Arterial Thrombosis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Mar 16, 2023
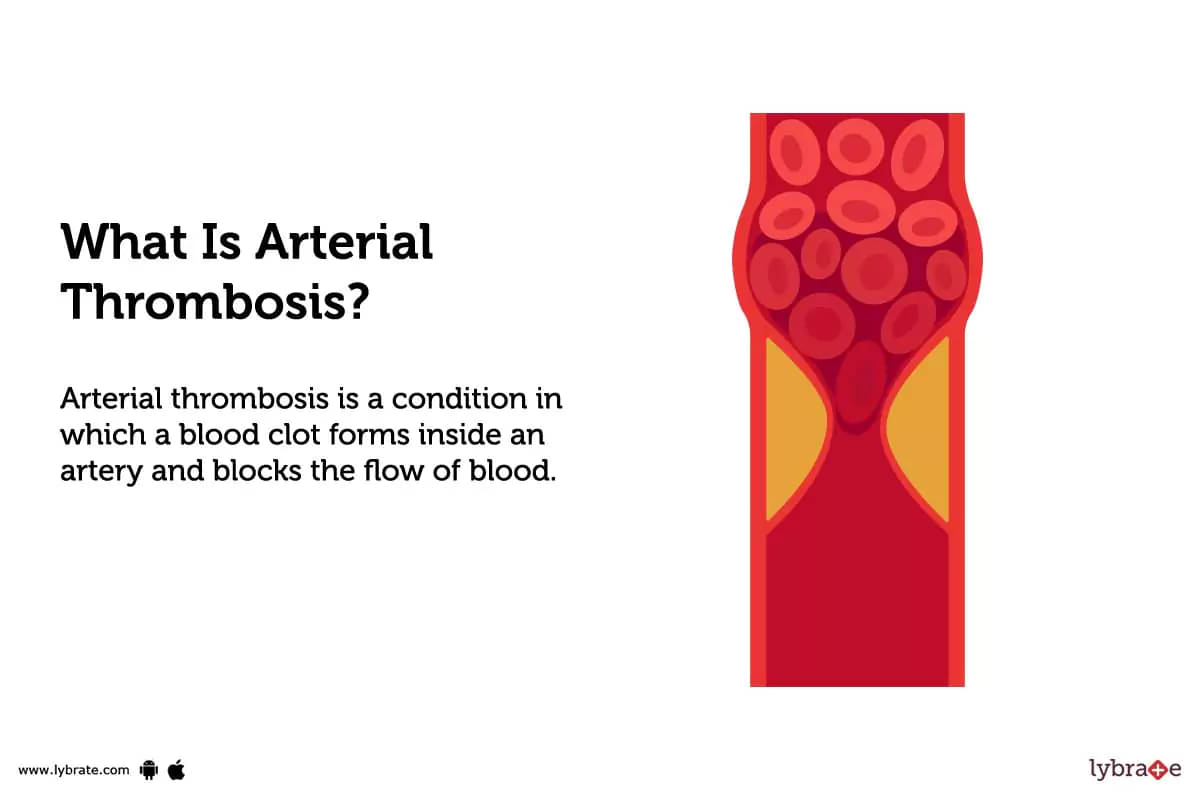
What is Arterial Thrombosis?
Arterial thrombosis is a condition in which a blood clot forms inside an artery and blocks the flow of blood.
The clot (also known as a thrombus) can form anywhere in the body, but usually appears in locations such as the legs, arms, heart, or brain.
Types of Arterial Thrombosis:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): This kind of arterial thrombosis is characterised by the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, often in the legs or thighs. It may cause pain, swelling, and discomfort in the afflicted region, in addition to a higher risk of pulmonary embolism if the clot travels to the lungs.
- Mesenteric Artery Thrombosis: This is a type of arterial thrombosis which occurs when a blood clot forms in one of the mesenteric arteries that supply oxygen-rich blood to the digestive organs, such as the stomach and intestines. Symptoms can include abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhoea, and weight loss.
- Carotid Artery Thrombosis: This is a type of arterial thrombosis which occurs when a blood clot forms in one of the major arteries leading to the brain - the carotid arteries - blocking off oxygen-rich blood from reaching the brain. Symptoms can include stroke-like symptoms such as sudden numbness or weakness on one side of your body, sudden confusion or trouble speaking, difficulty walking or maintaining balance, and vision loss in one eye.
What causes Arterial Thrombosis?
- Arterial thrombosis is caused by a blood clot that blocks an artery (a major blood vessel) and impedes the flow of oxygen-rich blood to organs and tissues.
- It most often occurs when cholesterol-rich plaque builds up in an artery, narrows it, and damages its inner wall which can eventually lead to a clot forming.
- Other causes include trauma or injury to an artery, disturbances in the natural clotting process such as with certain medications that thin the blood, or use of certain intravenous drugs such as heroin can cause acute arterial thrombosis.
- People who have elevated cholesterol levels or heart disease may also be more likely to develop arterial thrombosis.
What are the symptoms of Arterial Thrombosis?
The most common symptom of arterial thrombosis is pain in the affected area, typically in the legs or arms. This can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by tenderness, redness, and warmth in the affected limb.
Other symptoms include:
- Numbness or tingling sensation in the affected limb
- A bluish or pale hue to the skin
- A decrease in pulse rate in the affected area.
- In some cases, patients may experience muscle weakness or paralysis of the affected limb due to blocked arteries.
- In more severe cases of arterial thrombosis, patients may experience chest pain as well as difficulty breathing due to decreased oxygen supply to the heart and lungs caused by blocked arteries.
- Those with arterial thrombosis may also experience fatigue, dizziness, clammy skin, sweating, and fainting due to reduced blood flow throughout their body.
How can you prevent Arterial Thrombosis?
- Keep a healthy lifestyle, consisting of physical exercises and a nutritious diet.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Monitor and control high blood pressure, cholesterol, blood sugar levels and body weight.
- To prevent clots from developing in your arteries, follow your physician's instructions and take any prescribed medications.
- Follow up with healthcare professionals regularly for checkups and screenings as needed.
Arterial Thrombosis - Diagnosis and Tests
- Doppler Ultrasound: This test employs high-frequency sound waves to determine the speed and direction of blood flow in the arteries. It can help detect narrowing or blockages in the arteries caused by arterial thrombosis.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): MRA is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to provide comprehensive images of blood vessels, including those impacted by arterial thrombosis.
- Computed Tomography (CT) scan: A CT scan is an imaging test that employs X-rays to provide detailed images of the structures within your body, including those that may be impacted by arterial thrombosis.
- Arteriography: This specialised X-ray test shows detailed images of the arteries and can help diagnose arterial thrombosis. This method involves inserting a catheter into an artery in the leg or arm and injecting a dye into the circulation to make the artery visible on X-ray images.
- Venous Doppler Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to measure blood flow in veins and can help detect deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which can lead to arterial thrombosis if it travels from a vein to an artery.
What are possible complications of Arterial Thrombosis?
- Myocardial infarction: A sudden, life-threatening heart attack caused by clots blocking the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart.
- Stroke: Caused by clots that restrict or obstruct the supply of oxygen-rich blood to the brain.
- Loss of limb: Decreased circulation can result in tissue death, leading to gangrene and necessitating amputation.
- Renal failure: Clotting can cause severe damage to kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
- Shock: Caused by low blood pressure and organ dysfunction due to clotting.
- Pulmonary embolism: Clots can block arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the lungs.
Home Remedies for Arterial Thrombosis
- Consume a balanced diet with daily servings of fresh fruit and vegetables.
- Because of their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant characteristics, turmeric and ginger should be included into your diet.
- Regularly practice yoga and meditation to reduce stress levels in the body.
- Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol as they put added strain on the circulation system, leading to thrombosis or a stroke.
- Abhyanga (Ayurvedic oil massage) can be used daily to stimulate circulation throughout the body and reduce inflammation in affected areas of the body due to blocked arteries or veins caused by thrombus formation.
What to eat in Arterial Thrombosis?
- Eating a balanced and healthy diet is important to help reduce the risk of arterial thrombosis.
- Foods that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines, anchovies) and plant sources like walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and canola oil are beneficial for maintaining good cardiovascular health.
- Foods high in soluble fibre such as oats, barley, legumes (beans and lentils), apples, oranges, and strawberries may also help reduce the risk of arterial thrombosis.
- Adding more fruits and vegetables to your diet is another way to reduce the risk of arterial thrombosis.
- Whole grains are also beneficial for reducing the risk of arterial thrombosis as they provide fibre which helps reduce cholesterol levels. Examples include brown rice, quinoa, buckwheat, millet, whole wheat breads and pastas.
What not to eat in Arterial Thrombosis?
- Foods high in saturated fat: They include fatty cuts of meat, full-fat dairy items, and processed foods like snack cakes and pastries.
- Foods high in trans fat: Trans fats are found in fried foods such as French fries, doughnuts, and some margarines.
- Foods high in cholesterol: These include egg yolks, liver, and other organ meats, and shellfish such as shrimp and crab.
- Refined carbohydrates: White breads and pastas can cause blood sugar spikes that can increase your risk for artery clogging plaque buildup.
- Sugary drinks: Sodas and other sugary drinks can contribute to weight gain that puts you at greater risk for arterial thrombosis.
- Processed meats: Hot dogs, bacon, sausage, salami and other processed meats are high in sodium which can increase your risk for artery-clogging plaque buildup over time.
Arterial Thrombosis Treatment
- Angioplasty: A procedure in which a small balloon-tipped catheter is inserted into a clogged artery, and then inflated to compress the material causing the blockage.
- Atherectomy: A surgical procedure that removes atherosclerotic plaque from an artery using either lasers, microwaves, or mechanical devices.
- Thrombolysis: Involves administering medication (such as tissue plasminogen activator) to dissolve a blood clot in an artery or vein.
- Surgical Bypass: Involves redirecting flow around the blocked arteries with new vessels that bypass blockages by reconnecting below and above them.
Which doctor to consult for Arterial Thrombosis?
- A cardiologist is the best doctor to consult for arterial thrombosis.
- The cardiologist will be able to diagnose the condition and recommend appropriate treatment, including medications and lifestyle changes.
- A vascular surgeon may also be consulted, depending on the severity of the condition and any complications that may have arisen from it.
- It is important to seek medical advice from a qualified doctor as soon as possible to ensure proper treatment and prevent further complications from developing.
Which are the best medicines for Arterial Thrombosis?
- Anticoagulants: These medications reduce clot formation by preventing platelet aggregation and blocking clotting factors, including warfarin, heparin and aspirin.
- Antiplatelet Agents: These medications reduce blood clots by preventing platelets from sticking together and forming a clot before it can cause damage to the arteries. Examples include clopidogrel and aspirin.
- Fibrinolytics: These medications break down existing clots using drugs such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA).
- Thrombolytic Agents: These medicines help dissolve clots through infusions that target specific sites in the body monitored via imaging or other lab tests. Examples include streptokinase and reteplase.
- Thrombin Inhibitors: These drugs block an enzyme called thrombin from converting fibrinogen into fibrin which is involved in blood clot formation, thus reducing the risk of thrombosis occurrence or progression of artery disease. Examples include hirudins and bivalirudin such as Angiomax (bivalirudin).
How long does it take to recover from Arterial Thrombosis?
The length of recovery from arterial thrombosis is dependent on the severity of the problem and the treatment taken.
Generally, recovery can take several weeks or even months of rest and rehabilitation.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
The outcomes of the treatment are dependent on the sort of treatment administered as well as the reaction of the patient.
Results may or may not be lasting depending on the circumstances.
What are post-treatment guidelines for Arterial Thrombosis ?
- Avoid activities, such as heavy lifting, that place stress on the injured region.
- Take all prescribed medications as instructed by your doctor.
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation and prevent further arterial thrombosis episodes.
- Keep a healthy weight to avoid arterial thrombosis and other cardiovascular problems.
- Stop smoking or using tobacco products, since they may raise your chance of getting arterial thrombosis and other cardiovascular disorders.
- Monitor your blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels regularly, as they can be related to arterial thrombosis risk factors and can be managed with lifestyle changes or medications when necessary.
What is the cost of Arterial Thrombosis treatments in India?
The severity and complexity of the problem, as well as the hospital or health care centre that is used, are major factors that play a role in determining the total cost of treatment for arterial thrombosis in India.
Generally, costs can range from Rs 10,000-1 lakh depending upon outpatient/inpatient care, severity of thrombus and type of medication required.
What are side-effects of Arterial Thrombosis treatments?
- Increased risk of bleeding due to the use of anticoagulant medications like warfarin and heparin.
- The possibility of contracting an infection as a result of the insertion of intravascular devices such as catheters.
- Reactions to medications or other treatments, such as allergic reactions or skin rashes.
- Damage to surrounding organs from surgical intervention, such as removal of the clot.
- Formation of a new clot due to inadequate treatment or discontinuation of treatment too soon.
- Damage to blood vessels from long-term use of anticoagulant medications.
Arterial Thrombosis - Outlook/ Prognosis
If you have any problems with Arterial Thrombosis, you should see a doctor right away since they might create consequences such as 'renal failure, myocardial infarction, stroke, and so on' for which treatment time can vary from a few months to years depending on the seriousness of the condition.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Vascular Surgeon near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors