Jaw (Human Anatomy): Image, Function, Diseases, and Treatments
Last Updated: Feb 25, 2023
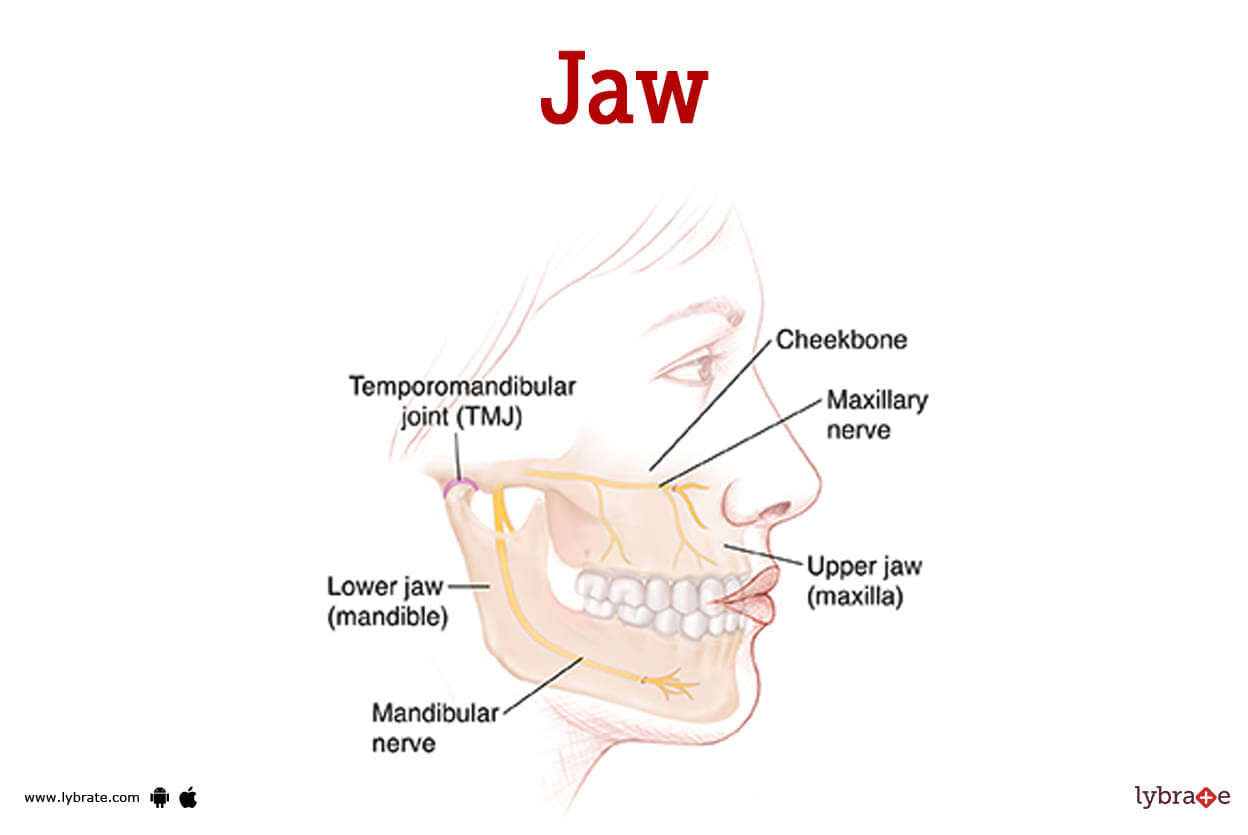
Jaw Image
Jaw, one of the two bones that form the framework of the mouth in vertebrates, the mandible and the maxilla; the mandible is the lower jaw and the maxilla is the upper jaw. Biting, chewing, and manipulating food all require functional jaws that move in different directions.
The mandible is made up of a horizontal arch that houses blood vessels and nerves as well as holding the teeth. There are two slender, vertical pieces (rami) on either side of the head that articulate with the glenoid cavity of the temporal bone of the skull to produce hinge joints.
In addition, the rami is where the chewing muscles attach. Chins are a uniquely human trait, since the central front of the arch is expanded and buttressed to create one. Chins are lacking in great apes and other animals.
As a whole, the upper jaw is anchored to the nasal bones at the nose's bridge; the frontal, lacrimal, ethmoid, and zygomatic bones within the eye socket; the palatine and sphenoid bones in the roof of the mouth; and the zygomatic bone (cheekbone) at the side, with which it forms the anterior portion of the zygomatic arch. The upper teeth are housed in the arched lower part of the maxilla. The large maxillary sinus is located within the body of the bone.
Function of jaw
In conjunction with the maxilla, often known as the upper jaw, the mandible performs an important function that is both structural and defensive. Not only does this bone serve as the home for the lower set of teeth, but it is also the passageway for vital nerves and muscles that run through and emerge from the skull.
Chewing and speaking are both made possible by the movement of the mandible, which governs the opening and closing of the mouth. Movements such as speaking, yawning, and laughing are made possible by the four muscles that connect to the mandible. These muscles help facilitate movements both up and down, as well as side to side.
Jaw Problems Include
- Fractures (Broken Bones): An injury to the mandible, often known as the jawbone, is medically referred to as a mandibular fracture. Only the nose and the cheekbones break more frequently than this sort of face fracture, but it's still rather common. The largest and most important bone in the lower jaw is the mandible, which is formed like a U.
- Dislocations of Jaw Bone: The term 'jaw dislocation' refers to a condition in which the lower portion of the jaw moves out of its typical position. In most cases, the healing process is successful, although it may result in complications in the future. If your jaw has become dislocated, you should seek medical attention as soon as you can. Under no circumstances should you attempt to realign a dislocation all by yourself.
- Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction: Your jawbone is connected to your skull by a joint called the temporomandibular (tem-puh-roe-man-DIB-u-lur) joint (TMJ). This joint functions like a sliding hinge. You have a joint on either side of your jaw. Both sides have joints. Pain can be caused in your jaw joint as well as in the muscles that control jaw movement if you suffer from TMJ problems, which are a kind of temporomandibular disorder (TMD).
- Osteonecrosis: Osteonecrosis of the jaw is a condition that results in a portion of the jawbone not being covered by the gums. This results in a condition that is difficult to heal. In order to be classified as ONJ, the condition must last for more than eight weeks. This joint functions like a sliding hinge. You have a joint on either side of your jaw. Both sides have joints.
- Cancers: Cancer of the jaw is a relatively uncommon form of head and neck cancer and just one of many different kinds of oral cancer. According to the American Society for Clinical Oncology, the various cancers that affect the head and neck account for approximately 4 percent of all cancers diagnosed in the United States. Head and neck malignancies frequently metastasis to the floor of the mouth, the tongue, the tonsils, the salivary glands, or the palate. This is the most common cause of jaw cancer.
- Ameloblastoma: Ameloblastoma is a rare form of tumour that begins in the jaw, most frequently in the area that is close to your molars or wisdom teeth. It is composed of the cells that contribute to the formation of the enamel that covers and protects your teeth. The tumour may cause you to experience pain or swelling, and it may also alter the appearance of your face. It is possible that, if left untreated for an extended period of time, it will develop into cancer and spread to your lymph nodes or lungs.
- Primary Intraosseous Carcinoma: Primary intraosseous carcinoma is an extremely uncommon kind of squamous cell cancer that originates in the bone.
- Sclerosing Odontogenic Carcinoma: Sclerosing odontogenic carcinoma is an extremely uncommon kind of primary intraosseous cancer that originates in the bone.
- Odontogenic Carcinoma: A rare form of odontogenic (originating in the tissues that create teeth) cancer, known as clear cell odontogenic carcinoma. An extremely uncommon kind of odontogenic epithelial cancer known as ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma
- Odontogenic Carcinosarcoma: an extremely rare odontogenic tumour.
- Odontogenic Sarcomas: Odontogenic sarcomas are defined as malignant tumours of connective tissue that incorporate epithelium.
- The Lower Jaw is positioned back too far: It may be challenging to bite when the lower jaw is positioned too far back (a condition known as retrognathia). It seems as though the chin is wasting away or shrinking.
- The Lower Jaw is positioned very far forward: When the lower jaw is too far forward, also known as prognathia, it causes the chin to stick out. It's possible for the lower teeth to protrude outward and overlap the upper teeth.
- Teeth don't meet (open bite): An excessively large upper jaw is frequently the cause of an open bite. Because of this, one may end up with a 'gummy smile. ' Possible causes for the challenge include a short lower jaw in the rear. An open bite may also be the result of habitually sucking on the thumb for an extended period of time or having an incorrect position of the tongue both at rest and when swallowing. If you have an open bite, it may be tough for you to close your lips.
- The Jaws are not even (asymmetry): Jaws that are uneven are either larger or smaller on one side compared to the other. It's also possible that one side is too far forward or back. It's possible the face seems crooked or off-center.
- Temporomandibular Joint And Muscle Disorder (TMD): According to a trusted source, TMDs are the leading cause of jaw pain and impact close to 10 million people in the United States. TMJ is another name that sometimes gets used to refer to TMD. Temporomandibular joints are the hinge joints located on either side of the jaw. Many distinct things can contribute to temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pain. It's also possible to get TMD for a number of different reasons all at once.
- Dental issues: If bacteria are allowed to accumulate on your teeth and gums, you run the risk of developing dental caries, periodontal disease, and dental abscesses. Especially if they are not treated in a timely manner, these illnesses might result in damage to other parts of your body in addition to your mouth. They might cause discomfort in the jaw as well as in the ears.
Test for Jaw
- Panoramic Dental X-ray: A very low dose of ionising radiation is all that is required for a panoramic dental x-ray to capture an image of the patient's entire mouth at once. It is something that dentists and oral surgeons do on a regular basis in the course of their work and it is something that can be used to plan treatment for dentures, braces, extractions, and implants.
- CBCT Scans: CBCT scans, which stand for cone beam computed tomography, take thousands of pictures of a patient's teeth, jaws, facial bones, and sinuses. Once the photographs are assembled, a complete 3D picture may be seen. Dental CT scans provide your doctor with a more in-depth look at your facial anatomy than traditional x-rays can.
- MRI scans: To examine the soft tissues located in and around the jaw joints, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be utilised in certain circumstances. These photos demonstrate the location of the disc, the inflammation, and the potential for jaw locking. Your healthcare professional can use this information to determine whether or not the disc in your TMJ is working normally and is in good shape.
- CT scan: A CT scan, also known as a computerised tomography scan, is when multiple X-rays are obtained from a variety of positions and then pieced together to show more specific information about the jaw.
Jaw Treatment
- Use of Oral Appliances: Night guards are worn solely while sleeping, whereas splints are worn 24 hours a day. Your healthcare provider should be able to decide the kind of oral appliance that best fits your needs.
- Remedial Dental Treatments: Undergo remedial dental treatments. These procedures involve the replacement of missing teeth as well as the utilisation of crowns, bridges, or braces in order to bring your bite into normal alignment and balance.
- Avoid Excessive Jaw Movements: Reduce the amount of time you spend yawning and chewing. Do not rest your chin on your hand, and do not hold the telephone with your shoulder and ear in close proximity to one another. Maintaining proper posture can help alleviate pain in the neck and face.
- Chemotherapy for Jaw: Carboplatin and 5-FU are a combination that is frequently utilised. When it comes to reducing the size of oral cavity and oropharynx tumours, this combination therapy is more effective than using each medicine on its own. Cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, and docetaxel are one another combination that is frequently utilised. Occasionally, chemotherapy is used in addition to a targeted drug or immunotherapy.
- Radiotherapy for Jaw: The blood flow to the jawbone can be negatively impacted by radiotherapy, which can lead to the death of tissue within the jawbone in some cases. This condition is referred to as osteoradionecrosis. The vast majority of individuals who undergo radiotherapy will never be diagnosed with osteoradionecrosis (ORN). It's important to note that there are several potential danger factors.
- Maxillary Osteotomy: The upper jaw is the area that is operated on during this procedure, which is performed to treat open bites or cross bites. The teeth and upper jaw need to be brought forward to match the lower jaw and teeth.
- Mandibular Osteotomy: Overbite and a jutting lower jaw are only two of the many dental problems that may be fixed with this operation. For a forward or backward shift of the lower jaw, your surgeon will make incisions in the rear of your mouth.
- Bimaxillary Osteotomy: The procedure known as bimaxillary osteotomy is surgery that is performed on both the patient's upper and lower jaws. When a disease affects both jaws, this procedure may be necessary.
- Genioplasty: A genioplasty can correct issues such as a weak or misshapen chin. By making a cut in the front of the jaw where the chin bone is located, the jaw and chin can be reconstructed.
- Jaw Wiring: Wiring the jaw is done either to position the jaw in a certain spot or to give support in the event that the jaw is fractured or broken.
- Arthrocentesis: To do arthrocentesis, tiny needles are used to inject fluid into the TMJ, making it a less invasive operation. The term arthrocentesis describes this method in further detail. This may assist to lubricate the joint and wash away any leftover debris or inflammatory byproducts in the area.
- Arthroscopy: Cannulas are very small tubes that are placed into joints as part of the arthroscopy procedure. The surgeon will next perform the operation on the joint utilising a thin scope known as an arthroscope and small instruments.
Jaw Medicine
- Botox Injections: Injections of Botox for cosmetic purposes are an example of a more intrusive treatment procedure. Botox's botulinum toxin can be injected into the jaw muscles to keep them from clenching, which could reduce TMJ-related jaw discomfort. These injections will have an effect that lasts for several months at a time and may require more treatment at a later period.
- Treatment options for Fungal Infections: It includes applying an antifungal cream to the affected area or taking an antifungal pill orally. A fungal infection close to the jaw can be treated with a variety of antifungal medications, some of which include luliconazole, itraconazole, clotrimazole, fluconazole, and others.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections: It is often known as PRP, are used as a treatment for joint pain. Growth factors can be found in platelet-rich plasma (PRP).
- Dietary Supplements: Dietary supplements formulated to accelerate the growth of facial muscle . Through proper nutrition It is normal practice for doctors to provide nutritional supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin to their patients in order to alleviate their patients' discomfort and speed up the recuperation of their joints.
- Neuropathic Pain Treatment: It has been demonstrated that the anticonvulsant Pregabalin, which is used to treat neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia, can alleviate jaw pain .
- For Bone Mass Loss: The group of drugs known as bisphosphonates encompasses quite a few distinct classes of pharmaceuticals. With their assistance, the rate at which bone mass is lost can be halted or slowed, which results in bones that are stronger.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What causes hurting jaw?
What disease causes jaw pain?
How can I adjust my jaw myself?
What helps inflammation in the jaw?
What is the main cause of jaw pain?
When should I worry about my jaw?
How do you treat a jaw problem?
What are some diseases of the jaw?
Can jaw pain heal itself?
Table of content
Find Dentist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors