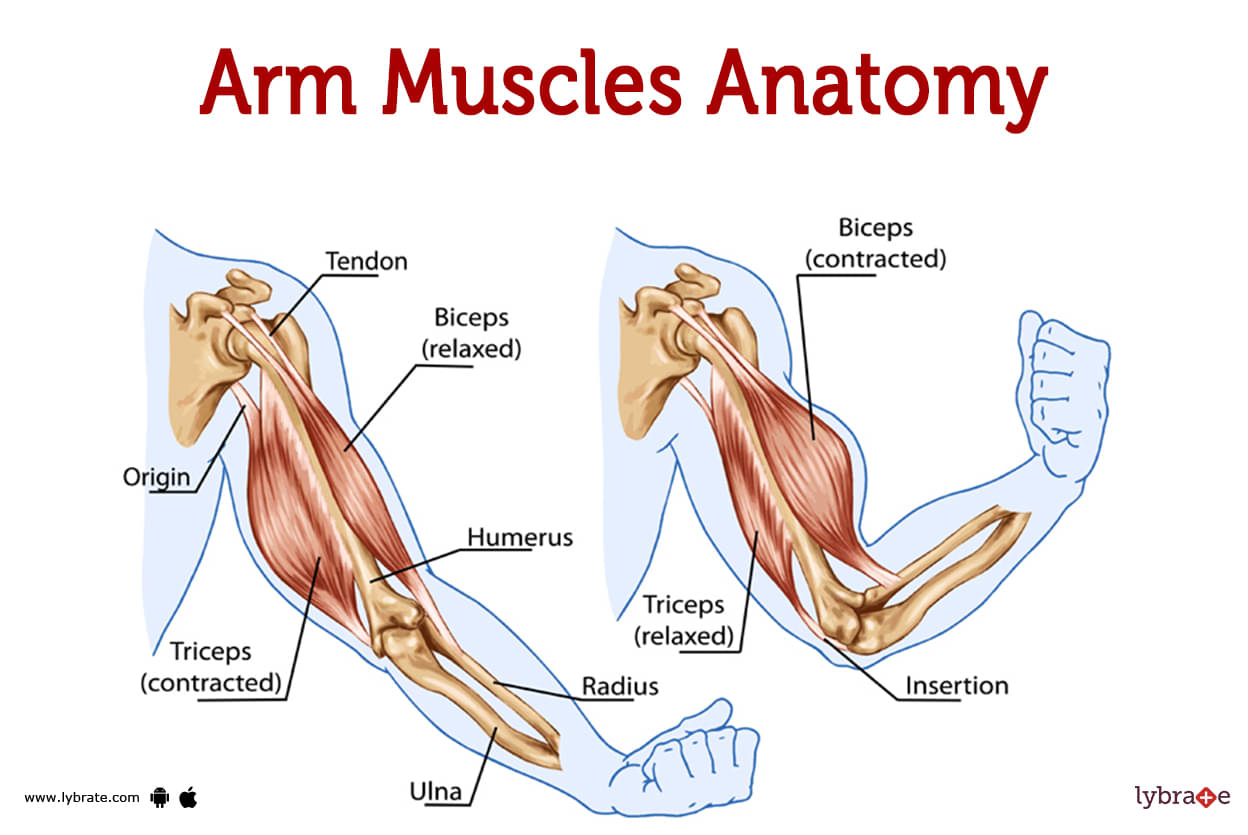
Arm Muscles Image
There are many muscles in the upper arm (the part of the arm between the shoulder and elbow) and forearm (between your elbow and wrist). This group of upper-body muscles helps you move your arms in big and small ways.To perform fine motor activities like threading a needle, your forearm muscles are essential.
What are the arm muscles?
- The upper arm and the forearm together contain more than twenty muscles (the area between your elbow and your wrist). Fine motor tasks, like wiggling your fingers or buttoning your shirt, rely on the strength in your arms.
- Additionally, you can perform large motions with them, such as extending your elbow, bringing your arms above your head, or performing push-ups.
- In your innermost layers of your arm are a set of muscles. When you flex (contract) some muscles, you can see their outlines clearly since they are close to the skin's surface.
- Muscles in your arm and shoulder are connected to their bony attachments via tendons.
- Muscle strains in the arm can occur from overexertion or ripping of the muscle. Overuse and the lifting of excessively heavy objects are common causes. Remember to warm up before working out your arms, and to stop if you start to experience any pain.
How to build arm muscle?
Exercises like bicep curls, tricep dips, and push-ups are great for developing strong arms. In order to challenge the muscles and promote muscle growth, you will need to gradually increase the weight or resistance employed in these workouts.
How to stop muscle twitching in the arm?
Arm twitching can be stopped by treating potential contributing factors such exhaustion, stress, or an electrolyte imbalance. You can increase your water intake, rest, and stress-reduction efforts by doing things like yoga and meditation.
What muscles are used in arm wrestling?
Biceps, triceps, forearm, and wrist flexors are all put to action in a match of arm wrestling. The biceps and triceps are responsible for the majority of the arm's range of motion, while the forearm and wrist flexors provide additional stabilisation and control. These muscles get an extreme workout during an arm wrestling match because they produce the force that determines who comes out on top.
What muscles does arm wrestling use?
It's not just the forearm muscles that get a workout during an arm wrestling match. The biceps are responsible for the bending motion, while the triceps straighten the elbow. Arm wrestling also requires the use of the muscles in your forearms and wrists in order to maintain a firm grip on your opponent's hand.
Arm Muscles functions
Mentioned below are the functions of the arm muscles:
What is the purpose of the arm muscles?
A person's ability to move their arms, hands, fingers, and thumbs is dependent on the strength and coordination of the muscles in their upper arms and forearms. Both large and small movements, like throwing a ball, require the use of specific muscles.
What is the purpose of the forearm muscles?
Our ability to move and control our hands and wrists depends on the strength of the forearm muscles. They enable humans to grasp items, write, and do a wide variety of other common actions. Arm wrestling, throwing a ball, and playing an instrument are just a few examples of sports and hobbies that put a premium on strong forearm muscles. Maintaining a healthy and robust set of musculature is crucial for achieving these goals.
What is the purpose of the upper arm muscles?
The upper arm muscles allow you to lift objects, throw a ball, or even just wave hello. They support your body weight and keep your arms steady while you're standing or seated. The upper arm muscles are crucial since they enable you to perform a wide range of actions with your arms. The muscles in your upper arms need frequent exercise and stretching to remain strong and healthy.
Where are the forearm muscles located?
The forearm is a collection of muscles that runs from the elbow to the wrist. The forearm muscles stabilise and support the arm, as well as govern wrist and hand mobility.
The forearm muscles include the flexor carpi radialis, extensor carpi radialis longus, flexor carpi ulnaris, and extensor carpi radialis brevis. These muscles help people to grasp, seize, and hold items by synchronising their activities.
Where are the upper arm muscles located?
Between your shoulder and elbow is where you'll find your upper arm muscles. They facilitate arm motion and weight lifting. The biceps and triceps are the two most prominent muscles in the upper arm. The biceps muscle, which is placed in the front of the upper arm, helps with elbow flexion and lifting heavy objects.The triceps muscle is located at the upper back of the arm and is responsible for extending the elbow and providing additional pushing power. These muscles work together to provide you tremendous strength and dexterity in your arms.
What do the arm muscles look like?
Your skeleton includes the muscles in your arms as well as your bones. Skeletal muscles are a subtype of the muscle group known as striated muscles. The skeletal muscles are made up of a significant number of individual fibres. The striped appearance that these fibres take on as a result of their clustering is referred to as striating.
Arm Muscles Conditions and Disorders
The muscles in your arms are vulnerable to a wide variety of illnesses and ailments. The following are some typical examples:
- Strains: Muscle strains happen when a muscle is overworked or when it is suddenly and forcefully moved. Symptoms include soreness, edoema, and fatigue in the afflicted muscle.
- Sprains: Sprains happen when a ligament (a strong, flexible band of tissue that joins bones) is overstretched or ripped. If you fall and land on your outstretched hand, for instance, this can happen to your arm.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of a tendon, known medically as tendinitis (a tough, fibrous cord that connects muscle to bone). It's characterised by discomfort, edoema, and weakening in the affected area, and it can be brought on by overuse or repetitive strain.
- Bursitis: When the fluid-filled sacs termed bursae become inflamed, they no longer function as intended, increasing friction between bones and muscles and leading to painful symptoms known as bursitis. As a result of overuse or repetitive strain, the affected joint may become painful, swollen, and stiff, making normal movement impossible.
- Fractures: When bone tissue separates from its surrounding tissue, this is called a fracture. There may be pain, edoema, bruising, and restricted movement after a fracture.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: A condition that happens when the median nerve in the wrist becomes compressed, producing pain, numbness, and weakness in the hand and fingers.
- Tennis elbow: Pain and swelling on the outside of the elbow, usually as a result of overuse or repeated motions..
- Golfer's elbow: Pain and swelling on the inside of the elbow, usually as a result of overuse or repeated motion.
- Tendinopathy: Symptoms include localised pain, swelling, and weakening, and the term 'tendonitis' is used to describe a wide range of conditions that can affect tendons.
- Rotator cuff tear: A tear in the muscles and tendons of the rotator cuff of the shoulder causes discomfort, weakness, and a restricted range of motion in the arm that is affected by the injury.
What are some common signs or symptoms of conditions affecting the arm muscles?
- Pain: To put it simply, pain is a typical sign of many illnesses and disorders affecting the muscles in the arms. You may experience it whether you move your arm or when you're at rest, and its intensity can range from mild to severe.
- Swelling: Inflammation of the muscles or joints in the arms can cause swelling. Redness and warmth to the touch could also be present.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness makes it hard to move the arm or lift heavy objects.
- Numbness or tingling: Tingling or numbness could indicate nerve compression or irritation if it occurs in the muscles of the upper arm or the fingers.
- Bruising: Muscle trauma or internal bleeding can cause bruising in the arm.
- Difficulty moving the arm: Arm stiffness, weakness, or soreness could indicate issues with the muscles or joints that control arm movement.
Arm Muscles tests
- Physical exam: During a physical examination, your doctor will assess whether or not your arm muscles are swollen, sore, or weak. They may also have you test your range of motion in your arm by trying various motions.
- X-rays: Radioactive rays are used to make images of the body's interior with an X-ray machine.
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (often known as an MRI) is a diagnostic procedure that combines powerful magnets and radio waves to provide detailed images of the body's internal structures. If your doctor suspects that you have a problem with your muscles, tendons, or other tissues in your arm, he or she may recommend an MRI.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound is a diagnostic imaging process that produces pictures of organs and tissues located deep within the human body by employing sound waves of a high frequency to make the images. If your doctor suspects an issue with your muscles, tendons, or other tissues in your arm, he or she may recommend an ultrasound.
- Nerve conduction studies: Studies of nerve conduction are used to evaluate the health of a patient's nerves. If your doctor thinks you're having nerve issues in your arm, he or she may recommend a nerve conduction study.
Arm Muscles Treatments
- Rotator cuff repair: When the shoulder muscles and tendons that help raise and rotate the arm become torn, a rotator cuff repair procedure is performed to restore their normal function. At the time of operation, the ripped muscle or tendon will be reattached to the bone.
- Tendinitis surgery: Inflammation of the tendons in the arm can be treated by surgery for tendonitis. If the tendon is torn, the surgeon will remove it and perhaps reconstruct it.
- Carpal tunnel release: The compression of the median nerve in the wrist is what causes carpal tunnel syndrome, which may be treated with this surgical technique. Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused when the median nerve becomes compressed. Following the creation of a very small incision in the wrist, the physician will strive to free the compressed nerve.
- Tennis elbow surgery: The term 'tennis elbow surgery' refers to a specific surgical treatment used to treat lateral epicondylitis, an inflammatory condition that produces pain and swelling on the outside side of the elbow. The surgeon will cut out the diseased tissue and maybe fix the torn tendons or muscles.
- Golfer's elbow surgery: Medial epicondylitis, or golfer's elbow, is a painful ailment that produces inflammation and tenderness on the inside side of the elbow, and can be treated with surgery. In addition to removing diseased or injured tissue, the surgeon may also repair torn muscles or tendons.
Arm muscles Medicines
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) are a family of pharmaceuticals used to treat pain and inflammation. They are safe for long-term usage and have few negative effects. They reduce inflammation by preventing the body from generating certain chemicals. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines include ibuprofen and naproxen.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids are a class of anti-inflammatory drugs. Tendinitis and bursitis are two common ailments that they are used to treat. Both oral and local injection administration of corticosteroids are effective.
- Muscle relaxants: Muscular relaxants are a class of drugs used to ease tight or spastic muscle tissue. They may be used to treat carpal tunnel syndrome and other disorders characterised by painful muscular spasms or cramps.
- Antidepressants: Antidepressants are a class of drugs used to alleviate symptoms of depression and other mental illnesses. To alleviate discomfort and promote restful sleep, some antidepressants, including amitriptyline, may be prescribed.
How can I keep my arm muscles healthy?
Make sure you warm up your arm muscles thoroughly before utilising them to avoid injury. Muscles are safer against strain and injury if they are warmed up first. The intensity of your workout should be built up gradually. Never lift anything that causes you pain, and put the weight down immediately if you do.
When should I call my doctor about my arm muscles?
f you are experiencing pain, swelling, or discomfort in your arm muscles, it is generally a good idea to call your doctor. This is especially true if the pain is severe or persistent, or if you have any other symptoms such as fever or difficulty using your arm. It is also important to call your doctor if you have any other concerning symptoms, such as numbness or tingling in your arm, weakness in your arm or hand, or difficulty moving your arm. These symptoms could be a sign of a more serious problem, and it is important to get them checked out as soon as possible.
Table of content
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors