Heart Conduction System (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases, and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 17, 2023
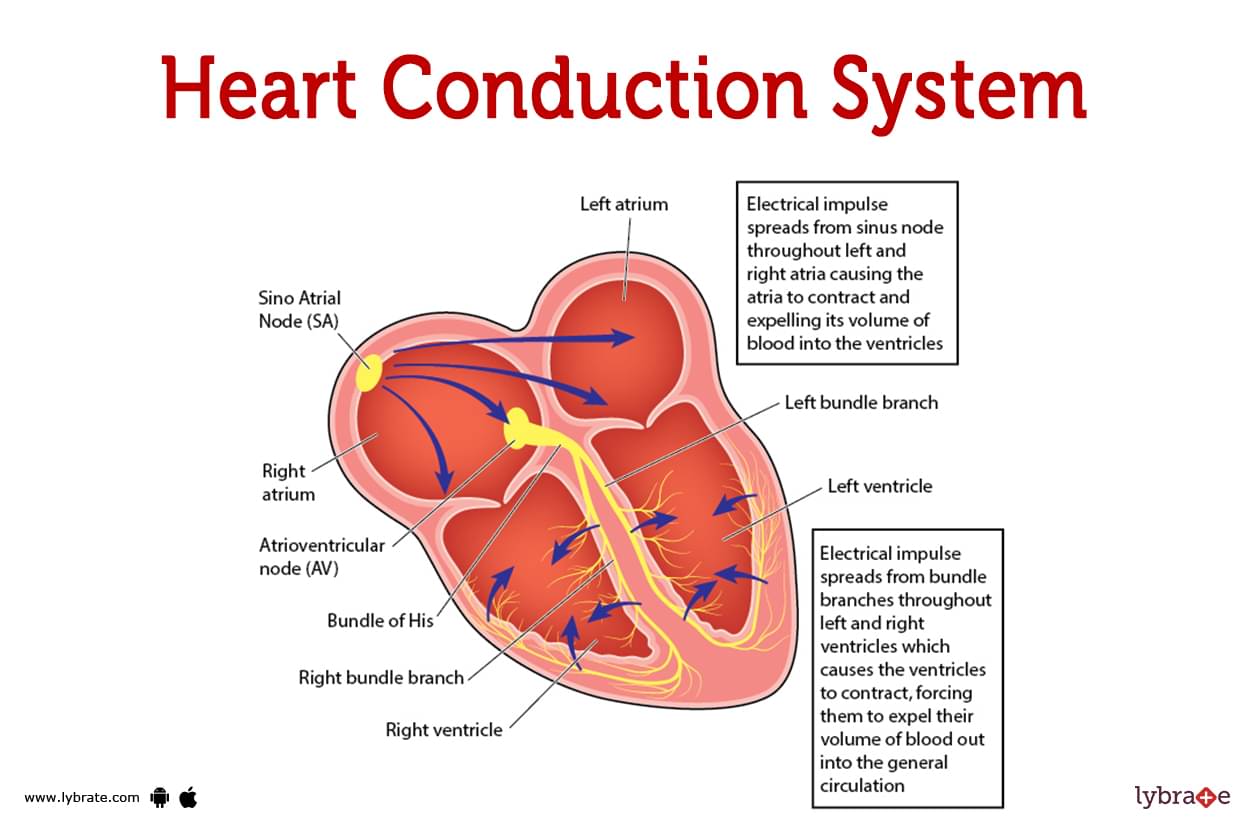
Heart Conduction System image
- Your heartbeat is controlled by a network of nodes, cells, and signals called the heart conduction system. Electrical signals move through your heart every time it beats. These signals cause various heart regions to enlarge and contract.Your body's blood flow is governed by the heart's contraction and relaxation.
- Your heart beats as a result of the conduction system of the heart,a system of electrical signals, specialised cells, and nodes. Two different kinds of cells regulate the rate of your heartbeat:
- Conducting cells are used to transmit the electric signals.
- Muscle cells control the contractions of your heart.
- The signal to begin a heartbeat is sent via your heart's (cardiac) conduction system. Additionally, it transmits impulses to your heart, instructing various areas to relax and contract (squeeze). Blood flow from your heart and to the rest of your body is regulated by this mechanism of contracting and relaxing.
Heart Conduction System Functions
The circulatory system in your body is circulated by your heart. With each beating, electrical signals go via the heart's conduction channel. To start it, your sinoatrial (SA) node produces an excitation signal. Similar to how electricity travels through connections to household appliances, this electrical signal
This is where the excitation signal goes:
- The atria of your heart are telling them to constrict.
- The signal is delayed by the atrioventricular (AV) node until all of the blood has left your atria. The signal is carried to the Purkinje fibres through the His bundle, which is the central bundle of nerve fibres.
- The Purkinje fibres cause the bottom chambers of your heart, known as the ventricles, to contract.
- These actions cause your heart to totally constrict. Your heart conduction system produces tens of thousands of signals per day to keep your heart beating.
How does the rest of your Heart's Electrical Conduction function?
Electrical signals are delivered to your heart's conduction system, causing it to enlarge and contract. The beating of your heart controls the blood flow. A consistent, regular heart rate should be maintained via the electrical conduction system. Additionally, it aids your heart's ability to slow down when you need to rest or speed up when more blood and oxygen are required.
What constitutes the Cardiac Conduction System's components?
Your heartbeat is controlled by a system called the cardiac conduction system, which is made up of specialised cells and nodes. This is the list that we have: Somatometria Node, The atrioventricular bundle, the junction that connects the heart to the spine, the central nervous system, and a number of different bundles of Purkinje fibres etc.
Sinoatrial Node
The natural pacemaker of your heart is referred to as your sinoatrial node. It transmits the electrical signals that cause the heartbeat to begin.
The right atrium of your heart's upper chamber houses the SA node. It is near the edge of your atrium, close to your superior vena cava (vein that brings oxygen-poor blood from your body to your heart).
Your SA node's ability to send electrical signals quickly or slowly is regulated by your autonomic nervous system. Depending on what you are doing, this area of the neurological system controls the hormones that regulate your heart rate. Your heart rate, for instance, rises while you exercise and falls when you are sleeping.
Your autonomic nervous system consists of:
- Your SA node starts to work more quickly as a result of the sympathetic nervous system's 'fight or flight' response, which raises your heart rate.
- Your parasympathetic nervous system's (relax and digest response) effect on your heart rate causes your SA node to function more slowly.
Atrioventricular Node
The electrical signal from the SA node is slowed down by the atrioventricular node.Every time, the signal is delayed by same amount (a fragment of a second).
With the delay, you can be sure that just before contractions end, all of the blood has left your atria. The atria make up at the top of the heart.They send blood to the ventricles from the rest of your body.
Your AV node may be found in the Koch Triangle at this time (between the septal flap of the tricuspid, the coronary sinus, and the membranous section of the interatrial septum). This gets quite close to the heart of the matter.
Bundle Of His
Another term for the bundle of His is the atrioventricular bundle. It is a nerve cell branch that emerges from the AV node. This fibre bundle transports the electrical signal from the AV node to the Purkinje fibres.The physical partition separating the right and left ventricles, known as the interventricular septum, is lined with the bundle of His. The bundle of his is made up of two parts:
- Your left bundle branch sends the signal to your left ventricle through the Purkinje fibres.
- The right bundle branch provides electrical impulses to the right ventricle through the Purkinje fibres.
Purkinje Fibres
- Branching off of specific nerve cells are the Purkinje fibres. They quickly transmit electrical signals to the right and left ventricles of your heart.
- Your ventricle walls' subendocardial surface is where your Purkinje fibres are located. The inner layer of tissue that lines the chambers of your heart, known as the endocardium, includes the subendocardial surface.
- When the Purkinje fibres convey electrical signals to your ventricles, they contract. When the ventricles contract, blood moves from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery and then to the lungs, but from the left ventricle to the aorta. The aorta is the biggest artery in the body. It carries blood supplied by your heart to your body's other organs.
Heart Conduction System Conditions and Disorders
- Arrhythmia: irregular heartbeats, including atrial fibrillation and others
- Bundle Branch Block: a heartbeat that is not regular and may be caused by an obstruction of the Purkinje fibres on one side of the heart.
- Heart Block: a disruption in the normal flow of electrical impulses between the ventricles and the atriums of your heart.
- Long QT Syndrome (LQTS): On occasion, your ventricles will contract and release at an abnormally slow rate, which can result in syncope or sudden cardiac arrest.
- Premature Ventricular Contractions: a rapid heartbeat that can lead to palpitations or what's known as a 'skipping heartbeat' in the ventricles of your heart.
- Sudden Cardiac Arrest: A serious disruption in the regular rhythm of your heart that can completely halt its function and lead to death if the condition is not treated as soon as possible.
Heart Conduction System Tests
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): It is the primary test that is performed in order to evaluate the activity of the heart. One of the most helpful diagnostic tools for a wide range of heart diseases is a graphical representation that shows the electrical activity of the heart.
- Echocardiogram: The preferred diagnostic method for accurately visualising cardiac anomalies is echo. Any problems with the heart muscle's and the heart valves' ability to pump blood are directly visible through echocardiography.
- Cardiac Stress Test: It entails utilising a machine or medications that act as cardiac stimulants to urge the heart to beat at its strongest. This could make it easier to identify those who have coronary artery disease.
- Cardiac Catheterization: After being inserted into the major artery in the groin, a catheter is placed into the blood vessels. Then, a physician can perform stenting or other operations after reviewing X-ray scans of the coronary vessels to check for any obstructions.
- Holter Monitor: When an arrhythmia is suspected, a portable cardiac monitor can be worn. It is a special gadget that continuously tracks cardiac activity.
- Event Monitor: The doctor suggests an event monitor, a patient-worn portable cardiac monitor, when a rare arrhythmia is suspected. In the event of a cardiac arrhythmia, the stimulation activity is then recorded, allowing for an accurate diagnosis of the disorder.
Treatments for the Heart Conduction System
- Angioplasty or PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty): It is a form of cardiac surgery where a major artery is catheterized, a tiny balloon is inflated in blocked coronary arteries, and a stent is supplied to keep the artery open.
- Coronary Artery Stenting: In this kind of heart surgery, a wire mesh is placed into the narrowed coronary artery to enhance blood flow and treat disorders like angina pectoris.
- Thrombolysis: The patient receives specific thrombolytic medications through intravenous injection that may break the clot, which causes cardiac issues. In contrast to thrombolysis, stenting is favoured since it has less negative effects.
- AED (Automated External Defibrillator): An AED is used to determine the heart's rhythm during cardiac arrest and has the ability to stimulate the heart with a synthetic electrical impulse.
- ICD (Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator):A surgically implanted cardioverter defibrillator is being used to monitor heart activity & input electrical impulses as required in situations of severe arrhythmia.
- Pacemaker: Individuals with cardiac rhythm abnormalities such arrhythmia, tachycardia, Irregular heartbeats, bundle branch block, etc. were recommended to use a pacemaker to maintain the heart's normal rhythm.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: Its benefits include a lower likelihood of persistent angina and the ability to accomplish total revascularization, but the risks of major surgery include a bigger danger of morbidity and death as well as a higher chance of a recurrent cardiac event.
Heart Conduction System Medicines
- Beta-blockers for maintaining rhythm and blood pressure: They also reduce the strain on the heart, resulting in a reduced heart rate and preventing various situations like heart failure and arrhythmias. Some of the common salts used by cardiologists are carvedilol, bisoprolol, and metoprolol succinate.
- Angiotensin Receptor Blockers for Maintaining Blood Pressure :They interfere with the metabolism of the angel tendons, blood pressure regulation, and cardiac output maintenance. Only experienced doctors should provide some prescription salts, such as Valsartan, Candesartan, and Losartan.
- Aspirin for thrombolysis: It is a first line drug to prevent the formation of blood clots, which also reduces the risk of a heart attack.
- Clopidogrel (Plavix) for the prevention of coagulation disorders: A loading dose of Clopidogrel reduces the formation of clots. This drug prevents the coagulation of platelets and their combination. It is also considered an important drug at the time of any cardiovascular event.
- Antiarrhythmic Medications for Heart Attack: The medicine that helps in reducing the heart rate and is helpful in maintaining its electro myogenic activity. They are also helpful in preventing arrhythmia and heart block.
Table of content
Find Cardiologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors