Ascites: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 06, 2023
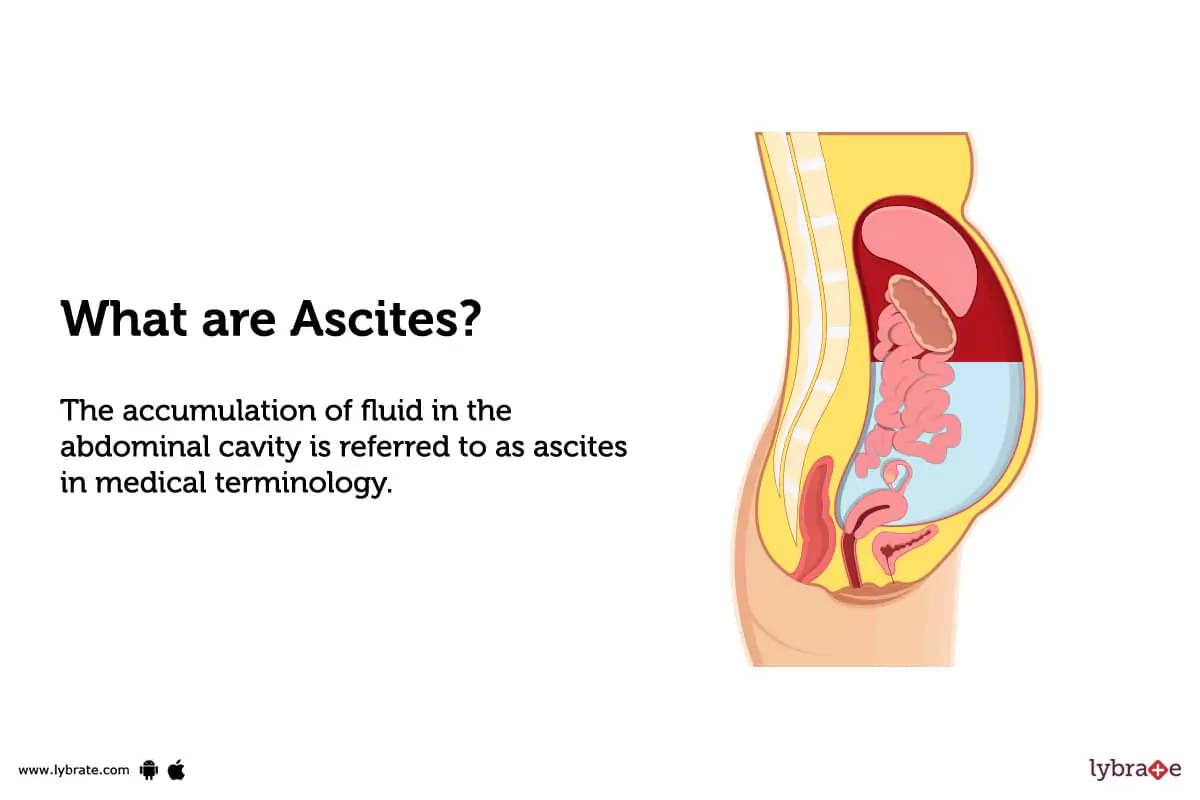
What are Ascites?
The accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity is referred to as ascites in medical terminology. This fluid is typically composed of water, proteins, and electrolytes.
Types of Ascites
There are three main types of Ascites:
- Infective Ascites: This type is caused by a bacterial infection in the abdomen leading to an overproduction of abdominal fluid. This may cause infection, fever, and liver damage.
- Malignant Ascites: This type is usually associated with cancers that spread to other organs, such as ovarian cancer or liver cancer causing ascites to collect in the abdominal area due to increased pressure from tumours blocking the lymphatic system or metastasizing directly into the peritoneal cavity . It can also be caused by pancreatic or ovarian cancer as well as tube drainage from these organs which may become blocked due to a tumour growth in these areas.
- Non-infectious/Non-malignant Ascites: This type is usually caused by chronic liver diseases such as cirrhosis, portal hypertension, hepatic failure, Budd-Chiari syndrome and kidney failure that leads to water retention due to poor sodium reabsorption in the body’s circulatory system resulting in fluid accumulation in the abdominal area.
What causes Ascites?
Ascites are caused often due to liver or kidney disorders.
Other conditions, such as cancer, congestive heart failure, and certain infections, such as HIV/AIDS and hepatitis C, may also bring on this condition.
Other causes include trauma or injury to the abdomen, blockage in the veins that return blood from the intestines, cirrhosis of the liver, and peritonitis.
What are the symptoms of Ascites?
- Abdominal swelling: An increase in abdominal size caused by the accumulation of fluid inside the abdominal cavity.
- Weight gain: Unexplained weight gain caused by an accumulation of fluid inside the abdomen.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing that is caused by fluid building up around the lungs, making it difficult to take a deep breath.
- Pain and discomfort: Pain or tenderness in the upper or lower abdomen when pressure is applied.
- Decreased appetite: Feeling full after eating only a small amount of food, leading to unintentional weight loss or lack of appetite.
- Nausea and vomiting: Periods of nausea accompanied by occasional vomiting due to build up of toxins in the body due to an inability for them to be expelled naturally as normal.
How can you prevent Ascites?
- Avoid alcohol & tobacco usage: Limit or avoid alcohol and tobacco usage, as they can worsen the fluid accumulation in the abdomen.
- Eat a healthy diet: Consume a balanced and healthful diet that is low in sodium and saturated fat, and high in complex carbohydrates, fibre and fruits/veggies.
- Get regular exercise: Exercise regularly as this can decrease your risk for cirrhosis, which is a leading cause of ascites.
- Follow doctor's orders: Follow any prescription treatments from your doctor such as diuretics (water pills), dietary changes, medications or surgery if needed to help reduce fluid accumulation.
Ascites - Diagnosis and Tests
- Physical examination: During a physical examination for ascites, a doctor typically evaluates the abdomen to determine if there is swelling or enlargement. He or she may also ask questions about any symptoms the patient has experienced, such as weight gain, abdominal discomfort or changes in appetite.
- Ultrasound: Ascites can often be detected on ultrasound by noting the presence of free fluid within the abdominal cavity.
- CT Scan: CT scans, also known as computed tomography scans, are imaging tests that employ X-rays and a computer to generate comprehensive images of the organs, blood vessels, and tissues inside the body. A CT scan of the abdomen may show fluid in the abdominal cavity associated with ascites.
- Liver function tests: Liver function tests are blood tests that evaluate the amounts of enzymes and proteins in the blood, which might signal changes in liver health. These tests can help to diagnose diseases or conditions affecting the liver, such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, fatty liver, and ascites.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test looks at the number of red and white blood cells as well as platelets in the blood, providing an indication of whether an infection is present or not.
- Electrolytes: This test measures the level of minerals such as sodium, potassium, and chloride which help maintain body fluid balance. Abnormal levels may indicate any number of conditions including liver disease and fluid retention caused by ascites.
What are possible complications of Ascites?
- Hypovolemia: Abnormally low level of blood volume.
- Increased abdominal pressure and discomfort: Pressure on other organs, pain and breathing difficulties can occur.
- Hypercoagulability: An increased risk of deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism or mesenteric ischemia.
- Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP): Abdominal bacterial infection that may lead to sepsis.
- Portal hypertension: Rising blood pressure in the portal vein causing liver cirrhosis, bleeding varices and hepatic encephalopathy.
Kidney damage can also occur due to electrolyte imbalance and fluid overload produced by ascites.
Home Remedies for Ascites?
- Drink boiled water with a teaspoon of ginger, lime juice and rock salt to reduce fluid build up in the body.
- When you eat bitter gourd on an empty stomach, it helps your body get rid of excess fluids.
- Have water soaked in cumin seeds mixed with honey daily to boost liver and kidney functions and detoxify your system.
- Regularly drink coriander tea prepared with juniper berries, cardamom and cinnamon for healthier liver functions.
- Consume kaipakayalu made up of dhania powder, special rock salt,ginger paste and jeera paste for improved digestive health.
What to eat in Ascites?
- Include a variety of colourful produce, legumes, and healthy grains in your daily diet.
- Instead of eating red meat, consider eating fish or chicken.
- Take in some healthy fats from foods like avocados and almonds, but don't go overboard.
- Dehydration may be avoided by consuming the recommended daily amount of water, which is six to eight glasses.
What not to eat in Ascites?
- Avoid salty, high-fat, and processed foods and beverages.
- Limit sodium intake to no more than 2,000–3,000 milligrams per day.
- Avoid foods with added sugar or high amounts of naturally occurring sugars.
- Limit your daily alcohol intake to no more than one drink for women and two for men.
Ascites Treatment
- Bed rest and sodium-restricted diet: To help reduce ascites, patients should follow a low-sodium diet and rest.
- Medications: Ascites can be managed through medications to reduce the build-up of salt in the body and to treat infections that can occur in people with ascites.
- Paracentesis: This is the most common surgical treatment for ascites and involves removing excess fluid from the abdominal cavity by inserting a needle and draining it away.
- TIPS: In more severe cases, a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) may be performed to help reduce the pressure in the abdomen caused by ascites.
- Laparoscopy/ Laparotomy: If other treatments are ineffective, laparoscopy or laparotomy may be used to insert a shunt or patch to help drain fluid away from the area.
- Cytoreductive Surgery: In rare cases, a major surgical procedure called cytoreductive surgery may be necessary to remove parts of organs which have been damaged by cancer or infection.
Which doctor to consult for Ascites?
A doctor specialising in Liver diseases, Gastroenterology or Internal Medicine should be consulted if Ascites is suspected.
Which are the best medicines for Ascites?
- Diuretics: These are the most common treatments for ascites. They help the body remove excess fluid by increasing urine production.
- Albumin: It is an albumin supplement used to decrease edema and remove excess fluid from the body.
- Octreotide: This is a synthetic hormone used to treat refractory ascites by decreasing intestinal secretion of water and electrolytes, thereby reducing abdominal swelling due to excess fluid accumulation.
- Antibiotics: Certain antibiotics may be prescribed for bacterial infections associated with ascites, as well as other infections elsewhere in the body that can lead to complications such as peritonitis or sepsis that further exacerbate ascites symptoms.
How long does it take to recover from Ascites?
Ascites can be managed successfully with medications and lifestyle changes, with the majority of people making a full recovery. However, recovery times vary depending on the underlying condition, the severity of the ascites and treatments used.
With proper medical care and treatment, most cases of ascites can be resolved in 4 to 6 weeks. Improved nutrition and exercise can help speed up recovery time in milder cases.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
No, the results of treatment for ascites are not permanent. Treatment is typically used to manage the symptoms and reduce the buildup of fluid in the abdomen. This can help control discomfort, reduce inflammation, and prevent long-term complications. With ongoing monitoring and medical care, some people are able to maintain managed levels of fluid in their abdomen for an extended period of time. However, relapse may occur due to certain factors such as liver damage or cancer progression.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- Post-treatment guidelines for ascites include monitoring of abdominal girth and weight, lab tests to check electrolyte balance, vital signs, and other biomarkers of the condition.
- The use of diuretics and medications that reduce fluid accumulation may also be prescribed.
- A low-salt diet may be recommended to help reduce fluid retention.
- In some cases, a procedure known as paracentesis may be performed to drain large amounts of fluid from the abdomen if it is causing discomfort or interfering with breathing or other activities.
- Close monitoring and follow up should also include watching for signs of infection as well as other potential complications due to the condition or its treatment such as kidney failure, electrolyte imbalances, urine changes, generalised swelling not just in the belly area, low blood pressure on standing, abnormal nutrition state (lack of proteins) etc.
What is the cost of Ascites treatments in India?
Depending on the underlying reason and the degree of the symptoms, ascites treatments in India vary in price. Generally, the cost for an initial hospital visit may range from ₹1,000-2,000, with additional treatment costs depending on medications and procedures.
Common treatments such as diuretics or paracentesis can cost between ₹3-5,000 while more complex treatments such as a TIPS procedure can cost up to ₹50,000.
What are side-effects of Ascites treatments?
A common side effect of ascites treatment is fatigue, due to the body having to work harder to filter out excess fluid.
Ascites treatments may also cause fatigue and a decreased appetite.
Other possible side effects include abdominal pain, swelling of the abdomen or legs, increased heartbeat, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances such as low potassium levels.
Ascites - Outlook/ Prognosis
Complications associated with ascites, such as 'hypovolemia, hypercoagulability, and renal damage,' need immediate medical treatment from a trained physician. Depending on the severity of the problem, the duration of necessary treatments may vary from a few months to years.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Hepatologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors