Appendix (Anatomy): Appendix Image, Location, Definition, Function, Conditions, Tests, and Treatments
Last Updated: Feb 25, 2023
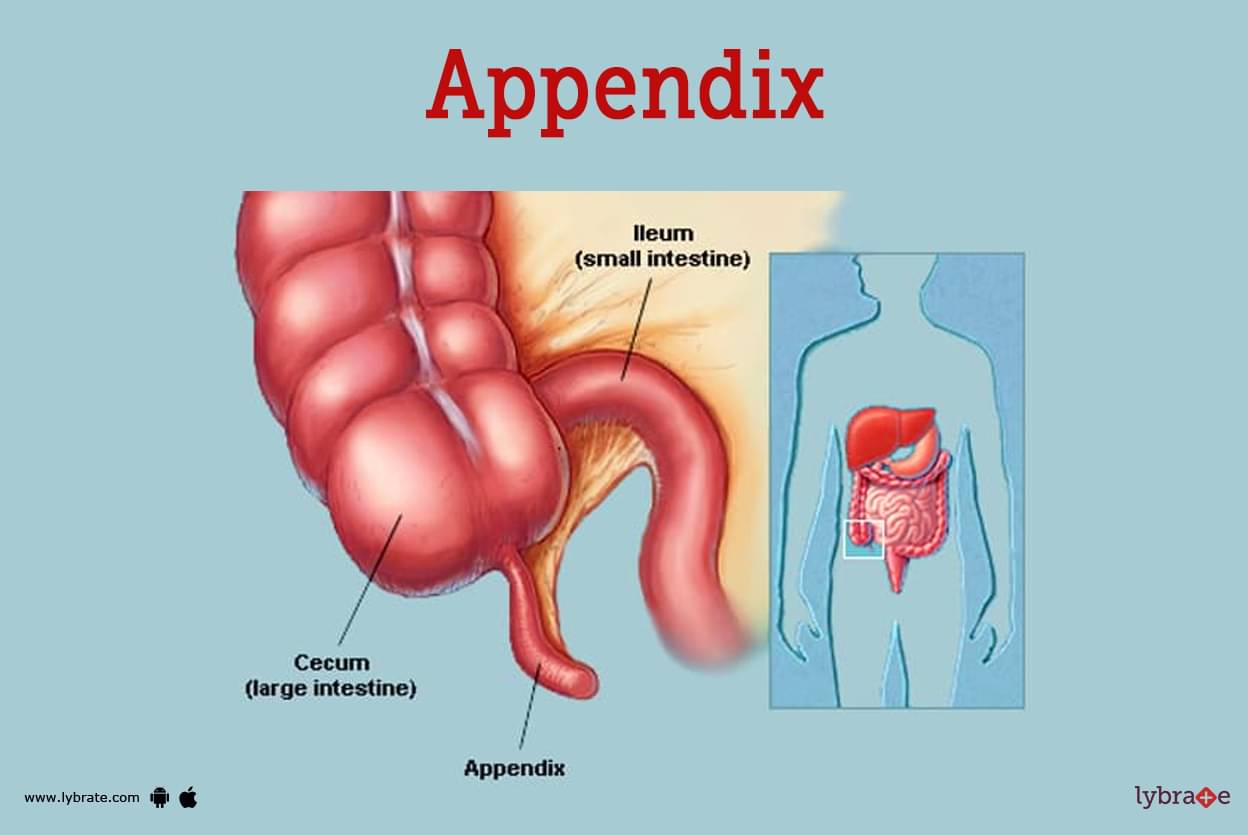
Appendix Image
The vermiform appendix is a diverticular structure that emerges from the caccum's posteromedial wall about 2 centimetres below its ileocaecal junction.
The length of the appendix varies between 2 and 20 centimetres (average 9 cm). The standard width is about 5 millimetres.
The angulated circular lumen in the appendix is small in comparison to the thickness of its wall. Starting from the inside and working out, the four layers that make up the appendix wall are the mucosa, submucosa, muscular layer, and serosa.Appendix has 3 parts i.e. base, body and tip.
The appendix can be located in the right iliac fossa of majority of people. The beginning of the appendix is always in the same location, but the rest of the organ can be in any one of the following places. These roles are frequently denoted by the hour hand that moves around the face of a clock.Intraluminal capacity of appendix is 0.1mL
Functions of Appendix
Its function is not fully understood, but several theories have been proposed:
- Immune function: The appendix may play a role in the immune system by harboring beneficial bacteria that can repopulate the large intestine after a bout of diarrhea.
- Evolutionary function: The appendix may have been important in the past for digesting tough plant matter, but it is no longer needed in humans.
Overall, the appendix is considered to be a non-essential organ and the body can function normally without it. One theory suggests that the appendix 'reboots' the digestive system after an illness that causes diarrhea by acting as a repository for healthy bacteria. This theory is supported by the observation that the appendix is present in most people who have diarrhea. It is possible to remove the appendix through surgical procedures with no discernible adverse effects on the patient's health.
Disorders of Appendix
- Appendicitis: Appendicitis is a condition in which the appendix frequently becomes inflamed and infected, and it even has the potential to rupture for reasons that are not fully understood. In addition to feeling sick to one's stomach and sick to their stomach, this causes excruciating pain in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen.
- Subhepatic appendix: - When the appendix is in this abnormal position, it is located in the right hypochondrium beneath the liver. This is considered to be an abnormal position for the appendix. It is a developmental aberration that takes place when the caecal bud fails to descend properly during embryogenesis. Both the caecum and the appendix originate from a caecal bud that develops after the arterial portion of the loop of the midgut.
- Tumors of the appendix: Carcinoid tumours of the appendix are the most common type of appendix tumour, and they are the cause of periodic flushing, wheezing, and diarrhoea. Carcinoid tumours of the appendix are responsible for these symptoms. Epithelial tumours in the appendix are growths that, depending on their severity and length of time, can either be benign or cancerous. Appendix cancers are extremely uncommon.
- Appendicular perforation: A perforation of the appendix can cause an obstruction of the small bowel, which is characterised by symptoms such as bile vomiting and constipation. In this situation their will be abdominal distension and ascites when it comes to chronic stage.
- Appendix Testis Torsion: - torsion of vestigial appendage joined with testis is occurred due to heavy lifting or strenuous work. In spite of the fact that it serves no purpose, more than half of all males are born with this appendage. Despite the fact that this condition does not pose any danger to one's health, it can be quite painful. In most cases, the only treatment that is required is one to manage the patient's pain.
- Acute appendicitis: - It is a very painful condition called acute appendicitis, which occurs when the appendix becomes inflamed and filled with pus. Additionally, a fever may be caused by the condition.Edematous & inflammed cascal wall of appendix: - It is a condition of appendix in which pain occurs in appendix and it leads to appendicitis.
- Inflammed bone in appendix: - It is a condition of appendix in which pain occurs in appendix and it leads to appendicitis due to bone present in appendix.
- Gangenous base of appendix: - Our conventional knowledge of the causes of gangrene and perforation of the appendix is that it takes place when the appendix lumen becomes obstructed, which results in increased transmural pressure, venous stasis, and arterial thrombosis, all of which lead to gangrene of the wall of the appendix. However, more recent research has shown that the mechanism of gangrene and perforation of the appendix may be different.
- Appendicuar lump: - An appendicular lump is one of the outcomes that can occur as a result of acute appendicitis, and it typically manifests itself on the third day after the inflammation has begun. This mass is caused by an inflamed appendix that is encircled by a greater omentum, bowel loops, and an edematous cecal wall and ileum. This configuration results in the formation of a lump. Within the right iliac fossa, there is a firm but tender mass that can be felt.
Appendix Tests
- Medical examination: above the right iliac spine or should we say of the right flank region acute or chronic pain in abdomen which can show tenderness or redness at the time of medical examination.
- Abdominal CT: A diagnostic imaging examination known as a computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis can be performed. A specialised x ray machines takes a 3d representation of the appendicular area and determines whether there is any anomaly present or not.
- FOBT: A faecal occult blood test, often known as a FOBT, examines a sample of your stool (poop) to determine whether or not it contains blood. Blood that is occult is blood that cannot be seen with the unaided human eye.
- Hydrogen breath test: This is a test to determine whether an individual is lactose, fructose, or sucrose intolerant. Glucose is a type of sugar that, if it is present in the small intestine, will be broken down by bacteria, which will result in the production of hydrogen or methane gas.
- Appendix biopsy: In the course of a colonoscopy, a sample of colon tissue may be extracted in order to be analysed further. Colon biopsies can assist in the diagnosis of colon cancer, as well as infections and inflammations.
- Psoas test in appendicitis: When the appendix is retrocecal, it rests on and irritates the right psoas major when it is inflamed (appendicitis). The involuntary extension of the right thigh causes a worsening of pain in the right iliac fossa in people with this illness.
- Obturator test in appendicitis: The obturator internus muscle might be aggravated by a spelvicly located appendix. Lower abdominal discomfort is brought on by the flexing and medial rotation of the right thigh onto the abdomen.
- Rovsing's sign: It is a clinical finding that suggests acute appendicitis (the inflammation and possible infection of the appendix).
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI Scan): It is a type of medical imaging technology. This approach uses computer-generated radio waves in a magnetic field to provide detailed pictures of abdominal tissues such as the liver, intestines, appendix, gallbladder, and pancreas, among others.
- Abdominal Ultrasound: It is a non-invasive treatment used to examine abdominal organs or tissues. It uses ultrasonic waves to visualise and diagnose issues in abdominal structures such as the small intestine, large intestine, and appendix.
- pH Testing: The acidity levels of the oesophagus are monitored using a tube across the nose or injecting a capsule into the oesophagus. It is used to determine the efficacy of treatment for GERD (Gastrointestinal reflux disease). as well as for appendicitis diagnosis
- Gastric Emptying Study: It is a scan that aids in determining the ability of the stomach to empty by labelling a radioactive chemical with solid food and seeing its movement on a scanner.
Appendix Treatment
- Hemicolectomy: A hemicolectomy is a form of surgery that removes a section of your large intestine known as your colon. Part of your colon can be removed without changing how it functions in your digestive system.
- Ochsner sherren regimen: The main premise is to admit, administer intravenous fluids and antibiotics, and continuously monitor for improvement or worsening of symptoms. The Ochsner-Sherren regimen is a treatment method for a patient who is suspected of progressing from acute appendicitis to the production of an inflammatory phlegmon.
- Laparoscopic appendectomy: Keyhole surgery (laparoscopy) for appendix removal usually results in speedier recovery than open surgery. An appendectomy is a surgical operation that removes the appendix through a succession of small incisions.
- Open appendectomy: A 2 to 4 inch long cut or incision is created in the bottom right side of your tummy or abdomen. The muscle splitting and retraction sequence is repeated with the fascia of both the internal oblique muscle and the transversus abdominis. It is also regarded as a more intrusive method for treating chronic appendicitis since a wound is made during surgery, increasing the likelihood of sepsis.
- IV fluid resuscitation: The basic objective of fluid resuscitation is to preserve organ perfusion (hemodynamics), as well as substrate concentrations (oxygen, electrolytes, among others).
Appendix Medicines
- Laxatives for treating bowel obstruction causing appendicitis: Constipation can be treated with medications in a variety of methods, including stimulating gut muscles and boosting the quantity of water absorbed by the body. Lubiprostone, a chloride channel activator that increases the quantity of fluid released by the digestive tract, is one example.
- Histamine (H2) blockers which prevents appendicitis: Histamine increases stomach acid release; inhibiting histamine lessens acid production and GERD symptoms, among other things. Cimetidine and Famotidine are a couple of examples. it protects against appendicitis
- Proton Pump Inhibitors for preventing appendicular lump: These are in charge of directly inhibiting the acid pumps in the stomach. Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Esomeprazole, and Dexlansoprazole are a few examples. When proton pump inhibitors are used for an extended length of time, several adverse effects develop. They also prevent digestive problems such as appendicitis and appendicular lmb.
- Anti-Diarrheal Agent for preventing appendicitis: Loperamide is also used to treat chronic or recurring diarrhoea caused by dumping syndrome, ulcerative colitis, or Crohn's disease, for which it is prescribed. This indirectly lessens the risk of appendicitis.
- Prebiotics for development of appendix flora: They are used in therapeutic treatment to increase the activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut, allowing a more constant pH level in the gut to be maintained as needed.
- Probiotics for redevelopment of appendix bacterial flora: They contribute healthy microbes to the ecology of the gastrointestinal tract, including as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, and are thus advantageous.
- Antibiotics for appendcitis: Prescribed to have a synergistic impact with other therapies, the cause of which may or may not be an infection caused by h. pylori. Antibiotics are administered directly into the stomach over the course of treatment in an effort to repair the tissue that has been compromised by the infection.
- Antiparasitic drugs for gut parasties: Albendazole, mebendazole, and praziquantel are three medications that are often used for the treatment of infections that are disseminated due to a parasitic origin. Azithromycin, ciprofloxacin, and tetracycline are a few examples of antibiotics that are commonly used in the treatment of bacterial infections.
- Antiviral Medications for appendicitis for viral infection: Several antiviral medications, including entecavir, tenofovir, lamivudine, adefovir, and telbivudine, are able to help in the battle against the virus and limit its capacity to damage your intestines. These antiviral treatments can also help in the fight against hepatitis C.
- Chemotherapeutic Drugs for appendicular carcinoma: In spite of the incurability of the illness, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are both viable therapeutic options for patients with intestinal cancer. In severe conditions, the intestines might need to be removed surgically or transplanted with organs from a donor.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are used to treat any possible infection that might be the root cause of the symptoms, even if a diagnosis has not yet been established. In most cases, antibiotics cannot effectively cure appendicitis when used on their own.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the symptoms of your appendix?
What exactly does the appendix do?
What are the 5 signs of appendicitis?
What causes appendix?
Can you get appendicitis from stress?
How do you check for appendix at home?
Can appendicitis go away on its own?
Table of content
Find General Surgeon near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors