Bartholin Cyst: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 01, 2023
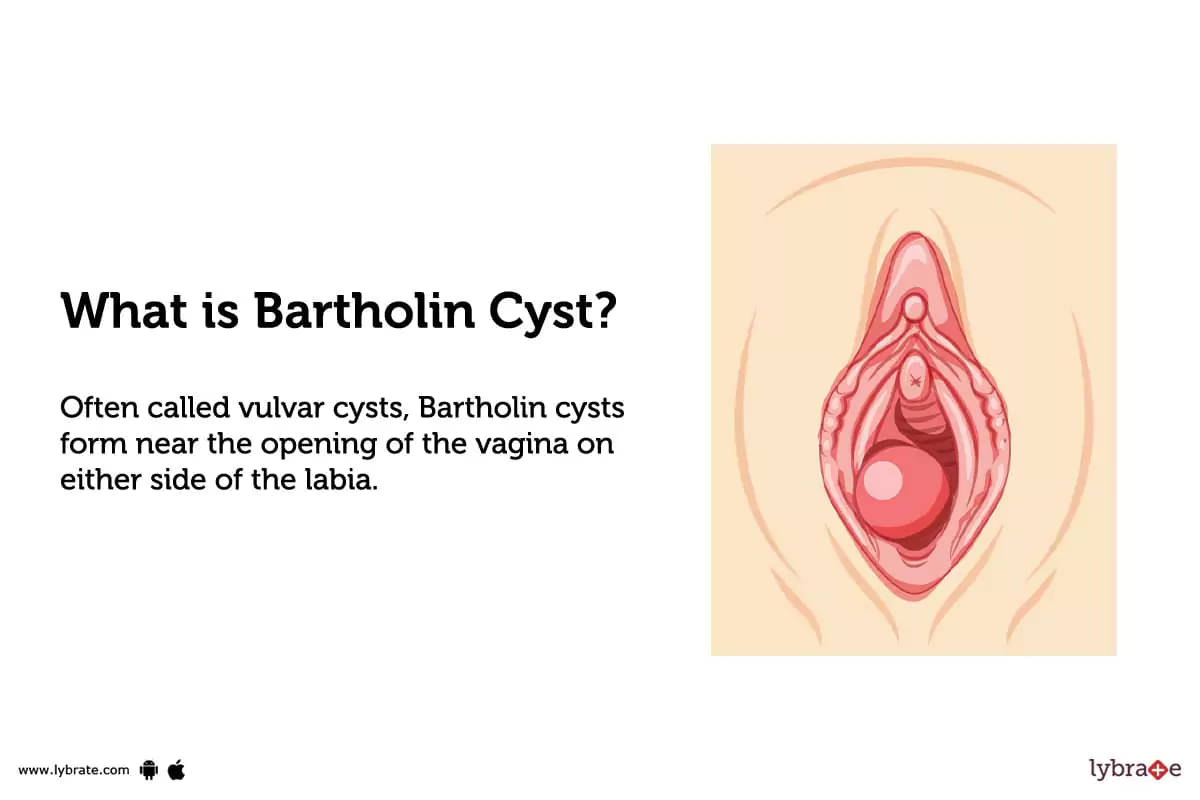
Bartholin Cyst
Often called vulvar cysts, Bartholin cysts form near the opening of the vagina on either side of the labia. Bartholin cysts are named after the Bartholin's gland, which is present on either side of the vaginal opening and produces a fluid to keep the vagina lubricated.
A Bartholin cyst forms when one of these glands' openings are blocked, resulting in a buildup of mucus. In most cases, it only affects one of the two Bartholin glands. Occasionally, Bartholin cysts are small and not painful. Infection of the cyst by bacteria may lead to an abscess. Medical treatment may be required for Bartholin cysts that are infected.
What are the symptoms of Bartholin Cyst?
The majority of Bartholin cysts are small and not severe. In the absence of symptoms, you might not realize you have a small cyst because you can't usually feel Bartholin's glands. Symptoms of Bartholin's cyst include:
- A painless, small lump near the vaginal opening
- Vaginal redness near the opening
- The area around the vaginal opening swells
- Cysts may cause discomfort during walking, sitting, or sexual contact, particularly if they are large. When a cyst becomes large, it can cause significant pain.
In the event of an abscess (infection), Bartholin cysts may show the following symptoms:
- It starts out as a lump that grows rapidly within a few hours or days.
- The pain is likely to be excruciating.
- A yellow or white pus may accumulate in the gland.
- There is a possibility that you will feel unwell and have a high temperature; your skin will appear red, hot, and tender over the abscess.
- As a result of the tender swelling, sitting down, walking, or sexual intercourse becomes painful.
- Discharge from the vaginal area may also occur in some women.
Bartholin Cyst Causes
There are small openings in Bartholin's glands that allow fluid to flow out. Blockages in the ducts cause the backup of fluid which causes cysts.
A blocked duct can be caused by an injury or irritation, as well as an excessive amount of skin growth.
An abscess can result from an infected Bartholin's cyst. The infection may be caused by bacteria such as Escherichia coli (E. coli) and bacteria associated with sexually transmitted illnesses such as gonorrhea and chlamydia.
The growth of a cyst can sometimes be caused by an infection. It is possible to obtain a cyst infection from bacteria such as Escherichia coli and bacteria that cause gonorrhea and chlamydia
How can you prevent Bartholin Cyst?
Despite our best efforts, bartholin's cysts cannot be prevented. However, there are some dos and don’ts that if followed will help you deal with bartholin’s cyst better
Dos in Bartholin Cyst
- Practice safe sexual intercourse
- Maintain a proper vaginal hygiene
- To keep hydrated and reduce bacteria levels in your urine, dilute cranberry juice with water and drink regularly.
- Wear loosely fitted cotton underwear
Don’ts in Bartholin Cyst
- Don’t engage in unprotected sexual intercourse as the Bartholin cyst is linked to sexually transmitted infections
- Don’t be careless about your vaginal hygiene and cleanliness
- Don’t wear tight underwear that doesn’t allow your vagina to breathe
- Don’t forget to eat healthily and keep yourself hydrated.
Bartholin Cyst - Diagnosis and Tests
Physical examinations are required to diagnose a Bartholin cyst. The only way to diagnose a Bartholin's cyst is by consulting your doctor. Their examination will include evaluating the cyst's size and looking for signs of infection. STIs or other bacterial infections may need to be tested if the cyst produces discharge.
Women over 40 years of age may undergo a biopsy in order to rule out vulva cancer. An examination under a microscope is conducted after a small piece of tissue is removed from the cyst.
The cyst on the Bartholin gland may require surgical removal if your healthcare provider suspects that it is cancerous. The Bartholin gland has a low risk of developing cancer, however, it is more likely to develop if you are over 60.
What are the possible complications of Bartholin Cyst?
The cyst fluid can be infected with bacteria, which can cause a buildup of pus called a Bartholin's abscess. An abscess like this can be painful.
In order to combat the infectious agent that is causing pus buildup, a doctor might prescribe a broad spectrum of antibiotics.
Symptoms of the abscess can develop rapidly. The following symptoms may be observed around the abscess:
- Redness in the area
- Tenderness
- Heat sensations from the area
- Sexual activity can cause pain
- Fever
- Leakage and rupturing
Home Remedies for Bartholin Cyst
Bartholin’s cyst is a common condition and may be treated at home without surgery. However, an infectious cyst needs medical help, and surgery may be inevitable in such cases. Some home remedies that can help with a bartholin’s cyst are:
- Sitz Bath
- An effective way to reduce the discomfort caused by Bartholin's cysts is to take a sitz bath.
- In addition to reducing irritation, it promotes Bartholin cyst drainage and encourages healing.
- This home remedy for Bartholin cysts also sanitizes the area and reduces the chances of infection.
- Warm Compress
- Using warm compresses for Bartholin cysts promotes drainage, which helps to speed up healing.
- Infection and inflammation can also be reduced through its ability to kill bacteria.
What to eat in Bartholin Cyst?
Unfortunately, there are no guaranteed dietary plans to reduce the risks of Bartholin cysts. Maintaining proper hygiene and keeping your intimate area clean are the two beneficial ways to minimise the risk. You can also use a sitz bath for relief when experiencing discomfort due to a Bartholin cyst. Nonetheless, a nutritious and healthy diet is usually recommended to heal with your recovery process.
What not to eat in Bartholin Cyst?
In the case of a Bartholin cyst, no restrictions are required with regard to food because cysts don't form an association with a particular diet. However, avoiding an unhealthy diet may help your body heal faster.
When should I call the doctor?
Taking a sitz bath may relieve a painful lump, but in case of persistent pain, you should contact your healthcare provider. Seek medical attention if you suspect infection or if your symptoms are severe.
The presence of a cyst on your vagina could be indicative of a more serious problem if you are older than 40. Your healthcare provider should be contacted as soon as possible in such a case.
Can a hormone imbalance cause a Bartholin cyst?
It is also possible to experience vaginal dryness and other symptoms in conjunction with hormonal shifts and imbalances related to menstruation (getting your period). A Bartholin cyst is not likely to result from this.
Are Bartholin cysts caused by endometriosis?
An abscess or cyst forms when fluid or pus accumulates inside one of the Bartholin glands. In the vaginal opening, these glands are located on each side. Small cysts can appear in the vagina when endometriosis is present. Endometriosis can cause cysts called endometriomas when it affects the ovaries. This is comparatively a rare condition.
Do Bartholin cysts develop as a result of stress?
There is no evidence that stress causes Bartholin cysts. Infections in the vaginal area, sexually transmitted infections or bacterial infections can cause Bartholin's cysts.
Is a Bartholin cyst an STD?
Sexually transmitted diseases (STIs) do not include Bartholin cysts. Bartholin cysts are often caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs), but the cyst itself isn't considered an STD or STI.
Bartholin Cyst Treatment
Surgical treatments are usually not necessary for asymptomatic, early Bartholin cysts. However, getting professional help or consulting your doctor is always recommended. There are several factors that will determine the treatment for a cyst, including its size, the patient's discomfort level, and whether or not the cyst is infected. There are various treatment options available:
- Surgical Drainage- The treatment of Bartholin cysts that recur or are painful or uncomfortable requires surgical drainage. Local anesthesia or intravenous sedation is usually used to drain the cyst. It is necessary for the doctor to make a small incision over the cyst in order to drain the fluid from it. Approximately six weeks after the incision is made, a small tube (catheter) is inserted within the cyst. By doing this, the fluid accumulated is continuously drained out, allowing the bartholin's cyst to drain completely.
- Marsupialization- There may be a need for marsupialization if cysts recur. Approximately 6mm of permanent opening is created by placing sutures (stitches) along either side of the incision. There may be a need to place a catheter for a few days in order to drain the fluid completely and prevent reoccurrence.
- Antibiotics- Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat an infected cyst or to prevent post-surgical infection following surgical drainage.
- Painkillers- Painkillers can be used to reduce inflammation and pain after a surgical bartholin cyst removal is done or for pain after surgical drainage.
- Bartholin cyst removal- Bartholin glands may be surgically removed in extremely rare cases when treatment does not work
Bartholin Cyst Treatment without surgery
A bartholin cyst may often be treated without a surgical treatment if it is not infected or the symptoms are not severe. Here are the different treatments that don't require a surgery:
- Home Care- You can help drain the cyst fluid by taking a warm bath or applying a moist, warm compress a few times each day. Cysts may be treated successfully at home in many cases.
- Medications- Pain and discomfort can be reduced with over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen (Tylenol). An antibiotic can be prescribed to you if the cyst becomes infected.
Bartholin Cyst Surgery
There Are multiple surgical methods to treat a bartholin cyst depending on the condition and symptoms of the cyst. You can minimise any risks involving the surgery with proper guidance and experience, and at Pristyn care, we connect you with experts and some of the most experienced surgeons. The surgical methods include:
Bartholin cyst drainage
An abscess can be drained completely by making a small surgical cut. As a result, symptoms are relieved quickly and recovery is accelerated.
- Local anesthesia may be used to perform the procedure.
- Approximately 1 to 2 cm of tissue is cut around the abscess site. Irrigation with normal saline is carried out in the cavity. It may be necessary to insert a catheter (tube) and leave it in place for 4 to 6 weeks. During the healing process, continuous drainage is possible. The procedure does not require sutures or stitches
- Within 1 to 2 days after the procedure, it is recommended that you soak in warm water. The catheter should be removed before engaging in sexual relations.
Marsupialization
Another option is marsupialization, a minor surgery that can be performed on women.
- A circular opening is created along the cyst to assist the gland in draining. A surgical procedure is performed to remove the abscess. In order to treat the cyst, stitches are placed around its edges.
- Anesthesia can sometimes be administered in the clinic before the procedure. Some patients may require general anesthesia so they can rest comfortably and not feel any pain.
- In the days following your surgery, you should soak in warm water. Following surgery, you cannot engage in sexual activity for 4 weeks.
- Pain medications can be taken orally after the procedure. Narcotic pain medicines may be prescribed by your provider if necessary.
Bartholin Cyst Excision
Abscesses that keep recurring may require removal of the glands entirely.
- A surgical procedure is used to remove the cyst wall in its entirety.
- In most cases, this procedure is performed in the hospital under general anesthesia.
- Following surgery, it is not recommended that you have sexual intercourse for four weeks.
Which are the best medicines for Bartholin Cyst?
Treatment for Bartholin's abscesses involves using antibiotics and medication because pathogens are mainly responsible for infection. Healthy women with uncomplicated abscesses do not need antibiotic therapy. When opting for antibiotic therapy you can go for antibiotics such as:
- Ceftriaxone
- Ciprofloxacin
- Doxycycline
- Azithromycin.
You can also take over the counter painkillers like:
- Naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn)
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), which may help with pain and discomfort.
Medicines usually subside the symptoms but are not always an effective measure against Bartholin cyst. Surgery, on the other hand, always shows positive results and gets rid of the problem for good.
How long does it take to recover from Bartholin Cyst?
As an abscess grows, its size, infection extent, and other factors influence the length of time Bartholin’s cyst drainage procedures take. After the abscess drains completely, complete recovery occurs within a few days.
What is the price of Bartholin Cyst treatments in India?
In India, surgical treatment can cost between Rs. 15,000 and Rs. 30,000, depending on the method used. Medical and non-medical factors such as treatment method, clinic/hospital choice, and doctor's fees may affect the final cost.
Does the Bartholin Cyst treatment have a permanent effect?
The abscess of Bartholin heals permanently once it has been drained thoroughly. The condition, however, may recur if new abscesses form.
Who is eligible for the Bartholin Cyst treatment?
Bartholin's cyst is a relatively common condition without very complicated treatment methods. A painless swelling or cyst may develop in one of the glands due to fluid accumulation, which may become infected and become painful abscesses. All such patients are eligible to seek treatment.
Who is not eligible for the treatment?
A small bartholin's cyst with no specific symptoms can easily be treated without surgery. Furthermore, it is recommended that people who suffer from bleeding disorders do not undergo surgical procedures to treat Bartholin's abscess.
What are the post-treatment guidelines for Bartholin Cyst treatment?
After the bartholin cyst drainage, there are some post-treatment guidelines that you must follow to make sure the wounded area heals faster and better:
- Sitz Bath- It is recommended to take a sitz bath within 24 to 48 hours or as directed. Take a sitz bath only after your packing is removed. It may be helpful to take a sitz bath to relieve swelling and pain. 3 to 4 sitz baths a day for 3 days are recommended. Make sure the bottom of your bathtub is covered with a clean towel. Get into your bathtub and fill it up to your hips with warm water. It is also possible to purchase a toilet-friendly sitz bath. Sit and take a 10-minute bath.
- Sanitary pads to absorb drainage- Make sure that you are wearing a sanitary pad to absorb the Bartholin cyst drainage from your wound. The bartholin cyst drainage procedure may last for a few weeks after your cyst is drained.
- Avoid sexual activities for a few weeks- Check with your healthcare provider to see if you are allowed to engage in sexual activity. There is a possibility that your drain will fall out due to sex. Additionally, it may increase the risk of infection.
- Vaginal Hygiene- Vaginal hygiene is important. It is always best to wipe from front to back. Make sure you shower every day. As soon as you are done showering, gently pat the area dry.
What are the side-effects of Bartholin Cyst treatments?
The treatment is very safe, and there are very few side effects. It is possible to experience some side effects if antibiotics are used improperly. The side effects of surgical procedures are also very limited. The surgical removal of Bartholin's gland is the most likely cause of side effects and complications.
Bartholin Cyst - Outlook / Prognosis
It is extremely rare for a Cyst to develop on Bartholin's gland. Fortunately, they can be treated easily if they arise. The majority of cysts don't cause symptoms, and can sometimes be treated at home, especially if they're so small.
More intensive treatment may be needed for recurrent infections. In case of recurrence of infection, it is crucial to consult your physician.
Get medical attention if you develop a cyst over the age of 40 or after menopause. A biopsy may be necessary to determine whether the cells are cancerous.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why bartholin cyst occurs again and again?
Why Bartholin cyst form pus?
What does a Bartholin cyst look like?
What does a bartholin cyst look like when it bursts?
What is released from a Bartholin Cyst?
What is the remedy if we found bartholin cyst early?
References
- Bartholin cyst or abscess- Medline Plus, NIH, U.S. National Library of Medicine [Internet]. medlineplus.gov 2019 [Cited 18 July 2019]. Available from:
- Bartholin’s Gland Cyst- American academy of Family Physicians [Internet]. familydoctor.org 2019 [Cited 18 July 2019]. Available from:
- Omole F, Simmons BJ, Hacker Y. Management of Bartholin's duct cyst and gland abscess. American family physician. 2003 Jul 1;68(1):135-40. [Cited 18 July 2019]. Available from:
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Gynaecologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors