Bone Marrow (Human Anatomy): Image, Function, Diseases, and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 17, 2023
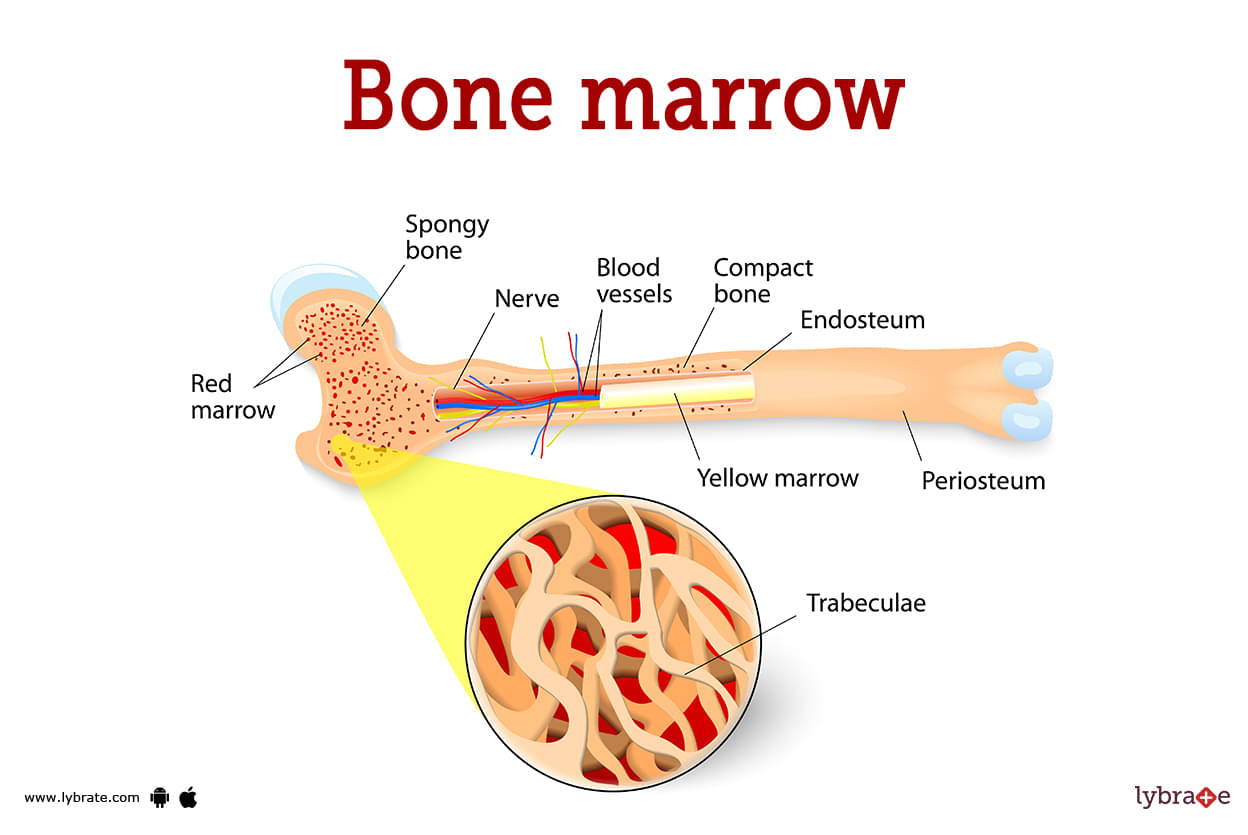
Bone Marrow Image
The cavities within the bones contain bone marrow, a soft, spongy substance. It is made up of stem cells that coat the bone marrow and also generate stromal and new blood cells. The whole body is filled with bone marrow, which is present in all bone cavities from birth.
However, as time goes on, it is discovered in the ribs, spinal bones, collar bones, cranium, pelvic bones, and limb bones. There are two primary forms of bone marrow. The term 'red bone marrow' also refers to myeloid tissue. It is made up of fibrous tissue that contains hematopoietic cells, commonly known as blood-forming stem cells because they play a role in the development of white blood cells, platelets, and red blood cells in adulthood.
The thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes are among the bodily organs where the lymphocytes completely develop after beginning to grow in the red bone marrow. Yellow Bone Marrow: Yellow bone marrow aids in the development of marrow stromal cells and contains more fat than Red bone marrow. The stem cells that create the body's connective tissues, including fat, cartilage, muscle, and bone cells, are called marrow stromal cells.
For red bone marrow to utilise and sustain bodily functions, yellow bone marrow stores fat and nutrients. Yellow bone marrow may change into red bone marrow and take over the role of white bone marrow in the event of an infection or significant blood loss.
Bone Marrow Functions
It is beneficial to the creation of both red and white blood cells, as well as platelets. In the absence of bone marrow, neither the circulation of oxygen throughout the body nor the defence against infections will be possible.
Even more significantly, the process that causes blood to clot would not be present. It is particularly crucial in preserving the mineral makeup of the body and safeguarding the key organs from any injury that may occur.
Therefore, the primary activities of bone marrow are hematopoiesis, the transportation of oxygen, a defence mechanism against foreign things that are damaging to our body, hemostasis, and the assistance in the removal of old cells from the circulation.
Bone Marrow Disorders
- Thrombocytopenia: Thrombocytopenia is a disorder that develops when the body's stem cells are unable to produce enough platelets to meet its demands. This might be from an autoimmune condition or a viral infection. Individuals under the age of 20 who have this disease often bruise or bleed internally.
- TAR Syndrome: Thrombocytopenia with missing radii is a condition in which gene mutations prevent enough blood platelets from forming. In each forearm of young children with this disease, the radius bone is absent at birth.
- Shwachman Diamond Syndrome: A genetic condition known as Shwachman Diamond syndrome causes the bone marrow to underproduce white blood cells. Myelodysplastic syndrome or aplastic anaemia might develop in a person with this condition. Additionally, it may result in changes in bone structure and pancreatic issues.
- Sideroblastic Anaemia: This kind of anaemia is caused by excessive iron in the red blood cells, which interferes with their proper formation. These anemias may be acquired or hereditary, and they often accompany myelodysplastic syndrome.
- Refractory Cytopenias: This kind of myelodysplastic syndrome, which mostly affects youngsters, is characterised by an insufficiency of certain blood cell subtypes.
- Reticular Dysgenesis: Low levels of white and red blood cells are caused by the uncommon gene mutation known as reticular dysgenesis. It primarily affects young children. Symptoms like sepsis, failure to thrive, diarrhoea, fever, recurrent infections including upper respiratory tract infections, oral candidiasis, perianal infections and abscesses can be seen.
- Severe Congenital Neutropenia: Infants with severe congenital neutropenia are affected by a variety of hereditary disorders. Infants with these uncommon disorders have low neutrophil counts and are more susceptible to infections.
- Kostmann Syndrome: Low neutrophil cells are a characteristic of the hereditary disorder known as Kostmann syndrome. Infections are more prone to spread to children with this illness. Myelodysplastic Syndrome: It is a set of illnesses that develop when stem cells transform in inappropriate ways, which causes a reduction in the quantity of blood cells. This is a kind of cancer that too exists.
- Pearson Syndrome: Pearson syndrome is not a hereditary condition and is brought on by a genetic alteration. This disorder primarily affects the synthesis of all blood cell types in the bone marrow, which leads to anaemia, weariness, and further infections.
- Dyskeratosis Congenita: Dyskeratosis congenita is a rare hereditary condition of bone marrow failure characterised by a reduction in the quantity of blood cells the marrow generates. Skin tissue deterioration and congenital defects are seen in this. Telomere alterations or gene mutations are to blame for this.
- Fanconi Anaemia: This genetic form of aplastic anaemia affects the formation of all blood cells in the bone marrow. Symptoms like low birth weight, Skeletal anomalies(the most common being no thumb or radius bone) and abnormal skin pigmentation can be seen.
- GATA2 Disorder: This is a condition where the GATA2 gene, which regulates the production of blood cells in the bone marrow, is altered. Children with GATA2 abnormalities often develop anaemia, which prevents them from having enough red blood cells to transport oxygen throughout their bodies.
- Cyclic Neutropenia: A hereditary blood condition known as cyclic neutropenia causes reduced amounts of certain white blood cells, primarily neutrophils. People with this disease are more prone to get infections quickly.
- Diamond Blackfan Anaemia: This illness is brought on by alterations to certain genes. Red blood cell production in the bone marrow is inadequate in those with Diamond Blackfan anaemia. They could have different bones and facial traits, as well as eye and renal issues.
- Dubowitz Syndrome: Dubowitz syndrome is a severe genetic condition that results in a number of morphological variations. People with this disease often get infections because their white and red blood cell counts are low, which lowers their immunity and makes them more susceptible to future infections.
- Barth Syndrome: White blood cells are impacted by the genetic condition known as Barth syndrome, which also leads to infections.
- Congenital Amegakaryocytic Thrombocytopenia: There are fewer platelets in the blood due to a hereditary disorder known as congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia. It may sometimes result in pancytopenia, which is a reduction in all three blood cell types.
- Congenital Dyserythropoietic Anaemia: CDA is a hereditary condition that causes the body to have insufficient red blood cells and oxygen levels.
Bone Marrow Tests
- Blood Testing: A complete blood count (CBC) is required to determine how the bone marrow functions. Red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and several other specialised blood cells may all be seen in a complete blood count (CBC). Reticulocyte count, which gauges how often your bone marrow produces new red blood cells, may also be included in this test.
- Aspiration of Bone Marrow: Bone marrow may also be examined directly. An aspiration of the bone marrow is used for this. A long hollow needle used for bone marrow aspiration is used to retrieve the marrow from a bone, usually the hip bone.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: Aspirations and biopsies of the bone marrow often take place concurrently. Even 2 needles or moving the same needle might be used by the professional. A biopsy is carried out by removing a tiny piece of bone that includes marrow for extra testing in addition to aspirating bone marrow for testing.
- FISH Test: Fluorescence in situ hybridization is another name for this procedure. This examination looks at the bone marrow's chromosomal composition. It may be used to identify aberrant cells and assess how well bone marrow illnesses are treated.
- Flow Cytometry: This technique may look for particular antibody characteristics in bone marrow cells. It is most commonly used to evaluate bone marrow, peripheral blood and other fluids in your body.
- Immunophenotyping: Immunophenotyping is a procedure that may recognise several blood cell subtypes in a bone marrow sample. It may be used to detect antibodies and discover antigen markers on cell surfaces.
- Tests for Kyotypes: These determine the quantity, arrangement, and order of chromosomes in a bone marrow sample.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction/PCR: The polymerase chain reaction is a very sensitive test that looks for biomarkers in bone marrow cells or blood. Whereas other tests have been ineffective, it can be used to find cancer cells.
- Retic Count Test: Reticulocyte count, reticulocyte percent, reticulocyte index, reticulocyte production index, or RPI are various terms for the same thing. This examination counts the reticulocytes in the blood. A very high or low count might indicate a major health issue, such as anaemia or problems with the bone marrow, liver, or kidneys.
Bone Marrow Treatment
- Platelet Transfusion Therapy for Immunodeficiency: Patients undergoing therapy for or preventing bleeding receive platelet transfusions due to the severely low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia). At all times, there should be at least 5,000 platelets per microliter of blood.
- Intravenous Gamma Globulin: Plasma contains protein fragments called gamma globulins, which are crucial for preventing infections. The risk of several bacterial diseases can be increased by severely low gamma globulin levels. Extremely low gamma globulin levels are a defining characteristic of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
- Fresh Frozen Plasma Transfusion For Immunodeificient Patients: Fresh frozen plasma (FFP), the fluid that carries blood cells, and cryoprecipitate, the portion of plasma that comprises clotting factors, may be transfused to patients who have abnormal or low amounts of blood-clotting proteins (commonly referred to as cryo for short).
- Blood Transfusion for Severe Anemia and Thrombocytopenia: Anaemia, or low red blood cell counts, can cause weakness, tiredness, and, in extreme circumstances, shortness of breath or a rapid heartbeat. When a patient is elderly or has a history of heart or blood vessel disease, most doctors will recommend red cell transfusions before any noticeable symptoms appear.
- Antihistamines for Autoimmune Disorders: This treatment reduces the body's inflammatory response and is useful in treating the overriding symptoms of autoimmune diseases when minor symptoms such as allergies, serious haemorrhages, and rashes appear in the many areas of the body for which these drugs are used. First-generation antihistamines include diphenhydramine, fexofenadine, acrivastine, azatadine, and clemastin.
Bone Marrow Medicines
- Nutritional Supplement for promoting Red Cell Production: When there are issues with microcytic or macrocytic anaemia, the administration of iron, folic acid, ferrous sulphate, Paris ascorbate, and zinc is useful in increasing red cell formation. The therapy of sideroblastic anaemia benefits from it as well.
- Intravenous Vitamin K Injections for treating Thrombocytopenia: When there is any type of hemolysis brought on by aplastic anaemia or sideroblastic anaemia, vitamin K is intravenously given to treat thrombocytopenia.
- Pancreatic Enzyme Supplementation: Lipase, amylase, and protease supplements are taken orally in the form of tablets and also administered orally in the form of syrups for the treatment of a variety of bone marrow marrow deficiency disorders as well as sideroblastic and aplastic anaemia. For Treatment of Iron Overload: Severe hemolysis and thrombocytopenia are associated with an elevated iron level in the blood as a subsequent effect. Deferoxamine is used for therapy of this condition.
- Prophylactic Antibiotics: Antibiotics used to treat bacterial infections, such as metronidazole, azithromycin, clindamycin, and amoxicillin, must be stored in a sterile environment to avoid the spread of germs to healthy cells.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does bone marrow do for the body?
Can a person live without bone marrow?
Is bone marrow cancer?
Is eating bone marrow good for you?
Is bone marrow disease serious?
Is bone marrow disease curable?
How do you get bone marrow disease?
How is bone marrow disease treated?
Table of content
Find Hematologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors