Ear (Human Anatomy): Ear Infections, Tests and Treatments
Last Updated: Feb 25, 2023
Ear Image
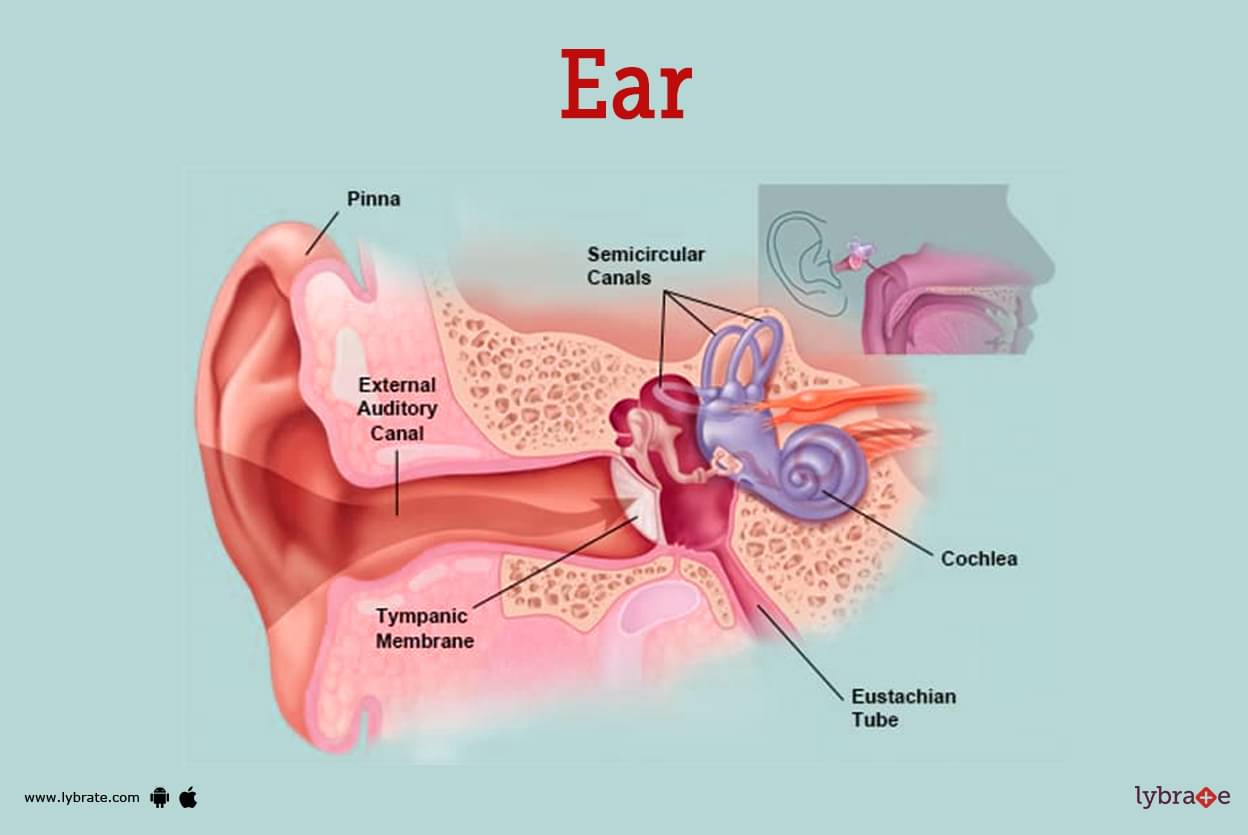
The ear is split into three portions in humans: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. The outer ear is made up of the pinna and the ear canal. Because the outer ear is the sole visible component of the ear in most animals, the term 'ear' frequently refers to just that.
The tympanic cavity and the three ossicles make up the middle ear.
The semicircular canals, which permit balance and eye tracking when moving, the utricle and saccule, which provide balance when stationary, and the cochlea, which enables hearing are all found in the inner ear, which is located in the bone labyrinth and comprises structures that are vital for multiple senses. The inner ear is located in the bony labyrinth.
The ears of vertebrates are placed on both sides of the skull in a symmetrical pattern so that they can more accurately localise the source of a sound.
Earrings and other types of ear jewellery have been used for thousands of years, and the ear has been the site of various surgical and cosmetic modifications, spanning a wide spectrum of cultures.
Earrings and other forms of ear jewellery are still used today.
Function of Ear
The ear has mainly 2 functions i.e.
- Hearing: When sound waves enter your ear canal, they cause the tympanic membrane, more commonly known as the eardrum, to vibrate and produce hearing. The three minuscule bones known as ossicles are the ones responsible for transmitting vibrations to the middle ear. The ossicles are responsible for the amplification of these sound waves before they are sent to the cochlea. Tiny hair cells within the inner ear, known as stereocilia, are responsible for converting the vibrations caused by sound waves into electrical energy, which is then transported along nerve fibres to the brain. The information is interpreted by your brain after that.
- Balance: Your semicircular canals in your inner ear are filled with fluid, and the hair-like sensors that line those canals detect sound. When you move your head, the fluid that is contained within these loop-shaped canals begins to slosh around, which in turn causes the hairs to move. This cycle continues until the hairs are no longer moving. These signals are transmitted to your brain by the hairs that are located within your inner ear through the vestibular nerve. In the very last step, but certainly not the least, your brain will send signals to your muscles in order to keep your equilibrium.
Ear Diseases
- Earache: A variety of conditions and conditions can give rise to ear pain.You still need to give serious consideration to each one of them, despite the fact that some of them are a lot more severe than others
- Otitis externa: It is a condition of the ear in which Inflammation or infection of the outer ear occurs. It is also known as swimmer's ear . Cases that arise all of a sudden are almost always infections, whereas chronic otitis is frequently a skin condition (dermatitis).
- Meniere's disease: It is a disorder in which the function of one side of the inner ear is damaged. Pain, vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss are some of the most common indications here.
- Tinnitus: Ringing in either or both ears is a symptom of tinnitus. In most cases, this is as a result of damage caused by prolonged exposure to loud noises or simply the natural process of ageing.Impaction of the cerumen, also known as earwax, can occur when ear wax clogs the ear canal or sticks to the eardrum. Hearing is impaired due to the eardrum's reduced ability to vibrate.
- Ruptured eardrum: The eardrum can be torn by exposure to infection, very loud noises, sudden shifts in air pressure, or foreign objects. Mostly the tiny hole closes up and heals on its own.
- Acoustic neuroma: The acoustic neuroma is a benign tumour that develops on the nerve that travels from the ear to the brain. Tinnitus, hearing loss, and vertigo are all potential symptoms.
- Mastoiditis: It is an infectious condition that affects the mastoid bone, which is present just on the posterior side of the ear. Leaving an infection in the middle ear untreated can lead to mastoiditis.
- Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: because of any sort of defect in ear functioning symptoms of vertigo occurs. These symptoms are occurring due to disruption of endolymph and perilymph.called as BPPV in medical terms although a acute disorder but can be considered tough to treat.
- Cholesteatoma: Cholesteatoma is a condition that will not be harmful in any way. It is the abnormal accumulation of skin that can be found within the middle ear and the bones that surround it. Hearing loss is frequently accompanied by an offensive-smelling discharge.
- Ear wax: Wax in the ear can protect the lining epithelium of the external auditory meatus from damage caused by water and the tympanic membrane from being damaged by insects by acting as a trap for them. The excess of car wax that was interfering with the patient's hearing was removed using a syringe.
- Otitis media: A perforation of the tympanic membrane can be caused by an infection in the middle ear or an injury sustained from the outside (otitis media). It's possible it'll damage your hearing in the middle ear.Otitis media, also known as an infection of the middle ear, is very common, especially in young children and infants. The pharyngotympanic tube is the pathway that infectious agents take to get from the upper respiratory tract to the middle ear.
- Hyperacusis: Hyperacusis is characterised by a reflexive and simultaneous contraction of the tensor tympani and the stapedius muscle to reduce the impact of extremely loud sounds and protect the cochlea from the damaging effects of noise. When the stapedius muscle is paralysed, the individual develops hyperacusis, which is an abnormally increased power of hearing.
- Otosclerosis: Otosclerosis is defined as an abnormal ossification of the annular ligament, which anchors the footplate of the stapes to the oval window. This results in deafness because it impedes the movement of the stapes. In adults, otosclerosis is the condition that most frequently results in conductive deafness.
- Ramsay Hunt syndrome: The Ramsay Hunt syndrome includes the following: Shingles is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus that can affect the facial nerve that is located close to one of your ears. The painful rash of shingles is only one of the symptoms of Ramsay Hunt syndrome, which can also cause facial paralysis and hearing loss in the ear that is affected.
- mastoiditis: Abscess of the mastoid, also referred to as mastoiditis Due to the infection that takes place in the mastoid air cells of the ear, this condition, which causes inflammation of the middle ear, is fairly common.
- Lower motor neuron type of facial palsy,: It is a condition of the ear and facial nerve that happens when the infection deteriorate the paper-thin bony wall of the facial canal. This condition affects the ear as well as the face.
- Cerebellar abscess: Cerebellar abscess is a condition that happens when infection spreads through the floor of the middle ear and into the cerebellum.
- Labyrinthitis: It is the medical term for inflammation that develops in the labyrinth as a result of an infection.
Ear Tests
- Ear exam: Visual examination is typically the initial line of defence against ear disorders. By checking the auditory canal using an instrument called otoscope, the eardrum can be viewed.Using tones of varied amplitude and frequency, an audiologist will give a series of tests to formally examine a patient's hearing in both ears.
- Computed tomography (CT scan): CT scan is a specialised type of imaging technique in which a 3d graphical image is being created of a body part and diagnosis of any sort of abnormality can be done.
- Magnetic resonance imaging: Radio waves in a magnetic field are used by a scanner to obtain images of the ear and the structures that surround it with a high level of resolution.
- Weber test & Rennie test: The Rinne and Weber tests are useful for making a diagnosis of hearing loss in patients. They can assist in determining whether or not you may be suffering from conductive or sensorineural hearing loss.
- Bone Conduction Testing: This information can be used by an audiologist to determine the type of hearing loss that you have. A pure-tone hearing test is one that evaluates how your inner ear reacts to sounds.
- Pure Tone Testing: Your capacity to hear sounds of varying volumes and pitches is evaluated with the help of air conduction during this particular kind of test, which is also referred to as pure tone audiometry. You will need to sit in a booth that has been specifically designed, and you will be required to wear headphones. A succession of noises will be played through the headphones at the same time. You will be prompted to either raise your hand or press a button each time you hear a tone that is played for you. After that, a chart on an audiogram will be made with the results.
- Speech Testing: The goal of this evaluation is to establish your speech reception threshold (SRT), or the lowest audible level at which you are able to understand speech more than half of the time. It measures your ability to differentiate speech from background noise in both calm and noisy environments.
- Tympanometry: During this test, the sensitivity of your eardrum to changes in air pressure will be evaluated. It is able to identify tumours, as well as fluid and earwax accumulations, perforations in the tympanic membrane, and accumulations of earwax.
- Acoustic Reflex Testing: This examination is used to assess the kind of hearing loss as well as the location of the hearing loss by analysing the involuntary muscular contractions of the middle ear (the ossicles, the cochlea, the auditory nerve, etc.).
- Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR): This kind of test is performed to check if the patient has sensorineural hearing loss. It is also a common diagnostic tool for testing the hearing of infants. Your brainwave activity will be tracked as it reacts to sounds of varying decibel levels.
- Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs): In the inner ear, hair cells vibrate to create sounds known as oscillatory auditory events (OAEs). The cochlea is stimulated and the brain's response is recorded using a tiny probe with a microphone and a speaker. People with normal hearing will put out signals, while those with a hearing loss of 25 dB or more will not. Examining the ear canal, middle ear fluid, and cochlear hair cells could reveal a blockage, fluid, or damaged hair cells, respectively, that are responsible for hearing.
Ear Treatments
- Tympanoplasty: Surgical procedures on the eardrum and/or the bones of the middle ear to repair the hearing mechanism in the middle ear
- Acoustic Neuroma Surgery Translabyrinthine: In order to gain access to the ear canal and remove the tumour, the surgeon must first remove the mastoid bone and any bone that may be present in the inner ear. When a patient's hearing is already severely impaired, surgeons frequently turn to this method.
- Acoustic Neuroma Surgery Middle Fossa: The superior surface of the internal auditory canal, which is positioned beyond the auditory meatus, is where the tumour is removed during the surgical procedure. This procedure is used when there is a good probability that your hearing can be saved and it is the method that we choose to use.
- Cochlear Implant Ear Surgery: Cochlear implants are an electrical device that can be inserted surgically and help provide sound for people who have severe hearing loss. These implants can be beneficial for people who have severe hearing loss. This severe form of hearing loss is often brought on by a condition that affects the inner ear, such as a lesion or a malfunction.
- Congenital Atresia Ear Reconstruction: Surgical reconstruction of the ear for patients who were born without certain anatomical components, including but not limited to the following:
- Ear canal
- membrane of the tympanic canal (eardrum)
- Ossicular chain in the context of the (middle ear bones of hearing)
- CyberKnife radiosurgery: Radiosurgery with a CyberKnife is a method that can be utilised to treat a variety of ear, nose, and throat ailments, as well as hearing loss, that are caused by diseases of the brain. It does this by directing a highly focused beam of radiation toward particular regions of the brain. Because the beam of radiation destroys the tissue that a surgeon would normally remove with a knife during an operation, the treatment does not entail any actual cutting at any point.
- Labyrinthectomy: A transmastoid surgical therapy for the treatment of vertigo and disequilibrium in which the remnant inner ear balancing function of the ill ear is eliminated in order to treat the sick ear.
- Myringotomy Eardrum Repair: A medical operation that involves cutting into the eardrum and draining fluid from the middle ear. In order to ensure adequate drainage, the surgeon will occasionally place a little tube in the centre of the ear.
- Irrigation (lavage): A gentle irrigation of the ear canal using salt water and diluted hydrogen peroxide can be an effective treatment for some cases of cerumen impaction. This treatment involves removing the cerumen from the ear canal.
- Positional exercises: Because they encourage movement of the particles that cause BPPV, certain exercise routines may reduce the severity of the condition's symptoms.
Medicines for Ear
- Antibiotics: Penicillin is the medication that is prescribed the most frequently for the treatment of ear infections. After waiting to see if the illness clears up on its own, physicians frequently recommend penicillin treatment as an antibiotic. The penicillin antibiotic that is prescribed the most frequently is amoxicillin. Nausea, vomiting, and a rash are all potential adverse reactions of amoxicillin.
- Cerumenolytics (ear-wax drops): A few drops of a solution containing mineral oil, as well as a mixture of hydrogen peroxide and water, or another preparation, will release wax that has become impacted.
- Antihistamines: Histamine blockers have a sedative effect on the inner ear, which can alleviate vertigo symptoms.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: . Although nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) cannot cure ear infections, they can decrease the associated pain. Ibuprofen is the most often used nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicine (NSAID); nonetheless, it is not recommended for children younger than 6 months. Ibuprofen produces side effects like nausea, dizziness, and constipation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are common diseases of the ear?
What are 2 common problems with ears?
What are the three main symptoms of Meniere's disease?
What is Meniere's disease caused by?
What is the most common ear infection and how is it caused?
Table of content
Find ENT Specialist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors