Cranial Nerves (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 17, 2023
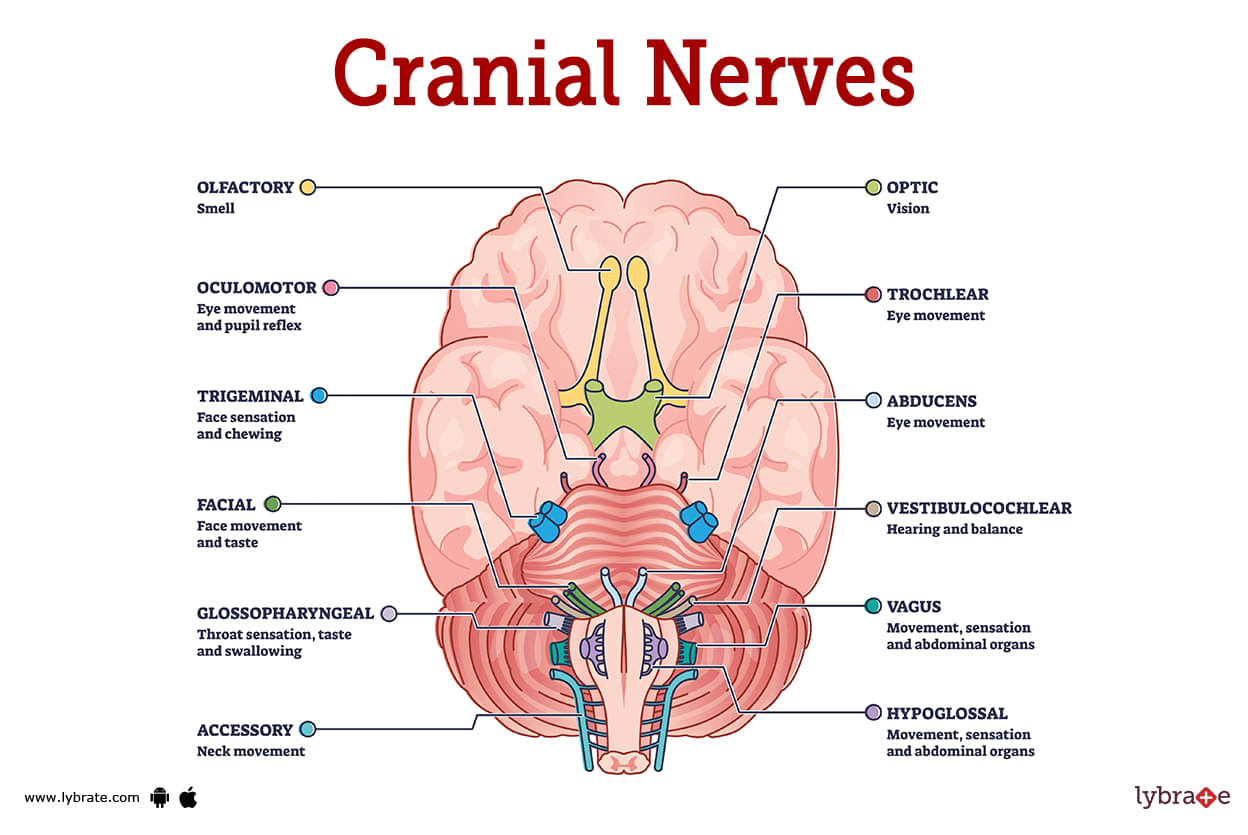
Cranial Nerves Image
The cranial nerves are a group of 12 paired nerves located in the back of the brain. Cranial nerves transmit electrical signals from your brain to your face, neck, and torso. Your cranial nerves assist you in tasting, smelling, hearing, and feeling sensations. They also assist you in making facial expressions, blinking your eyes, and moving your tongue.
What is the purpose of the cranial nerves?
- Cranial nerves control emotions and movement.
- Sensualize your sensory nerves.
- Hear.
- See.
- Smell and Taste.
- Nerves control the muscles and glands of the face. Sensorimotor cranial nerves exist.
Where is the location (origin) of the cranial nerves?
The brain is the source for two sets of cranial nerves. From the third to the twelfth cervical vertebrae, the brainstem is the source of both sets of cranial nerves. There are three separate regions of the brain stem (the medulla, the pons, and the midbrain) from which these nerves emerge, or at an intersection between three regions.
- The trochlear nerve (IV) originates in the midbrain, specifically in the back of brainstem. It has the longest course inside the skull from any of the cranial nerves.
- In between mid brain and pontine region the oculomotor (III) nerve is present.
- From pons region of the brain stem there is occurence of trigeminal nerve.
- At the junction of Pontine and Medulla the abducens nerve, facial nerve, vestibulocochlear (VI-VIII) nerve are originated.
- The medulla oblongata is the next brain structure after the olive which houses the glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves (IX-XI).
- Before the olive or we can say pons, the hypoglossal (XII) nerve is originated.
What is the longest cranial nerve?
Longest among the cranial nerves is the vagus nerve. Body movement and feeling are controlled by the vagus nerve. Different parts of your body, such as your tongue, throat, heart, and intestines, might be harbouring it.
What are the types of cranial nerves?
All 12 sets of cranial nerves have their roots in different regions of the brain. The olfactory and optic nerves are the first two nerves to develop from the cerebrum, whereas the other ten nerves develop from the brain stem. Names for each cranial nerve represent the functions associated with that nerve, while the roman numbers used to describe their numerical order reflect their anatomical location (I-XII).
- Olfactory nerve (I)
- Optic nerve (II)
- Oculomotor nerve (III)
- Trochlear nerve (IV)
- Trigeminal nerve (V)
- Abducens nerve (VI)
- Facial nerve (VII)
- Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
- Vagus nerve (X)
- Accessory nerve (XI)
- Hypoglossal nerve (XII)
Cranial Nerves Functions
Function of Cranial Nerves are as follow:
- Olfactory nerve: It provides us a sense of smell or aptitude to smell.
- Optic nerve: The optic nerve performs the essential role of allowing us to see.
- Oculomotor nerve: It provides us the ability to move around and blink your eyes.
- Trochlear nerve: It provides us eye movement freedom to look up, down, or in any direction between the two extremes.
- Trigeminal nerve: The main functions of this nerve is Facial and cheek sensations, oral flavor, and jaw articulation all play a part.
- Abducens nerve: It provides us the ability to freely move our eyes is crucial.
- Facial nerve: It helps the brain in Facial reactions and gustatory perceptions.
- Auditory/vestibular nerve: It controls the sense of hearing and is crucial, as is the feeling of balance.
- Glossopharyngeal nerve: It provides us the ability to taste and the ability to swallow liquids and solids.
- Vagus nerve: It helps in building the relationship between what you eat and how fast your heart beats.
- Accessory nerve (or spinal accessory nerve): It provides us the ability to use our muscles of the neck and shoulders.
- Hypoglossal nerve: It provides us the ability to move your tongue around in your mouth.
While sensory and motor activities are often considered to be synonymous, this is not necessarily the case with the cranial nerves. As a group, the five cranial nerves that control our senses of sight, smell, hearing, and touch are called the sensory cranial nerves.
However, the cranial nerves are responsible for transmitting motor and sensory signals to the head and neck. The motor nervous system, on the other hand, controls the actions of the muscles and glands. Only the vagus nerve goes below the collarbone to supply the organs in the chest and the belly.
Cranial Nerves Conditions and Disorders
- Traumatic olfactory nerve dysfunction: In this disorder, the olfactory epithelium, which includes nasal mucosa receptor neurons, is destroyed or the unmyelinated nerve rootlets that constitute the olfactory bulb are stretched. Anosmia and hyposmia are its symptoms.
- Ocular palsy: Ocular palsy causes one or more muscles to lose strength, causing the eyeball to spin less freely. Paralysis is a full lack whereas paresis is partial. They might be distinct or connected.
- Trigeminal neuralgia: Trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve, is affected by Trigeminal neuralgia. The trigeminal nerve sends face feelings to the brain. It affects one side of the face and may be felt around the eye, cheek, and chin. Trigeminal nerve pain is also strong.
- Hemifacial spasm: Blood vessels cut off the 7th cranial nerve, producing hemifacial spasm. hemifacial spasm is caused by a blood vessel hitting a face nerve, a tumour, or nerve injury. They're annoying but seldom deadly. Lower facial spasms may cause anger and pain. Hemifacial spasms may impact all facial muscles.
- Glossopharyngeal neuralgia: Glossopharyngeal neuralgia is a nerve compression. It causes acute, stabbing pain in the tonsils, tongue, ear, or throat. A small blood artery usually presses on neurons leaving the brainstem. Blood vascular irritation of the 9th cranial nerve causes this condition.
- Skull base tumours: Skull base tumours are craniopharyngiomas. Double vision, blindness, hearing loss, and vertigo are caused by cranial nerve tumours.
- Geniculate neuralgia: Blood vascular compression causes geniculate neuralgia. Symptoms include severe deep ear pain that is dull or scorching and feels like a 'ice pick in the ear.' Facial discomfort may also develop. Eating or speaking might irritate the ear canal.
- Lou Gehrig's disease: Lou Gehrig's sickness is ALS. Symptoms include muscle weakness. It affects the nervous system, affecting physical performance and muscular weakness. When nerve cells are diseased, the muscles they supply weaken. Unknown.ALS causes speech, swallowing, and movement issues. Breathing becomes hard.
- Bell's palsy: This temporarily weakens facial muscles. Pinched facial nerves cause this palsy. Facial nerve palsy causes drooping on one or both sides of the face. Without treatment, the condition disappears after a few months.
- Palsy of the abducens nerve: Damage to the sixth cranial nerve causes this illness. It's the most common kind of ocular motor paralysis in adults. The lateral rectus nerve controls the abductor muscle. Abducens nerve palsy causes esotropia from unopposed medial rectus activation.
- Microvascular Cranial Nerve Palsy (MCNP): When cranial nerves in the skull lose blood flow, this disease occurs. The person may not be able to move their eye. Also, double eyesight. Double vision occurs when a person perceives two identical pictures side-by-side or one above the other.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): To put it simply, it's a degenerative disorder where nerve cells die off and muscular tissue atrophys.
- Bell’s palsy: One side of the face sags and loses tone quickly. hemifacial spasms are involuntary facial muscular contractions on one side of the body.
- Internuclear ophthalmoplegia: When you look out to the side, you can't move your eyes together.
- Oculomotor palsy: If the third cranial nerve in your head is injured, one of your eyes will always be stuck in a position that makes it seem like you're looking down and to the side.
- Stroke: Your brain's blood supply has been interrupted, most likely by a blood clot or a burst blood vessel.
- Traumatic brain injury: Traumatic brain injury is the outcome of a sudden and strong impact to the head that results in the disruption or destruction of brain function.
- Trigeminal neuralgia: You have constant pain along the path of the fifth cranial nerve in your face.
What are the common signs or symptoms of cranial nerve disorders?
The symptoms of a malfunction of the cranial nerves may range from mild to debilitating, and include discomfort, dizziness, hearing loss, weakness, and even paralysis. A person's capacity to communicate emotion via facial expressions, talking, and swallowing may all be impacted by these diseases.
How can I keep my cranial nerves healthy?
It's possible to boost your brain, cranial nerve, and nervous system health by dietary and lifestyle changes. It is possible to:
- Get to and stay at a healthy weight that suits your build, gender, and age. Indulge in alcoholic drinks sparingly. Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are just a few examples of nutrient-dense foods that should make up a large portion of your daily diet.
- Getting regular exercise is very recommended. Keeping your blood pressure in check is something that has to be done regularly.
- As an example, if you have diabetes or another condition that increases your risk of nerve damage, be sure you're getting the proper treatment. Stop smoking.
Cranial Nerves Treatments
- Functional facial plastic surgery: For individuals who don't recover after surgery, this procedure may assist with facial asymmetry and eyelid closure.
- Microvascular Decompression: The Jannetta procedure is MVD. Trigeminal neuralgia is treated surgically. During this procedure, a minuscule sponge is put between the compressing vessel and the trigeminal nerve via a surgically produced skull hole. This sponge isolates the blood artery from the nerve. Neurovascular congestion reduces trigeminal nerve healing and discomfort. The surgery doesn't harm the nerve.
- Gamma knife Perfexion radiosurgery: Perfexion radiosurgery is accurate, powerful, and beneficial for brain problems, especially cranial nerve anomalies. It helps trigeminal neuralgia. The Perfexion concentrates 201 radiation beams on the brain. Rays can't destroy healthy tissue. They treat one area. The next day, patients may resume routine activities with minimal pain.
- Trigeminal nerve stimulation (TNS): TNS employs a tiny, battery-operated device to subtly activate the trigeminal nerve, which is located on the forehead. The deep brain regions that control moods and attentiveness to get messages when this nerve is stimulated.
- Percutaneous Glycerol Rhizotomy: This minimally invasive technique is outpatient. The surgery obstructs the trigeminal nerve's pain route. A needle enters the cranium via the mouth. An x-ray injects a harmless dye to confirm needle placement. A Gasserian ganglion injection uses glycerol. Glycerol causes mild nerve damage and facial numbness.
- Balloon compression: In balloon compression, a hollow needle is introduced through the face and aimed towards the trigeminal nerve. The doctor inserts a balloon-attached catheter via the needle. The doctor inflates the balloon to suppress trigeminal nerve pain impulses. Balloon compression decreases pain briefly.
- Radiofrequency thermal lesioning: This procedure destroys pain-related nerve fibres. After administering anaesthesia, the surgeon inserts a hollow needle through your face to the trigeminal nerve.
Cranial Nerves Medicines
- Antispasmodics: Antispasmodics, sometimes called anticholinergics and muscle relaxants, may help reduce stiffness and bowel or bladder difficulties after a spinal cord or cranial nerve damage.
- Antidepressants: Antidepressants like SSRIs and SNRIs may raise mood- and pain-regulating neurotransmitter levels. Psychiatric patient with cranial nerve irritation and mood swings.
- Anticonvulsants: Gabapentin may alleviate neuropathic pain in cranial nerve injury patients. Neuropathic pain occurs from nerve damage that affects pain signal hyperexcitability.
- Broad Spectrum Antibiotics For cranial nerve infection: Prescribe antibiotics for bacterial infections. During surgery, anti-inflammatory cranial nerve ointment may be used. Erythromycin, amoxicillin, ampicillin, ofloxacin, etc.
Table of content
Find Neurologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors