Achilles Tendon (Human Anatomy): Picture, Definition, Injuries, Pain, and More
Last Updated: Feb 25, 2023
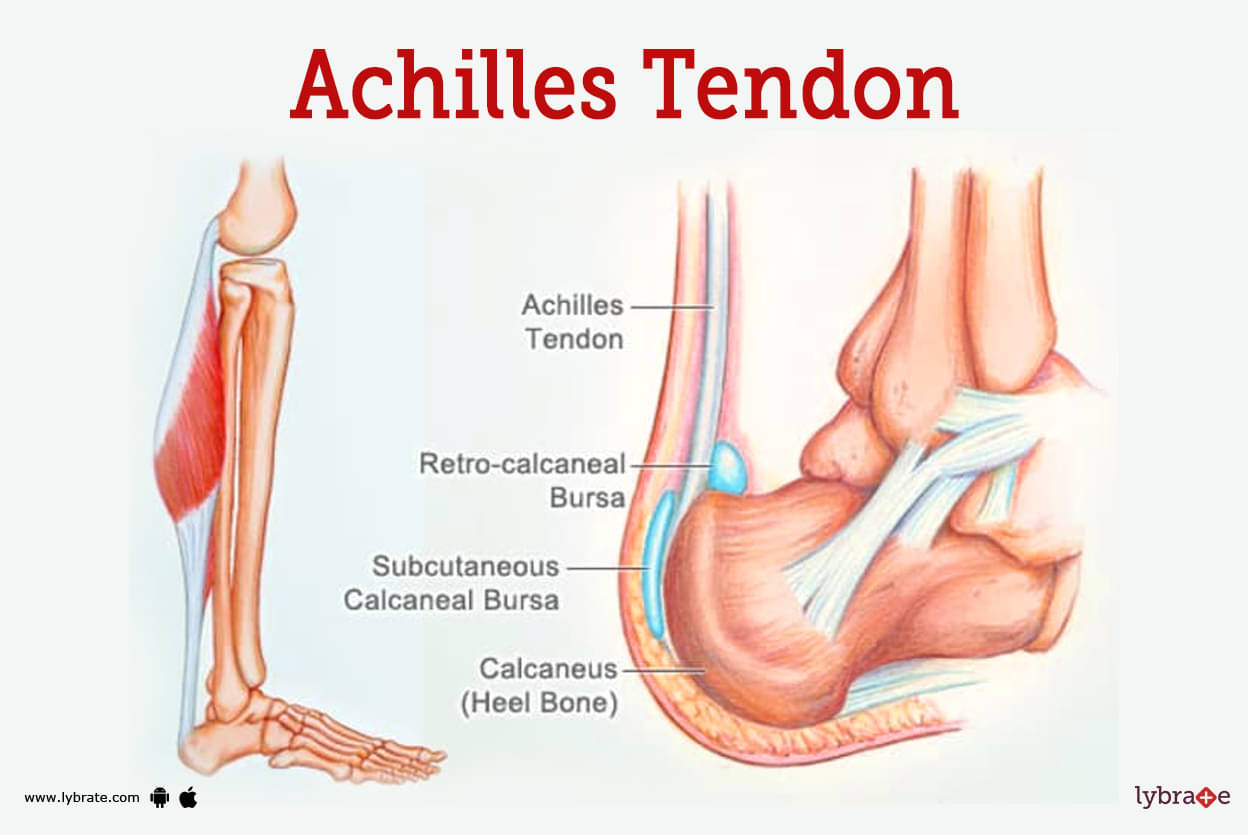
Achilles Tendon Image
The Achilles tendon, also known as the calcaneal tendon, is located in the centre of the back of the calf and runs all the way down to the heel. It does this by attaching the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles in the back of your lower leg to the heel bone in your foot. Your calf muscles are located in the rear of your lower leg. A strong band of fibrous tissue makes up this structure.
When the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, which are both considered to be calf muscles, merge together to form one band of tissue, this band eventually develops into the Achilles tendon at the bottom of the calf. The calcaneus is the next stop on its journey. The Achilles tendon at the heel is cushioned by bursae, which are small sacs filled with fluid.
This tendon is the biggest and most powerful of all of the body's tendons. When we walk, run, or jump, we are able to stand on our toes thanks to a movement that occurs when the calf muscles contract, which pushes on the Achilles tendon at the back of the heel. In addition to this, the Achilles tendon has poor resilience to damage since it only receives a restricted blood supply and is subjected to severe stresses. This is because of the high tensions that are imposed on it.
Functions of achilles tendon
Its main functions include:
- Plantar flexion: The Achilles tendon is the primary muscle responsible for plantar flexion of the foot. Plantar flexion refers to the movement of pointing the toes downward and is essential for activities such as walking, running, and jumping.
- Force transmission: The Achilles tendon transmits the force generated by the calf muscles to the heel bone, allowing for movement of the foot and ankle.
- Shock absorption: The Achilles tendon helps to absorb the impact of walking, running, and other activities, helping to protect the bones, joints, and muscles of the lower leg.
- Balance and posture: The Achilles tendon also helps with your balance and posture, as well as providing stability to the ankle and foot when standing, walking, or running.
- Maintaining proper Arch: Achilles Tendon also plays a crucial role in maintaining the arch of your foot which helps in providing better stability and balance.
Achilles Tendon Conditions
- Achilles tendon tear: A tear in the Achilles tendon may be very little, known as a microtear, or it can be very significant and cause significant pain. Pain, swelling, and restricted mobility are some of the symptoms that are present. It might happen all of a sudden when you are doing something, or it can come on gradually over time.
- Achilles tendon rupture: The Achilles tendon rupturing in its entirety is the root cause of the Achilles tendon rupture. It is possible for it to generate a popping sound while it is being moved. Pain and swelling in the lower leg are two of the symptoms that might be detected. Surgery, long-term immobilisation, or complete rest with no movement of the ankle are the treatment options for this rupture.
- Achilles tendinosis: This was once known as tendonitis. Sudden actions such as jogging or walking may produce an inflammation of the end of the Achilles tendon, which can lead to Achilles tendinosis. It was discovered that the patient was suffering from symptoms such as pain and stiffness in the back of the heel. It is possible that the healing process might be sped up by taking it easy for a few weeks, using cold packs, and stretching.
- Achilles peritendinitis: Achilles peritendinitis is a kind of the inflammatory illness known as paratendinitis. Paratendinitis may be caused by conditions such as seronegative arthritis, infection, or injuries caused by repeated motion or overuse.
- Achilles tendinitis: when Comparable to Achilles tendonosis, with the exception that the pain originates in the tissue surrounding the tendon and is caused by the tendon's overuse. Additionally, the discomfort is located at least 2 inches beyond the level of the heel.
- Achilles tendinosis (formerly tendonitis): Achilles tendinosis is a condition in which the Achilles tendon gradually thickens as a result of age or misuse. In addition to its thickness, the tendon is also weakening, making it more prone to more damage or even rupture.
- Achilles tendinopathy: The condition of having tendinitis or tendinosis that affects the Achilles tendon is referred to as Achilles tendinopathy.
- Achilles or heel (calcaneal) bursitis: Bursitis of the Achilles tendon or the heel (calcaneal) bursa occurs when the fluid-filled sac that cushions the Achilles tendon at the heel becomes inflamed. The constant use of shoes with a low profile may irritate the bursa, which in turn can cause discomfort in the back of the heel. The fact that it is made worse by wearing shoes is the most typical symptom.
Achilles Tendon Tests
- Physical examination for tendonitis: To look for Achilles tendon problems, an examiner checks for pain, swelling, warmth, thickening, or discoloration around the heel and leg. A knot on the back of the leg may be present with Achilles tendon rupture. Most cases of tendinopathy without a rupture can be diagnosed by physical exam and often do not need further testing.
- Thompson test for Achilles tendon rupture: Lying prone (on one’s stomach) or while kneeling on a chair, an examiner squeezes the calf. The end of the foot should move down in response; if it does not, an Achilles tendon rupture may be present.
- Knee flexion (Matles) test for Achilles tendon rupture: A person lies face down and bends the knee slowly to a right angle. During this movement, the toe end of the foot should point away from the leg slightly; if it doesn't, an Achilles tendon rupture may be present.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI scan) for tendonitis and osteomyelitis: An MRI scanner uses a high-powered magnet and a computer to create highly detailed images of the ankle and leg. An MRI scan is the best test to diagnose an Achilles tendon rupture or other problems but it may not always detect tendinopathy.
- Computed tomography (CT scan) for tendon rupture: A CT scanner takes multiple X-rays, and a computer constructs detailed images of the ankle and leg. An MRI scan is superior to a CT scan in diagnosing Achilles tendon problems.
- X-ray film for tendon rupture: A plain X-ray film may identify problems with the bones or ankle joint, but it cannot diagnose Achilles tendon problems.
- SERUM calcium test for tendon rupture: A calcium blood test measures the amount of calcium in your blood. If there is too much or too little calcium in the blood, it may be a sign of a wide range of medical conditions, such as bone disease, thyroid disease, parathyroid disorders, kidney disease, and other conditions.
- Serum Urea and creatinine: They are useful in determining the nitrogenous compounds that are the final result of metabolism. Urea is the major metabolite that is formed from the turnover of protein in tissue and in the body's food. It accumulates in the bone in the form of crystals and reduces bone mineral density.
- Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibody for osteomyelitis and myostitis of tendon: Despite the fact that the levels can be high in other rheumatologic disorders linked with inflammatory arthritis, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, the levels are generally elevated in rheumatoid arthritis.
- RA factor for rheumatoid arthitis of tendon: The presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) can be determined using a blood test. The immune system creates an autoantibody called rheumatoid factor. Autoantibodies like RF target healthy cells and tissues rather than their intended targets, such as germs and viruses.
- CRP LEVELS for arthiritis: Higher levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), an inflammatory marker, are associated with increased fracture risk, although previous studies on CRP and bone mineral density (BMD) have yielded conflicting results.
- SERUM VIT D3 for bursitis: To ensure adequate levels for optimal health, a blood test can determine the concentration of vitamin D in your system. Strong bones and teeth can only be maintained with enough vitamin D. In addition to its health benefits, regular exercise helps maintain your muscles, nerves, and immune system functioning regularly.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI scan) for tendonitis and osteomyelitis7: The most common and accurate way is with a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan. DEXA uses low-dose x-rays.
- Bone mineral density (BMD): IT IS A test measures how much calcium and other types of minerals are in an area of your bone. This test helps your health care provider.
Achilles Tendon Treatments
- RICE therapy: Most Achilles tendon injuries can be treated with RICE: Rest, Ice, Compression with a sports bandage, and Elevation.
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter medicines like acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen (Motrin), and naproxen (Aleve) can lessen the pain of most Achilles tendon problems. For more severe pain, prescription pain relievers may be necessary.
- Heat: Alternating ice and heat therapy may improve the pain of bursitis near the Achilles tendon.
- Footwear: Wearing shoes with good support that are right for your feet may help avoid continual injury to the Achilles tendon. Custom-made orthotics, heel lifts, and certain splints and braces are sometimes helpful.
- Physical Therapy: Although modifying or decreasing activity is important, particular stretches and exercises may be helpful to rehabilitate tendon problems, especially when they are persistent.
- Immobilization: Many moderate to severe Achilles tendon conditions require immobilization of the ankle joint. This may require wearing a special boot or a leg cast for several weeks.
- Achilles tendon surgery: Surgery can often reattach a ruptured Achilles tendon. Following surgery, immobilization of the ankle is necessary for several weeks.
Achilles tendon Medicines
- NSAIDs: As well as being used to treat aches and pains in other parts of the body, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) are a family of medication that are used to address discomfort in the knee. Feverish conditions can also be brought under control with its application within the human body. Examples of usual drugs that fit within this group are ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen sodium. Naproxen Indomethacin with ibuprofen Ketorolac Diclofenac Meloxicam Celecoxib.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): Platelet-rich plasma, often known as PRP, is a mixture of several growth factors that is injected into a joint, most commonly the knee. This not only assists in reducing inflammation but also has a positive impact on the healing process of injured tissue. Platelet-rich plasma, also known as PRP, is a mixture of several different growth factors. Osteoarthritis, according to some reports, is another condition that can benefit from PRP treatment.
- DMARDs: DMARDs are medications that affect the course of disease and are used to treat rheumatic conditions. Patients who are suffering from autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis are often prescribed this class of drug in order to alleviate the pain that they are experiencing. Methotrexate, adalimumab, baricitinib, and tofacitinib are some of the disease-modifying antirheumatic medicines (DMARDs) that are now available on the market. Sulfasalazine
- Nutritional supplements: Physicians provide nutritional supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin to decrease the pain of person and boosten the healing process in joints.Vitamin D and Calcium supplements are given as per age and deficiency of the requred elements for normal bone growth and metabolism.
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs): they are a class of drug used to treat depression, OCD, bedwetting, migraines, tension headaches, and multiple pain disorders for example Amitriptyline
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI): they are drugs placed in class of antidepressants that help treat depression, anxiety etc Milnacipran/Duloxetine
- Pregabalin: it is an anticonvulsant used to treat neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. It's also used to treat partial onset seizures when taken with other seizure.
- Cortisone injections: When treating some types of ankle arthritis, cortisone injected into the ankle joint might be helpful. The inflammation in the ankle joint may be reduced and the associated pain alleviated with the use of cortisone.
- Bisphosphonates: They belong to a class of drugs that can either stop or decrease the process of bone loss, making for stronger bones. Inhibiting osteoclasts, which are responsible for the removal and reabsorption of minerals such as calcium from bone, is the primary function of bisphosphonates (the process is known as bone resorption). zoledronic acid. Both alendronate and risedronate were used.
- Hyperuricemia treatment drugs: Allopurinol, which inhibits xanthine oxidase, Febuxostat, which inhibits xanthine oxidase, Probenecid, which inhibits tubular resorption of uric acid in PCT Pegloticase, and Rasburicase, which is a Recombinant uricase that catalyses uric acid to water soluble, are all effective medications for the treatment of Gout as well as Tumor
- Antibiotics for tendonitis of Achilles tendon: Antibiotics are a type of drug that is used to treat bacterial disorders that affect the tendon, such as tendonitis. One of the most common conditions that antibiotics are used to treat is cellulitis.
- Corticosteroids: Patients who suffer from specific kinds of myositis and tendonitis that could be present in the calf muscle and ankle muscles may be given prescriptions for cortisone-like medications such as prednisone, betamethasone, and dexamethasone, as well as other pharmaceuticals that are comparable to cortisone.
- Antiviral medicine for viral infections of tendons: Amantadine, rimantadine, zanamivir, oseltamivir, ribavirin, acyclovir, ganciclovir, and foscarnet are just some of the medications that belong to this class that are frequently prescribed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are 2 signs of Achilles tendonitis?
Does Achilles tendon heal on its own?
How do you know if you have damaged your Achilles tendon?
How do I get my Achilles tendon to stop hurting?
Can I walk if I tore my Achilles tendon?
What is the fastest way to heal Achilles tendonitis?
What are 3 ways an Achilles tendon can be injured?
How long does an Achilles tendon take to heal?
Table of content
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors