Angioplasty: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 04, 2023
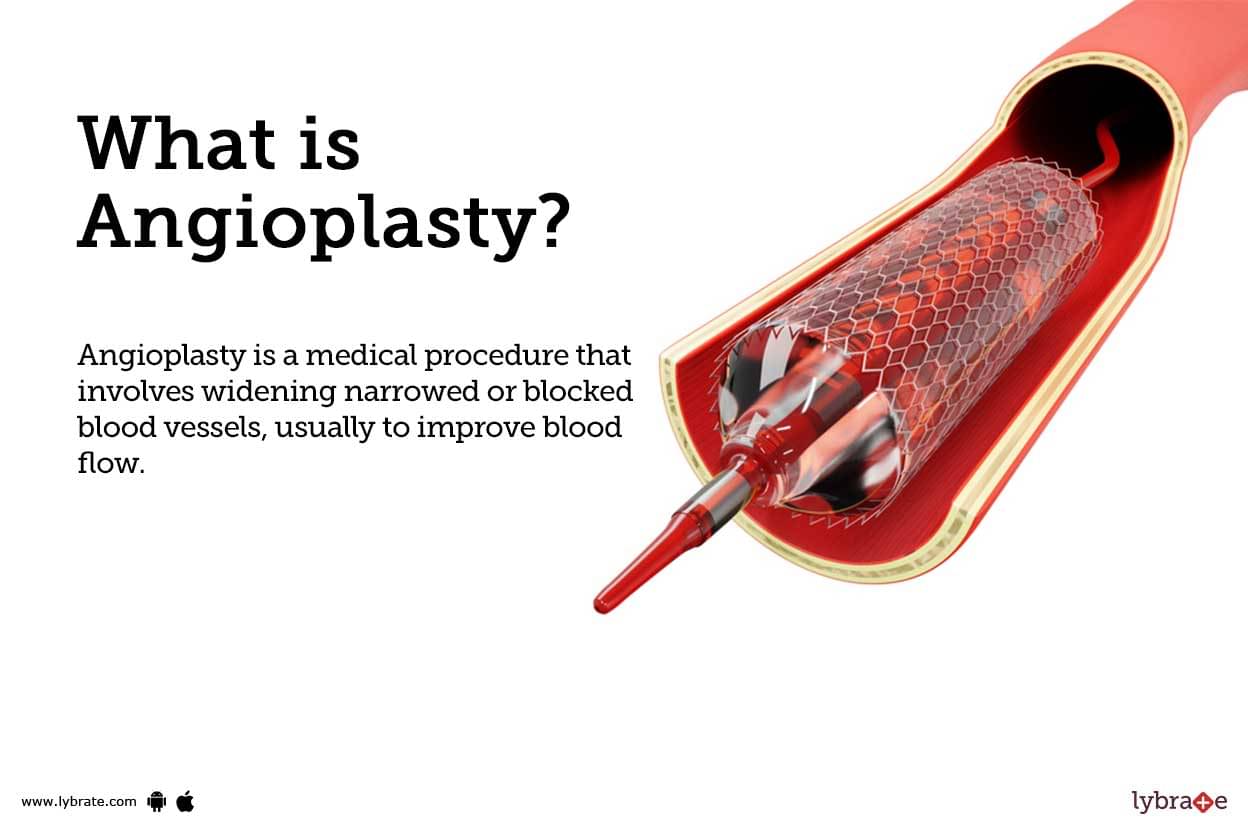
What is Angioplasty?
Angioplasty is a medical procedure that involves widening narrowed or blocked blood vessels, usually to improve blood flow. It is typically done using a balloon-tipped catheter inserted through the skin and guided to the site of narrowing or blockage.
Types of Angioplasty:
- Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty (PTCA): This is the most frequent form of angioplasty. A balloon-tipped catheter is inserted into an artery in the groyne or arm and into a blocked coronary artery during this surgery. The balloon is then inflated to expand the artery, improving blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Atherectomy: This type of angioplasty uses a device inserted through an artery in the groyne or arm and into a blocked coronary artery. The device then shaves away plaque buildup from within the vessel, which helps restore normal blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Brachytherapy: In this procedure, a radioactive source is placed directly into plaque buildup within narrowed arteries using a thin tube called a catheter. The radiation helps break down hardened plaque, allowing for better blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Stent Placement: This type of angioplasty involves placing metal mesh tubes (stents) within narrowed arteries to help prop them open and improve blood flow to the heart muscle.
Benefits of Angioplasty
The benefits of angioplasty are many, including:
- Lower risk than traditional surgery: Traditional open heart surgery requires anaesthesia, a longer hospital stay and more recovery time. Angioplasty is far less invasive and can be done with local anaesthesia with minimal recovery time.
- Quick relief: Angioplasty provides immediate relief of symptoms associated with blocked arteries such as chest pain or shortness of breath.
- Reduced long-term risk: Blocked arteries can cause serious problems in the long run such as heart attack or stroke; angioplasty can help reduce these risks by restoring normal blood flow in the affected area and increasing overall health and wellbeing.
- Improved quality of life: People who undergo angioplasty often report an improved quality of life due to increased energy levels, improved sleep patterns, and better overall physical functioning after treatment compared to before it was performed.
Why is Angioplasty done?
- Angioplasty is a medical procedure used to open blocked or narrowed blood vessels that supply blood to the heart.
- It is typically done when a person has coronary artery disease, which is caused by plaque buildup in the arteries that can lead to chest pain, heart attack, and other cardiovascular problems.
- It may also be used to treat other conditions such as peripheral arterial disease and carotid artery disease.
What are the risks of Angioplasty?
The most common risks associated with angioplasty include-
- Bleeding: Bleeding can occur at the site where the catheter was inserted during the procedure, as well as in other areas of the body.
- Infection: Infection is a risk with any invasive medical procedure and angioplasty is no exception.
- Heart Attack: Although rare, there is a risk of having a heart attack during or shortly after the angioplasty procedure due to plaque rupture or blockage of an artery.
- Stroke: As with heart attacks, strokes are also a possible complication of angioplasty due to plaque rupture or occlusion of an artery.
- Restenosis: Restenosis occurs when the artery that was opened during angioplasty becomes narrowed again due to scarring or further buildup of plaque. This may require additional procedures to correct.
How do I prepare for Angioplasty?
- It is critical to follow your doctor's instructions and take any prescription drugs as indicated in order to prepare for angioplasty.
- Certain medicines, such as aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and blood thinners such as warfarin, may need to be stopped prior to the treatment.
- It is also critical to inform your doctor if you have any allergies or other medical issues that might interfere with the treatment.
- In the days leading up to your angioplasty, you should drink plenty of fluids and avoid caffeine, alcohol, and smoking.
- You should also dress comfortably in clothing that will allow easy access for medical staff during the procedure.
- On the day of your angioplasty, be sure to arrive at least an hour early so you can complete paperwork and any necessary tests or screenings before the procedure begins.
- It is recommended that you bring a friend or family member with you for support throughout the process.
How is Angioplasty done?
- During an angioplasty, a cardiologist inserts a thin tube called a catheter through an artery in the arm, groyne, or neck and threads it up to the heart.
- The catheter's tip is then inflated with a tiny balloon to expand the artery and enhance blood flow.
- Once the balloon has been inflated, a stent (a tiny mesh tube) may be inserted into the artery to help keep it open.
- The treatment takes less than two hours and is performed under local anaesthetic.
- Afterward, you may need to stay in bed for several hours or overnight before returning home.
Before the procedure
- Your doctor will evaluate your medical history and do a physical assessment before the surgery to detect any potential dangers.
- Your doctor may also order blood tests, X-rays, or other imaging tests to get a better understanding of your condition.
- During this time, you should discuss with your doctor any questions or concerns you have regarding the surgery.
During the Procedure
- During angioplasty, you will be given either general anaesthesia or local anaesthesia depending on the severity of your condition and type of procedure being performed.
- Once you are sedated, a thin tube called a catheter is inserted into an artery in your arm or groyne area and guided through the arteries to reach the blocked artery in need of widening.
- The catheter is then inflated with a tiny balloon to open the blockage and restore appropriate blood flow through that artery.
- In rare circumstances, a stent may be used to maintain the artery open after it has been inflated.
After the Procedure
- After angioplasty is completed, you will be taken into recovery where vital signs such as heart rate and breathing will be monitored for several hours until they return to normal levels.
- You may experience some discomfort at the site where the catheter was inserted but this should go away within a few days after surgery.
How much does Angioplasty cost?
- The cost of an angioplasty procedure can vary greatly depending on the complexity of the procedure and the specific hospital or health care provider. Generally, angioplasty can range from 15,000 rs to 1,00,000 rs.
- Factors such as location and type of facility can also affect the cost.
- In addition to the procedure fees, there may be additional expenses for medications, follow-up visits, lab tests, and other related costs.
What to eat after Angioplasty?
- Following angioplasty, it is critical to have a balanced diet low in saturated fat, cholesterol, and salt.
- It is also critical to consume a variety of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, healthy grains, and low-fat dairy products.
- Consuming fish, almonds, and legumes can help lower your chance of getting heart disease.
- Furthermore, limiting sugary drinks and high-sodium meals might help keep your blood pressure under control.
Is Angioplasty safe?
- Angioplasty is a simple and successful surgery for opening restricted or obstructed blood arteries.
- Most angioplasty procedures are successful and complications are rare. However, as with any medical procedure, there is always some risk involved.
- Possible risks include bleeding, infection, stroke and heart attack.
Is Angioplasty painful?
- Angioplasty is usually painless, however patients may feel some discomfort during the surgery.
- After the procedure, patients may feel soreness in the chest and have some bruising near where the catheter was inserted.
- Most of this discomfort should resolve within a few days.
How long does it take to recover from Angioplasty?
- The recovery time following angioplasty can vary depending on the patient's health, the complexity of their procedure, and how well they follow their doctor's post-operative instructions.
- In general, most patients may return to normal activities within a few days to a few weeks.
- Some patients may take longer to recover depending on the severity of their condition or any other underlying medical issues that may have been present prior to the procedure.
What are the side effects of Angioplasty?
Like any invasive medical procedure, angioplasty carries a risk of side effects. These include-
- Bruising or bleeding at the site of catheter insertion.
- Swelling or pain at the location of catheter insertion.
- An allergic response to the anaesthesia or dye used during the treatment has occurred in rare situations.
- Damage to surrounding tissue from the ballooning process during angioplasty
- Blood clots forming in untreated areas of the artery.
- Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats) caused by trauma to a coronary artery during angioplasty.
- Heart attack if plaque breaks off and blocks an artery during angioplasty.
- Stroke if a clot breaks off and blocks an artery in your brain.
Angioplasty Aftercare:
After angioplasty, it is important to make lifestyle changes and follow your doctor's advice to reduce the risk of future blockages and improve overall health.
- Follow a healthy diet: A healthy diet can help lower cholesterol and blood pressure, both of which can reduce the risk of developing blocked or narrowed arteries.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help strengthen the heart muscles, lower cholesterol levels, lower blood pressure, improve circulation throughout the body and reduce stress levels. Every day, try to obtain at least 30 minutes of aerobic activity.
- Quit smoking: Smoking increases your risk for developing atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries). If you smoke, quitting is one of the best ways to reduce your risk for further blockages in your arteries or other cardiovascular health problems. Speak with your doctor about getting help quitting if you need it.
- Take prescribed medications: Your doctor may prescribe certain medications after angioplasty to help prevent new blockages from forming or existing ones from worsening over time. Be sure to take all medications as instructed by your doctor so that they are most effective in helping you manage any underlying conditions that may have caused your artery blockage in the first place (such as high cholesterol or diabetes).
- Follow-up with your doctor: It's important to keep all follow-up appointments scheduled with your cardiologist after angioplasty so they can monitor how well you're doing post-procedure and check for any potential complications that may occur down the line such as re-narrowing of an artery (restenosis).
Conclusion
Angioplasty is an effective treatment for blocked or narrowed arteries, and has been used successfully to treat heart disease and other circulatory disorders. It can also improve blood flow throughout the body, helping to reduce symptoms of a variety of ailments. Although there are certain dangers involved with angioplasty, the benefits vastly exceed the risks. With careful monitoring and follow-up care, angioplasty is a safe and effective option for many patients.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Cardiologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors