Aortic Dissection: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Mar 14, 2023
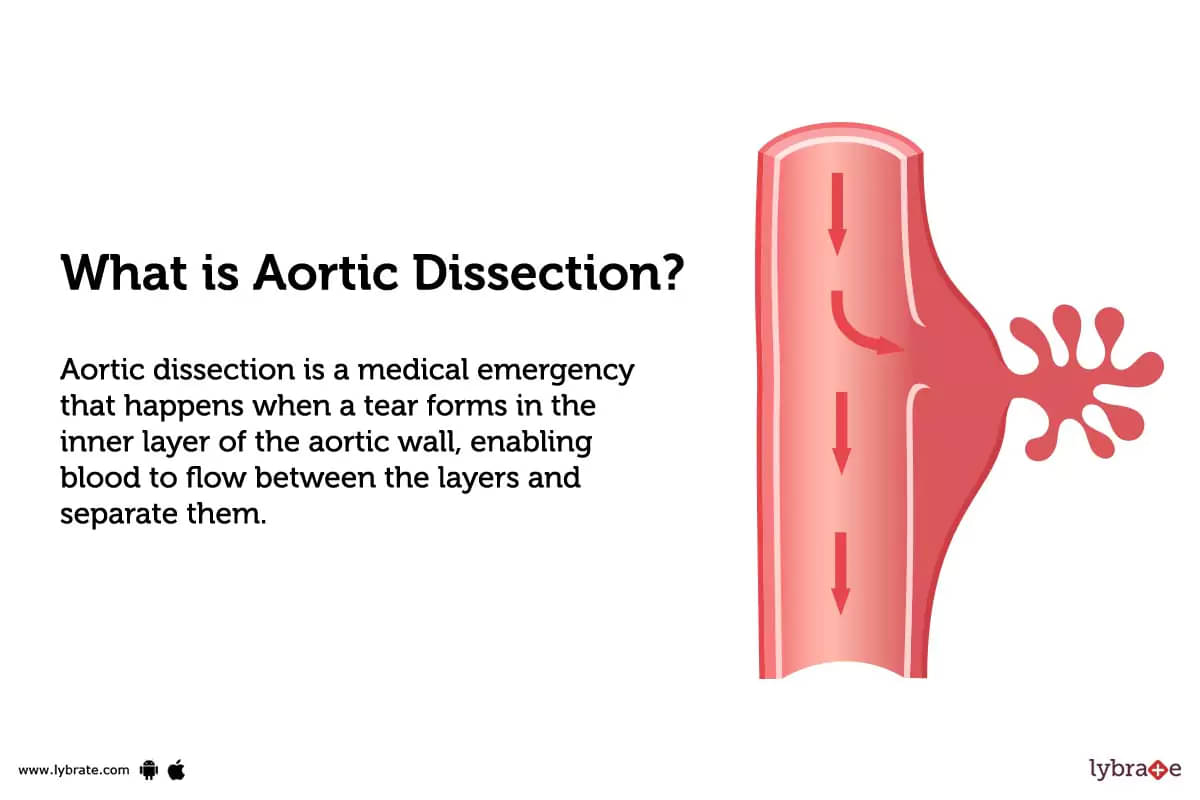
What is Aortic Dissection?
Aortic dissection is a medical emergency that happens when a tear forms in the inner layer of the aortic wall, enabling blood to flow between the layers and separate them.
Types of Aortic Dissection
There are two forms of aortic dissection: type A and type B.
- Type A: Type A aortic dissection involves the ascending aorta and is considered to be the most serious type. It is typically caused by an aneurysm or a tear in the inner wall of the aorta that can cause blood to flow between the layers of the vessel wall. This may cause a disturbance in blood flow and, if left untreated, can be fatal.
- Type B: Type B aortic dissection only involves the descending aorta and is less severe than type A. It is often caused by an injury or trauma to the chest or abdomen, such as after a car accident or fall, which can cause tears in the inner wall of the vessel and lead to disruption of blood flow.
What causes Aortic Dissection?
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled and long-term high blood pressure is one of the primary causes of aortic dissection.
- Connective tissue disorders: Abnormalities in connective tissues, tissues that support and bind organs together, such as Marfan syndrome or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome can lead to an aortic dissection.
- Genetic factors: Certain genetic factors like mutations in the genes which code for components of connective tissue can cause aortic annuloaortic ectasia (AAA).
- A blunt or penetrating injury: A forceful impact to the chest area can cause a tear in an already weakened wall of the aorta resulting in an aortic dissection.
- Medical procedures: Intense trauma during medical procedures such as thoracotomy or cardiac catheterization also increases risk of aortic dissection.
What are the symptoms of Aortic Dissection?
- Severe, sudden chest pain: Most people describe it as an intense, tearing, or ripping sensation that moves from the chest through the back.
- Back or abdominal pain: Often, the pain extends to one side of the back or abdomen.
- Dizziness or fainting
- Anxiety and sweating
- Having trouble breathing and a pounding heart.
- Loss of pulse in groyne or neck areas.
- Difficulty speaking/hoarseness of voice.
How can you prevent Aortic Dissection?
- Exercise regularly, maintaining a healthy weight.
- Avoid tobacco use or secondhand smoke exposure which can lead to damage of the aortic wall.
- Manage any existing conditions such as hypertension or Marfan Syndrome that may increase risk of aortic dissection.
- Ask the doctor about any high risk factors and whether certain medications are appropriate for you to prevent or reduce risk of aortic dissection occurrence.
Aortic Dissection - Diagnosis and Tests
- Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray can show the aortic dissection, or an enlargement of the aorta. It can also show any other existing conditions that could have caused the dissection, such as an aneurysm.
- CT scan: A computerised tomography (CT) scan is a three-dimensional image of the heart, lungs and blood vessels that can be used to diagnose aortic dissection. It can help identify any tears in the aorta or other abnormalities that may indicate aortic dissection.
- Echocardiogram (ECHO): An echocardiogram is a cardiac ultrasound that employs sound waves to provide pictures of the structure and function of the heart. It can help detect any abnormalities in the aorta that may indicate an aortic dissection.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI imaging creates comprehensive pictures of internal organs and structures, along with the heart and blood vessels, using magnetic fields and radio waves. It is used to diagnose aortic dissection by detecting any tears or abnormalities in the walls of the aorta, as well as any other existing conditions that could have contributed to it such as an aneurysm.
- Angiography: X-rays, MRI, ultrasound, and CT scans are all used in the medical imaging procedure known as angiography, which allows doctors to see the inside of blood vessels and other organs in the body. It mainly diagnoses and treats heart, brain, as well as other vital organ problems.
What are possible complications of Aortic Dissection?
- Hypotension
- Lung and abdominal organ ischemia.
- Arrhythmias (irregular heart beats).
- Heart failure and shock.
- Stroke or brain death
- Renal (kidney) failure
- Paralysis.
Home Remedies for Aortic Dissection
- Chew and drink a spoonful of garlic cloves, soaked overnight in honey or water.
- Make a paste of ginger, cumin seed and black pepper powder and apply on the affected area.
- Consume 1-2 tsp of castor oil daily with warm water or milk to ease symptoms such as chest pain, high blood pressure, and extreme fatigue.
- Drink coriander boiled in water to reduce inflammation caused by aortic dissection
- Prepare tea using holy basil leaves (tulsi) to reduce inflammation and treat chest pains connected with aortic dissection
- Drink a mixture of lemon juice, honey butter ghee and cinnamon powder mixed in warm water thrice a day for relief from deep chest pains due to aortic dissection.
What to eat in Aortic Dissection?
- It is important to eat a balanced diet which includes plenty of fruits and vegetables, lean proteins (fish, poultry, legumes, eggs), low-fat dairy products, and whole grain carbohydrates.
- Foods high in fibre such as oats, barley, lentils and beans can help lower cholesterol levels which may be beneficial for people with aortic dissection.
- Eating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids such as salmon, tuna, mackerel and sardines can help reduce inflammation in the body which may help reduce symptoms associated with aortic dissection.
- Drinking plenty of fluids throughout the day is also important for overall health and well-being when living with aortic dissection.
What not to eat in Aortic Dissection?
- Foods high in salt, such as processed and fast foods.
- Fatty and fried foods.
- High-cholesterol foods, such as red meat, full-fat dairy products, eggs, and some tropical oils.
- Caffeinated beverages
- Alcoholic beverages
- Foods that are highly acidic such as citrus fruits and juices.
Aortic Dissection Treatment
- Emergency surgery: To lessen the chance of potentially fatal consequences, surgery is required as quickly as possible to correct the aortic wall tear.
- Open surgery: During open heart surgery, a surgeon will make an incision in your chest, then remove the damaged part of your aorta and replace it with an artificial graft made of Dacron or other synthetic material.
- Endovascular grafting: A less invasive surgical treatment for aortic dissection. It involves placing an endovascular stent graft into the affected area via catheterization through small openings in your groyne or arm. The device stabilises and strengthens the wall of the aorta while allowing blood flow to continue normally through the artery.
- Thrombolytic therapy: This involves administration of thrombolytic drugs intravenously or intra arterially which breaks down clots and can improve blood flow in dissections involving major branches near the origin of dissection, such as celiac axis or superior mesenteric artery.
Which doctor to consult for Aortic Dissection?
Patients with aortic dissection should be seen by an experienced cardiothoracic surgeon or interventional cardiologist.
These specialists are typically found in larger university hospitals or specialised cardiac centres.
Which are the best medicines for Aortic Dissection?
- Beta-blockers: These drugs help reduce the risks of high blood pressure and improve the function of the aorta. Examples include atenolol, metoprolol, and propranolol.
- Vasodilators: These medications relax blood vessels, allowing more blood to flow through them and lessening the possibility of an aortic dissection. Examples include nitroglycerin and hydralazine.
- Antiplatelet agents: These drugs reduce clotting by preventing platelets from sticking together and forming clots in body vessels. Aortic dissection may be treated with antiplatelet medications like aspirin.
- Calcium channel blockers: These are used to lower the rate at which calcium is released into cells, thus reducing the risk of spasms in vascular muscles that can cause or worsen an aortic dissection. Verapamil is one commonly prescribed drug for this purpose.
- Statins: Statins inhibit cholesterol production in the liver and help to reduce inflammation associated with aortic dissection by blocking inflammation pathways in cells throughout the body. Examples include simvastatin, lovastatin, and pravastatin sodium (Pravachol).
How long does it take to recover from Aortic Dissection?
Patients may take several weeks to months to recover from an aortic dissection, with more serious cases taking even longer.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
The results of treatment for aortic dissection vary depending on the severity of the condition, patient’s age and overall health, and type of treatment received.
In general, non-surgical treatments typically provide more temporary relief while surgical interventions tend to offer longer lasting results.
Moreover, some lifestyle changes might need to be made in order to prevent further complications from arising in the future.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- After the treatment of an aortic dissection, it is important to watch for any signs of recurrent dissection or complications such as stroke and kidney damage.
- It is also important to control blood pressure and monitor for changes in heart rate or rhythm, or any other symptoms that may indicate an onset of an aortic dissection.
- Medications should be taken regularly to control blood pressure, especially if surgery was performed to correct the dissection.
- Patients should take lifestyle measures such as avoiding strenuous activity and maintaining a healthy weight in order to reduce the risk of recurrent dissections or cardiovascular issues due to high blood pressure or enlarged arteries from atherosclerosis.
- Regular follow-up appointments with doctors are recommended in order to track changes in health and address any concerns that may arise following treatment.
What is the cost of Aortic Dissection treatments in India?
Treatments for aortic dissection in India might vary significantly in price based on the kind of therapy and the facility.
The cost of surgery can range from ₹125,000 to ₹200,000 and the cost of an angioplasty can range from ₹100,000 to ₹150,000.
What are side-effects of Aortic Dissection treatments?
- Surgery: Possible side effects include heart attack, stroke, blood clots, infection, and even death.
- Thrombolytic drugs: Possible side effects can include bleeding, aneurysm formation, allergic reactions and increased risk of stroke.
- Medication: Common side-effects can include dizziness, headache, nausea and vomiting.
- Endovascular repair: Risks associated with endovascular repair are infection or kidney failure due to contrast dye used during the procedure as well as vascular injury or further dissection from catheter insertion or balloon inflation/deflation.
Aortic Dissection - Outlook/ Prognosis
Aortic dissection is a life threatening emergency that necessitates immediate medical attention since it may lead to serious problems such as arrhythmia, heart failure, Stroke, paralysis, the treatment for which can take anywhere from a few months to several years.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Cardiologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors