Inguinal Ligament (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 18, 2023
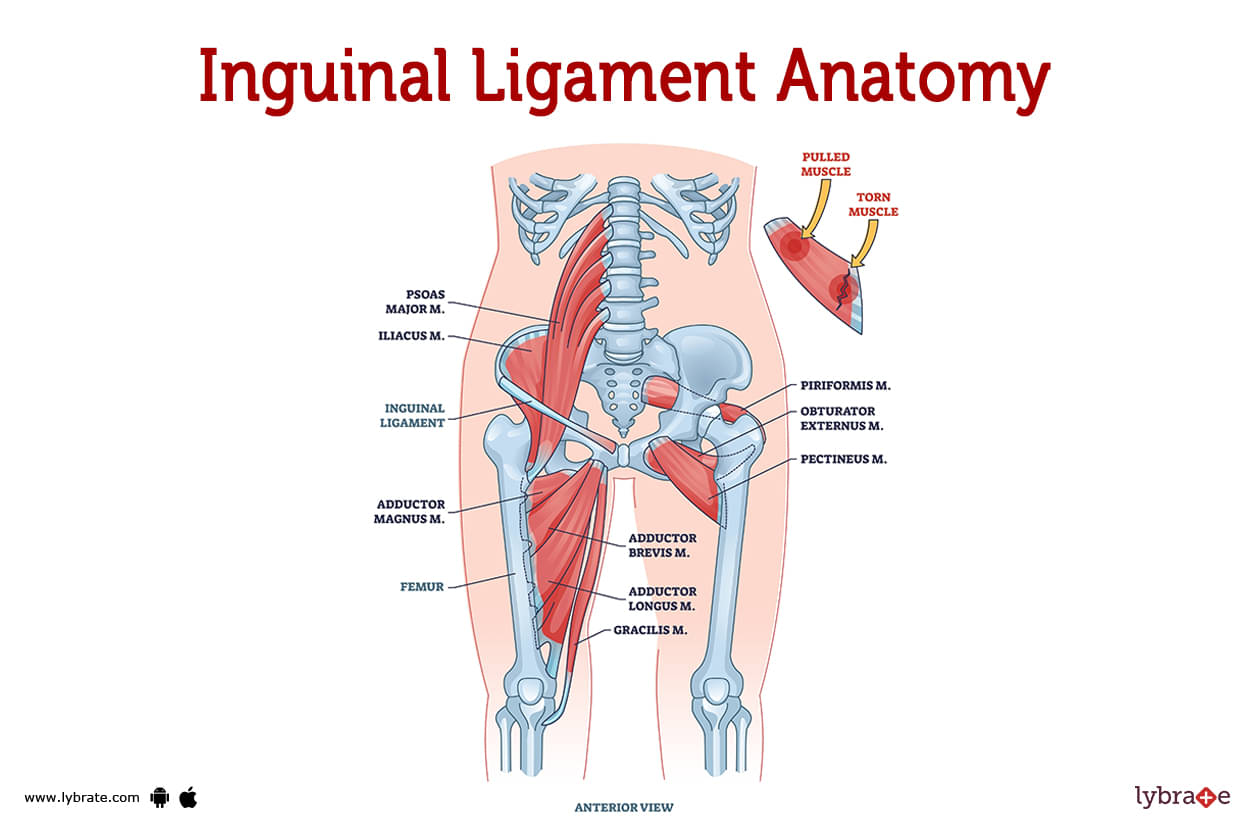
Inguinal Ligament Image
In the innermost part of the groyne is where you'll find the inguinal ligament, which is actually a collection of two bands that link the oblique muscles of the abdomen to the pelvis. They act as an anchor for the abdomen as well as the pelvis, providing support to the soft tissues in the groyne area. An inguinal hernia is a prevalent condition in this region of the body, particularly among males over the age of 40.
Inguinal ligament: what exactly is that?
In the region of the body's inguinum, there is a series of two narrow bands known as the inguinal ligament (the groin). The crease that forms where the lower part of the abdomen and the inner thighs meet is known as the groyne.The oblique muscles of the abdomen are connected to the pelvis by a ligament known as the inguinal ligament. From the ribs all the way down to the pelvis, the oblique muscles curl around the sides of the body. The pelvis is a region of the skeleton that connects the upper body (the trunk) to the lower body (the legs).
There are a few other names for the inguinal ligament, including the groyne ligament, Poupart's ligament, and the Fallopian ligament.
Where is the inguinal ligament?
The pelvis contains the inguinal ligament. Actually, there are two symmetrical bands. Beginning with the anterior superior iliac spine for each one (toward the back of the wing-like bones of the pelvis). The pubic tubercle, which is located extremely deep in the groyne at the bottom centre of the pelvis, is where the ligaments then flow in and down at an angle.
The inguinal ring and inguinal canal are located at the base of the inguinal ligament. The spermatic cord travels via these parts in males. The round ligament of the uterus goes through in females. The inguinal canal is a passageway for blood vessels and nerves in both sexes.
What’s the inguinal ligament made of?
The connective tissue that makes up the inguinal ligament contains collagen, a protein that holds tissue together. It also possesses relatively stretchable elastic fibres.
How can you tell if you have an inguinal hernia?
Sometimes, a piece of the intestine or fat can force into the inguinal area. The name for this is an inguinal hernia. A person can get a hernia if:
- They were born with a problem in their abdomen.
- Over time, straining or lifting heavy things makes the abdominal wall weak.
- Almost always, a person with an inguinal hernia has two signs:
- The groyne area has a lump or a bulge.
- Having pain in the groyne, especially when lifting, bending, coughing, or straining.
Inguinal Ligament Functions
The inguinal ligament serves several crucial functions:
- Anchor the oblique, abdominal, and pelvic muscles.
- Provide flexibility to the hips.
- Assist the soft tissues of the groyne.
- Facilitate the passage of nerves and blood vessels from the groyne to the legs.
Inguinal Ligament Conditions and Disorders
- Sportsmans Groin: Sportsman's groyne is a kind of inguinal hernia induced by groyne strain or trauma.
- Inguinal pain: Inguinal pain is uneasiness or pain located in the inguinal area.
- Round ligament leiomyoma: Round ligament leiomyoma is a type of benign tumor that can occur in the inguinal region.
- Inguinal Solitary Fibrous Tumor: An inguinal solitary fibrous tumour is a benign tumour type.
- Inguinal canal angioleiomyoma: Inguinal canal angioleiomyoma is a benign tumour that may develop in the vicinity of the inguinal canal.
- Liposarcoma in the Inguinal Canal: Liposarcoma in the inguinal canal is a form of cancer that can happen in the inguinal area.
- Swollen lymph nodes in the groyne: Swollen lymph nodes in the groyne can be a sign of an infection or another health problem.
Inguinal Ligament Tests
- Physical examination: A doctor will typically perform a physical examination to assess the function and movement of the inguinal ligament and surrounding structures. This may involve testing the strength and flexibility of the ligament, and observing any abnormalities in the groin area.
- Imaging tests: Detailed pictures of the inguinal ligament and neighbouring tissues may be obtained by imaging techniques like ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging. Inguinal hernias, ligament rips or ruptures, and other issues may all be diagnosed with the use of these examinations.
- Electromyography (EMG): An electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure for gauging muscle contractions and electrical activity. To identify nerve injury or muscular weakness, for example, which would have an effect on the inguinal ligament and adjacent muscles, this test may be performed.
- Studies of nerve conduction: Examining the velocity and amplitude of nerve impulses is the goal of nerve conduction research. Conditions, such as nerve entrapment or injury, that impact the nerves that innervate the inguinal ligament may be diagnosed using these examinations.
Inguinal Ligament Treatments
Disorders of the inguinal ligament may be treated in a variety of ways, with the approach used being determined by the underlying reason(s) for the problem. There are certain instances in which therapy may not be required since the symptoms might go away on their own. In other instances, therapy can be required in order to get to the root of the issue and improve the symptoms at the same time. Inguinal ligament problems have a variety of potential therapies, including the following:
- Relaxation: Providing the afflicted region with enough relaxation time might assist to decrease inflammation and promote healing of the ligament. This could include avoiding activities that are painful or uncomfortable, as well as making use of crutches or other supportive equipment, if necessary.
- Ice: Putting ice on the injured region may help decrease swelling and alleviate some of the pain associated with it. This may be accomplished by applying ice or a cold pack to the groyne area for a period of fifteen to twenty minutes at a time, many times per day.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy may enhance inguinal ligament strength and flexibility. This may include stretching and strengthening exercises and heat or cold treatment.
- Standard laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: Standard laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair is a surgical procedure that is used to repair a hernia in the inguinal area. This type of hernia occurs when a weakness in the abdominal wall allows a part of the intestine or other abdominal contents to protrude through the opening.
- Herniorrhaphy: Herniorrhaphy is a surgical procedure that involves repairing the hernia by sewing the weakened area of the abdominal wall back together.
- Hernioplasty: Hernioplasty is a similar procedure that involves using a mesh or other prosthetic material to reinforce the abdominal wall and prevent the hernia from recurring.
- Bilateral inguinal lymphadenectomy: Bilateral inguinal lymphadenectomy is the removal of lymph nodes from both sides of the inguinal area. This may be done during a laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair in order to check for the presence of cancer or other abnormalities in the lymph nodes.
Inguinal Ligament Medicines
- Steroids for reducing inflammation of Inguinal Ligament: Medications called steroids are often used to lessen inflammation. Steroids may be utilised in the case of the inguinal ligament to assist lessen edoema and irritation there. Prednisone and dexamethasone are a few of examples of steroids that can be used to lessen inguinal ligament irritation.
- Analgesics for pain in Inguinal Ligament: Drugs called analgesics are used to treat pain. Analgesics may be utilised in the setting of the inguinal ligament to assist control any pain or discomfort connected with the disease. Acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, are a few examples of analgesic treatments that may be helpful for discomfort in the inguinal ligament.
- Muscle relaxants for stiffness in Inguinal Ligament: The term 'electronic commerce' refers to the sale of goods and services through the internet. Muscle relaxants may be required to help decrease stiffness and increase mobility and flexibility in the aspect of the inguinal ligament. Cyclobenzaprine and carisoprodol are two muscle relaxants that may be effective for inguinal ligament stiffness.
- Antibiotics for infection in Inguinal Ligament: Antibiotics are drugs which are used to treat illnesses caused by bacteria. In the case of the inguinal ligament, antibiotics can be employed to manage any bacterial infections that may be producing or contributing to the problem. Penicillin, amoxicillin, and streptomycin are among drugs that may be effective for inguinal ligament infection.
How can I prevent inguinal hernia?
Although not all inguinal hernias may be avoided, you can reduce your risk by doing the following:
- Exercise on a regular basis without placing too much pressure on your groyne. Aerobics, mild weightlifting, and yoga are a few examples.
- Maintain abdominal strength with core activities such as crunches.
- Uphold a healthy weight.
Avoid some exercises that place additional stress on the abdominal wall and pelvic floor:
- Extremely strenuous workout.
- Performing jumping exercises.
- Extremely heavy lifting
- Squats.
Inguinal hernias may result from straining to defecate. Constipation and straining can be prevented by consuming large quantities of water and indulging in frequent physical activity.
When should I seek medical attention?
Because an inguinal hernia may have significant complications, you should consult a doctor if you develop any of the following symptoms:
- A bump or protrusion in the region of the groyne.
- Having discomfort in the groyne, particularly while lifting, bending, straining, or coughing.
Table of content
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors