Abdomen (Human Anatomy) - Image, Definition, Function, Diseases and More
Last Updated: Apr 08, 2023
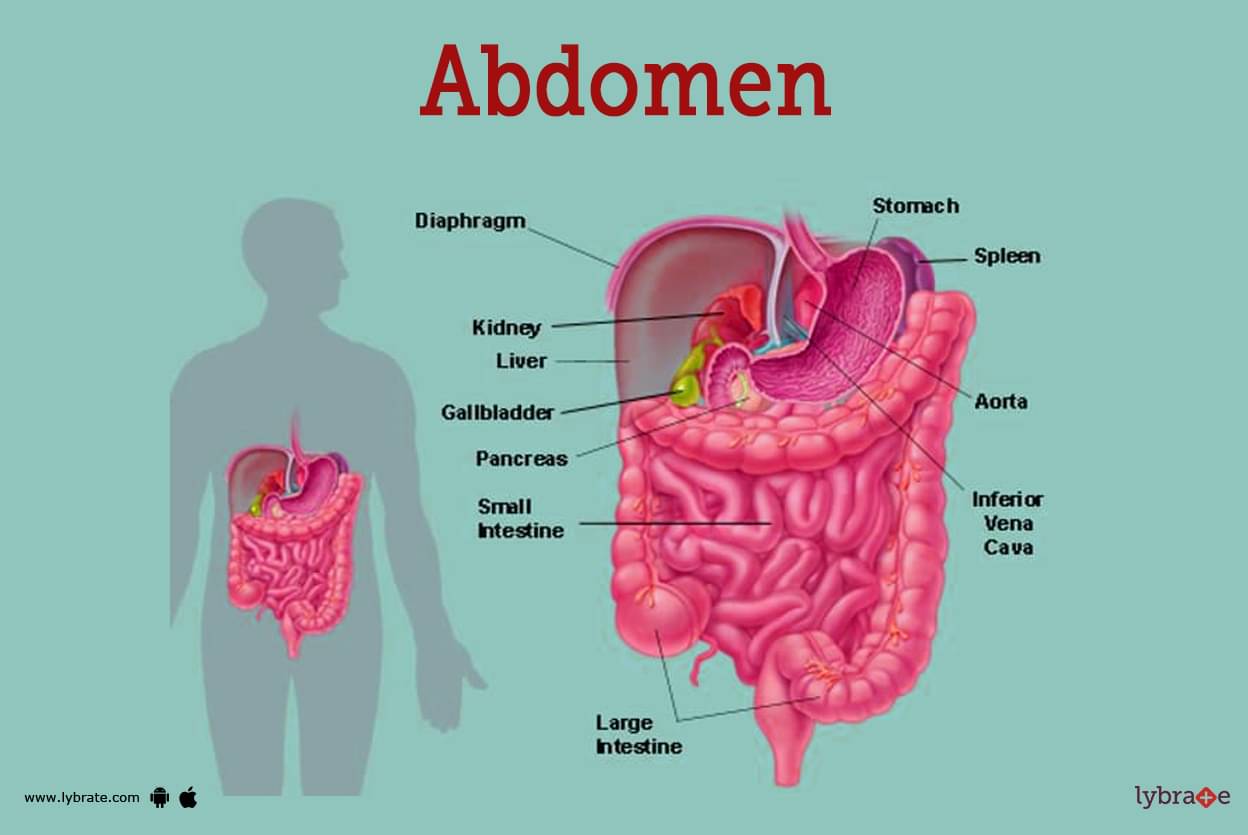
Abdomen Image
- The region between the thorax and pelvis is the Abdomen (which is also known as the belly). The upper surface of the abdomen is formed by the diaphragm. The abdomen ends at the level of pelvis bones. From this level, the pelvic region starts.
- The digestive organs such as stomach, small intestine, pancreas, liver and gallbladder are found in the Abdomen.The mesentery holds together these organs loosely in such a way that it allows them to expand and to slide against each other. The paired kidney and spleen are also found in the abdomen.
- Various crucial blood vessels such as aorta, inferior vena cava (IVC), and their numerous branches pass through the abdomen. A thin, tough layer of the tissue known as the fascia, helps in the protection of the abdomen anteriorly.
- The abdominal muscles and skin are found anterior to the fascia. The back muscles and spine are found in the posterior region of the abdomen.
Abdomen Functions
Following are the main functions of the abdomen in the human body:-
- Digestion: The stomach plays a key role in the process of digestion, breaking down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body. The small intestine, pancreas, and liver also play important roles in digestion, producing enzymes and other substances that help to break down food and absorb nutrients.
- Absorption of nutrients: The small intestine is responsible for absorbing most of the nutrients from the food we eat. These nutrients are then transported to the liver, where they are processed and used by the body.
- Waste elimination: The large intestine is responsible for removing waste products from the body. It absorbs water and electrolytes from undigested food material and forms solid stools, which are eliminated through the rectum and anus.
- Production of hormones and enzymes: The pancreas produces hormones, such as insulin, which regulate blood sugar levels, and enzymes that help to digest food. The liver also produces enzymes and hormones, as well as bile, which helps to digest fats.
- Protection of organs: The abdominal muscles help to protect the organs within the abdomen and provide stability and support to the spine.
- Regulation of body temperature: The liver helps to regulate body temperature by releasing heat through the blood vessels in the skin.
- Storage of nutrients: The liver stores nutrients, such as glucose, which can be released into the bloodstream as needed. The pancreas also stores hormones, such as insulin, which are released into the bloodstream as needed.
The abdomen is made up of several organs, including the liver, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, and spleen, as well as the abdominal muscles. These organs and muscles work together to perform a number of important functions in the body, and each organ's functions are given below:-
- Accessory Digestive Organs: The pancreas, liver, and gallbladder are the digestive organs. To promote digestion, these organs produce hormones (such as insulin), digestive enzymes, and bile through narrow tubes called ducts. The pancreas is an endocrine organ that helps the body break down food by producing digestive hormones and enzymes. Behind the stomach is where you'll find the pancreas.
- Liver: The liver, which is found in the right upper abdominal quadrant, produces the bile that aids in the digestion of lipids. In addition to producing hormones and regulating glycogen storage, the liver also plays a role in cleansing the blood. The gallbladder stores bile until it can be discharged into the small intestine from the liver. Located in the abdominal cavity, the gallbladder is to the right of the liver's right lobe.
- Spleen: The spleen is an active filtration organ that removes dead red blood cells and serves as a secondary lymphoid tissue. The spleen stores and recycles old RBCs, and it also metabolises the haemoglobin they contain. The left upper abdominal quadrant is where you'll find your spleen.
- Urinary System: The kidneys, ureters, and urinary bladder make up the urinary system, which is in charge of filtering blood and passing along waste products to the bladder for elimination. Some researchers classify these organs as pelvic even though they are positioned outside the peritoneum. In particular, the kidneys remove waste items from the blood, manage blood pressure, and maintain an appropriate blood pH. Urine is drained from the kidneys via the ureters and into the bladder. The function of the urinary bladder is to collect urine for later release through urination.
- Abdomen Processes: Digestion, respiration, posture, and balance, and mobility are all major responsibilities of the abdominal region. The activities of the key organs found in the abdominal cavity—which are linked to digestion have been outlined above. The abdominal area is also vital for breathing thanks to the respiratory system's auxiliary muscles. Muscles in this group are also responsible for things like maintaining posture, moving around, maintaining balance, coughing, urinating, vomiting, singing, giving birth, and defecating.
Abdominal Conditions
Peritonitis: The inflammation of the peritoneum (lining of the inner abdominal wall, which covers abdominal structures) is termed as peritonitis. It causes rigidity of the abdominal wall and severe pain. The peritonitis mainly occurs as a result of ruptured or infected abdominal structures or organs.
- Acute Abdomen: It is one of the medical conditions, where peritonitis or other emergency conditions may be present. In case of the acute abdomen, surgery is probably required.
- Appendicitis: In this disorder, the inflammation of the appendix at the region of the lower, right colon occurs. The surgery must be done for removal of such type of appendix with inflammation.
- Cholecystitis: In this disease, the inflammation of the gallbladder occurs, which results in the severe right side abdominal pain.It occurs due to the obstruction or blockage of the duct exiting the gallbladder by the gallstone.
- Dyspepsia: In this disorder, discomfort in the upper abdominal region occurs. It is also known as indigestion. It can also lead to the development of serious medical conditions from the benign symptoms.
- Constipation: In this type of the abdominal disorder, the bowel movement is less frequent (less than 3 bowel movements per week).
- Gastritis: In this type of the abdominal disorder, the inflammation of the lining of the stomach occurs, due to which symptoms such as nausea and pain occur. The alcohol intake, NSAIDs, H. pylori infection or some other factors can lead to gastritis.
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: The peptic term refers to the acid and the ulcers refers to open sores or erosions. The peptic ulcer disease occurs in the inner lining of the stomach or the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). The H. pylori infection or use of NSAIDs such as ibuprofen can lead to the peptic ulcer disease.
- Intestinal Obstruction: In this type of disorder, the blockage or obstruction of any particular region of the small intestine or large intestine occurs. Due to this, the digested materials passage through the intestine becomes difficult. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, vomiting etc.
- Gastroparesis: It is a medical condition, in which gastric emptying is delayed due to damage to nerves. Symptoms include nausea, heartburn, vomiting etc.
- Pancreatitis: In this type of disorder, the inflammation of the pancreas occurs. The most common aetiology for pancreatitis are alcohol intake and gallstones. Other aetiology includes drugs intake, trauma etc.
- Hepatitis: In this type of disorder, the inflammation of the liver occurs. The chronic alcohol intake, toxins, immune system or some medications can lead to hepatitis.
- Cirrhosis: In this type of disorder, the scarring or fibrosis of the liver due to chronic liver inflammation occurs.The most common cause of the cirrhosis are chronic alcohol intake and chronic hepatitis.
- Ascites: In this type of disorder, the abdominal swelling occurs due to accumulation of fluid in the abdomen. It is generally caused by cirrhosis.
- Abdominal Hernia: In this type of abdominal disorder, the protrusion of the intestine through the gap in the abdominal wall occurs.
- Abdominal Distention: In this type of disorder, the abnormal swelling of abdomen outwards occurs, due to bloating from gas.
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: In this disorder, the bulging or swelling in the aorta occurs. It can be caused due to atherosclerosis, infection in aorta, trauma etc.This disorder is life- threatening if it bursts due to enough enlargement of aorta.
Abdomen Tests
- Physical Examination: Through listening by stethoscope, palpation and percussion helps in the diagnosis of different types of abdominal diseases.
- Upper Endoscopy (Esophagogastroduodenoscopy or EGD): It is one of the diagnostic procedure, in which upper part of the digestive system (upto duodenum) is visualised and examined by inserting a endoscope (flexible tube with a camera at an end) through mouth.
- Lower Endoscopy (Colonoscopy Or Sigmoidoscopy): In this method, the endoscope is inserted through anus into the whole or entire colon. It is used to visualise and examine the mucous lining of the lower Gastrointestinal tract. It helps in detection of problems such as rectal bleeding, cancer etc.
- Abdominal X-ray: An X-ray of the abdomen is used to visualise and examine the abdominal organs and medical conditions such as intestinal perforation or obstruction.
- Computed Tomography (CT Scan): A CT scanner employs X-rays and a computer to produce images related to the abdomen and its structures. This technique assists in the analysis of the abdominal conditions e.g., appendicitis and cancer.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI Scan): It is a medical imaging technique or technology. This method employs computer generated radio waves in a magnetic field, to produce detailed images of the abdominal structures, such as liver, gallbladder and pancreas etc.
- Abdominal Ultrasound: It is a non- invasive procedure, which is employed to analyse abdominal organs or structures.It employs transmission and reflection of the ultrasound waves to visualise and detect problems in the abdominal structures e.g., gallbladder, kidneys and liver.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): It is one of the diagnostic techniques, which is used to diagnose and treat medical conditions in the abdominal structures such as liver, pancreas and gallbladder etc.
In this method, an endoscope progresses to the intestine, a tube is kept into the pancreatic duct and a fluid which obstructs X-rays is ejected into the tubes which supplies to the abdominal structures such as the gallbladder, liver, and pancreas etc.
- pH Testing: By employing a tube across the nose or inserting a capsule into the oesophagus, monitoring of the acidic levels of the oesophagus is done. It is used to diagnose GERD (Gastrointestinal reflux disease) or effectivity of treatment of Gastrointestinal tract.
- Upper GI Series (with small bowel follow-through): It is an X- ray examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract.It is a diagnostic procedure, in which x- rays of stomach and oesophagus is obtained after barium swallowing, to diagnose medical conditions such as ulcers or other diseases.
- Gastric Emptying Study: It is a scan, which helps in assessing the ability of the emptying stomach, by labelling a radioactive substance with solid food and visualising it's movement on the scanner.
- Biopsy: It is a medical diagnostic test, in which a small sample piece of tissue is taken and tested in the laboratory, which is used to diagnose medical conditions such as cancer, liver or other medical problems etc.
Abdomen Treatments
- Abdominal Surgery: Surgery is required in the case of serious abdominal conditions like cholecystitis, appendicitis, cancer of the colon or stomach etc.
- Pyloromyotomy: For the treatment of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, a longitudinal incision is made through the anterior wall of the pyloric canal all the way to the level of the submucosa..
- Sengstaken-Blakemore (SB) Tube: Surgery can be laparoscopic or keyhole surgery (numerous small incisions with the aid of a camera) or open surgery or a typical surgery (done by making one large incision).
- Endoscopy: The problems such as the rectal bleeding or cancer can be treated by tools on the endoscope.
- Ascitic Tapping: Patients with cirrhosis and severe liver disease frequently have paracentesis performed on them.In this procedure, a needle can be put it through skin to remove fluid from the abdomen when acute ascites, a swelling in the abdomen brought on by liver failure, causes discomfort.
- Gastric Ligation: Surgical ligation of bleeding vessels or wedge resection of stomach containing the arteriole.
- Gastropexy: Patients diagnosed with a big esophageal hiatal hernia are often candidates for the surgical therapy.. in which detorsion followed by fixation of the stomach is done.
- Flatus Tube: it is used for relieving the gaseous increase in stomach because of various infections and acid secretion
- Colonoscopic Detorsion: it is a therapeutic procedure for relieving the volvulus formation in the stomach.
- Endoscopic Banding Or Injection Sclerotherapy: In endoscopic sclerotherapy (EST), a sclerosant is injected directly into a varicose vein to cause thrombosis and obliteration of the vein.
- Balloon Tamponade: The double-lumen catheter of this tamponade balloon makes it possible to both inflate it with saline and drain blood from the liver. In order to stop variceal bleeding, balloon tamponade is only used sometimes today.
- TIPSS(Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Stent Shunting): TIPS, or transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, is a procedure in which the portal vein is connected to the hepatic vein under imaging guidance.
- Open Cholecystectomy: Surgery in which the gallbladder is removed via an open incision in the abdomen is known as an open gallbladder removal.
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Through four tiny incisions and the use of a camera, a cholecystectomy can be performed laparoscopically, earning it the name 'minimally invasive cholecystectomy.'
- Lobectomy: it is a procedure in which a portion of the liver, or the entire liver, is surgically removed. It is commonly used in cancer therapy.
Abdomen Medicines
- Histamine (H2) blockers: The histamine enhances secretions of the stomach acid; blocking histamine decreases secretions of acid production and GERD symptoms etc.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors: These are responsible for the direct inhibition of the acid pumps in the stomach. It is taken daily to make it effective against stomach acidity problems. Though, some side-effects are reported by taking proton pump inhibitors for several months.
- Chloride Channel Activator: Lubiprostone is part of the clinical category known as chloride channel activators. This is accomplished by boosting the amount of fluid that is already present in your intestines, which, in turn, makes it easier for faeces to go through your digestive tract.
- Anti-Diarrheal Agent: Loperamide is also used for chronic or recurrent diarrhoea caused by bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, or short bowel syndrome. This kind of diarrhoea may linger for weeks or months. Additionally, cholestyramine is used.
- Prebiotics: In the therapeutic treatment, they are used to boost the activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which allows for a more stable pH level in the gut to be maintained as required.
- Probiotics: They are beneficial to the ecosystem of the gut and provide beneficial microorganisms such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics, in combination with other treatments, may be used to treat an infection caused by H. pylori. During treatment, the antibiotics are given to the stomach in an effort to heal the damage caused by the infection. Antiparasitic drugs: In the treatment of parasites, some examples include metronidazole, praziquantel, and albendazole. In the treatment of bacterial infections, some examples include azithromycin, ciprofloxacin, and tetracycline.
- Antiviral Medications: A number of antiviral drugs, such as entecavir, tenofovir , lamivudine , adefovir , and telbivudine, can aid in the fight against the virus and lessen its ability to harm your liver.Hepatic Rejuvenation Medicine: including n-acetyl cysteine, trypsin, and vitamin K, are used as adjuvant therapy for the treatment of a wide range of hepatocellular diseases.
- Diuretics: Conditions other than edema that lead to fluid retention are also treated with these drugs, including cirrhosis and hypertension. Numerous medical professionals prescribe diuretics such aldactone, bumetanide, torsemide, hydrochlorothiazide, furosemide, and metolazone.
- Chemotherapeutic Drugs: Chemotherapy and radiation are effective treatments for liver cancer, despite the disease's untreatable nature. In extreme cases, the liver may be removed surgically or replaced with a donor organ.
- Statins: This class of drugs is known as lipid-lowering medicines, and it has other beneficial properties for slowing the development of acute or chronic liver disease, such as lowering oxidative stress and inflammation. Rosuvastatin, atorvastatin, etc., are all instances of statins.
- Corticosteroids: Drugs with anti-inflammatory properties work by preventing the recruitment of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) to areas of cellular and tissue injury, hence reducing inflammation. Methylprednisolone is an example of an effective corticosteroid.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What organs make up abdomen?
Is abdomen and stomach the same?
What is the lower abdomen called?
What is the reason of pain in lower abdomen?
How to reduce lower abdomen fat?
What is usg abdomen test?
Table of content
Find Gastroenterologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors