Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
About
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Bladder (Human Anatomy): Picture, Function, Location, Diseases and More
Last Updated: Feb 25, 2023
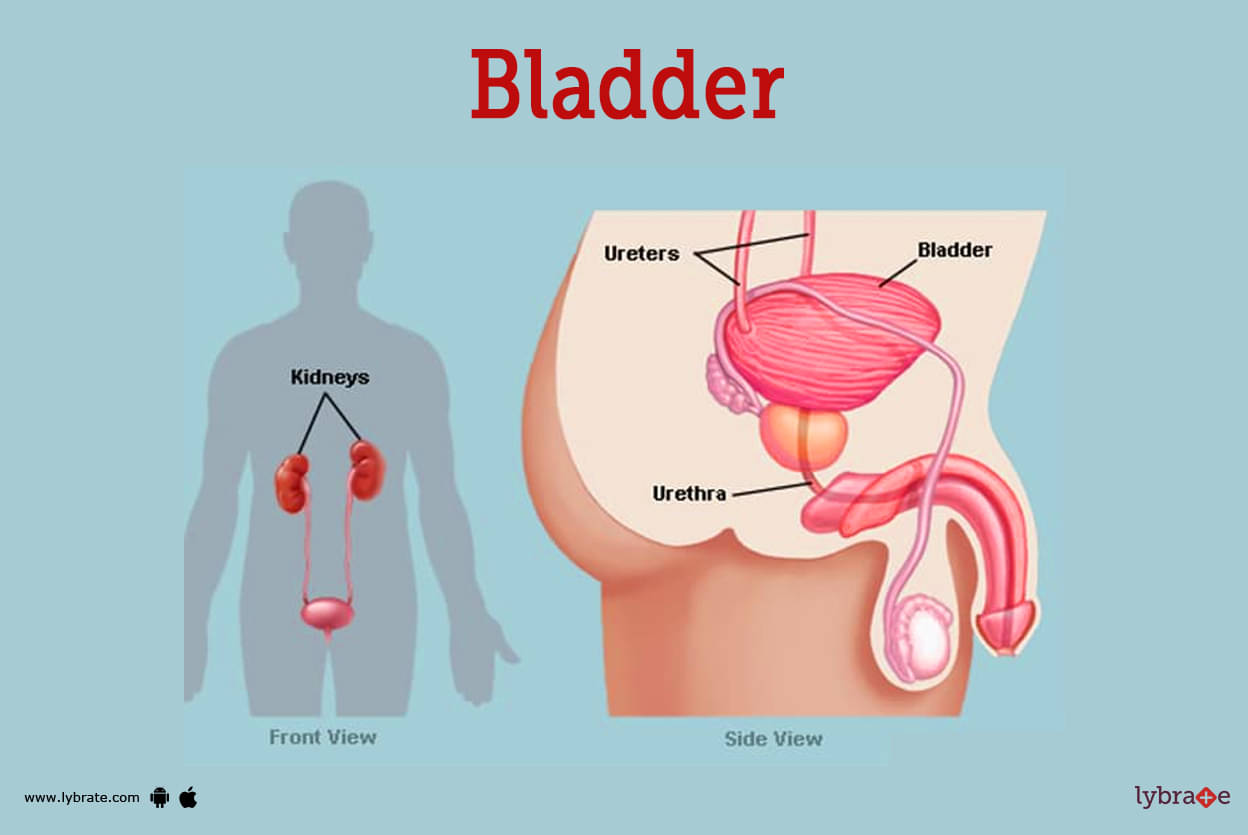
Bladder Image
The bladder is a hollow organ in your lower abdomen where pee is stored. Your bladder might be affected by a variety of disorders. It is located in the pelvic area just above and behind the pubic bone and is a muscular sac that holds the urine contents. Both men and women have a single urinary bladder present. When it is empty, the form and size of the bladder is comparable to that of a pear.
Bladder Functions
The bladder is a muscular organ that stores urine until it is eliminated from the body. Its main functions are:
- Storage: The bladder stores urine produced by the kidneys until it is eliminated from the body through the urethra. Layers of muscular tissue make up the bladder, which is responsible for stretching to accommodate urination. Under typical circumstances, the bladder may hold somewhere around 400 to 600 milliliters of liquid.
- Elimination: The muscles of the bladder contract and the urine is eliminated from the body through the urethra. Urine is stored in the urinary bladder until a signal that it is time to urinate arrives.
- Regulation of urine flow: The bladder has muscles that control the flow of urine through the urethra. These muscles contract to prevent leakage of urine and relax to allow the elimination of urine.
- Maintaining hygiene: The bladder helps to maintain proper hygiene by eliminating waste products from the body.
- Monitoring the body's fluid balance: The bladder helps monitor the body's fluid balance by sensing the amount of urine in the bladder and signaling the need to urinate when the bladder is full.
Overall, the bladder plays a critical role in maintaining the body's fluid balance and eliminating waste products from the body.
Bladder Conditions
- Hematuria: Hematuria means the presence of blood in the urine. It is possible that it won't do any damage. It can be caused by an infection or a dangerous ailment such as bladder cancer.
- Urinary retention: Urinary retention occurs when there is a blockage or when the action of the muscles in the bladder are inhibited as a result, urine does not escape the bladder as it typically would. If the bladder is retaining more urine than usual, there is a possibility that the bladder can expand as a result there is increase in the size of the bladder.
- Cystocele: When the pelvic muscles become weakened, most often as a result of delivery. This allows the bladder to push against the vagina, causing cystoceles. It is clear that they are having trouble passing urine.
- Bladder tamponade: A bladder tamponade is a blockage of the urinary bladder outflow caused by the growth of a large blood clot inside it. In most cases, surgery is required. Bladder cancer is frequently the cause of such severe behaviour.
- Nocturia: Wetting the bed, also known as nocturnal enuresis: Children who are 5 years old or older and who wet the bed at least once or twice a week for a period of at least three months are considered to have bed-wetting. It may be a behavioural issue brought on by the child's anxiety or lack of motivation, or it may be the result of an issue with the muscles that control bladder function not working properly.
- Dysuria: Often known as painful urination, refers to the experience of pain or discomfort during the act of passing urine. Inflammation of the urinary bladder, urethra, and/or external genitals may be brought on by an infection, irritation, or all three of these factors together.
- Urinary tract infections: UTIs are brought on by bacteria living in the urinary system. This may occur because of improper hygiene, females wiping from the anus towards the urine meatus, or the insertion of a catheter into the urinary meatus.
- Interstitial cystitis: Also called painful bladder syndrome. Interstitial means 'inside the tissues'' while 'cystitis' means inflammation of the urinary bladder. That is inflammation of the tissues inside the wall of the urinary bladder. Urgency and frequency of urine are two indications of this condition. Urinary incontinence: It is a common and frequently unpleasant issue that results from a lack of bladder control. Depending on how bad it is, you might sometimes leak urine when you cough or sneeze, or you might need to go to the bathroom so quickly that you can't get there in time.
- Bladder trauma: It is a rare injury that may be caused by a direct impact on a swollen bladder, high-energy traumas that disturb the pelvic floor, penetrating, and iatrogenic injuries, among other things.
- Neurogenic bladder: It is the result of injury or illness that disrupts the connection that normally exists between the neurological system and the function of the bladder. It is not curable, although the symptoms may be controlled and managed.
- Hunnler’s ulcer: They grow on the bladder wall and, like any ulcer, may bleed, leak, and vary in size.Fowler's syndrome: It contributes to urinary retention (the inability to pass urine regularly) in young women. Urinary retention in young women is uncommon, but it may be quite painful. The problem is in the urethral sphincter (the muscle that keeps you continent).
- Bladder diverticula: These are protrusions of the bladder urothelium and mucosa through the muscularis propria of the bladder wall, resulting in a thin-walled structure linked to the bladder lumen that poorly empties during micturition.Bladder diverticula may be caused by congenital or acquired factors.
Bladder Tests
- Urinalysis: A urine analysis can aid in the early detection of a number of urinary bladder and urinary problems, such as diabetes, urinary bladder stones, chronic kidney disease, and bladder infections.
- USG urinary bladder: This examination takes an image of the urinary bladder using sound waves.It can detect obstructions such tumours or stones, and irregularities in urinary bladder size and shape.
- CT scan: This imaging technique utilises x-rays to capture pictures of the renal system. If a UTI spreads to the urinary bladders, however, it might have devastating effects .
- Contrast Enhanced Computed Tomography CECT: In this scan X-rays are used for diagnosing specific diseases of the urinary bladder the image is enhanced through intravenous contrast dye better gives better prognosis For this test, intravenous contrast dye may be used, which urinary bladder patients may find concerning.
- MAG 3 Study: It is a test used for diagnosis of renal perfusion in which mercapto acetyl glycine is involved . It is known as the gold standard for diagnosis of renal perfusion.
- MRI: Due to the combined importance of the anatomical and functional information offered, as well as the unique contrast patterns that may be detected non-invasively, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of healthy and diseased urinary bladders offers considerable potential. Imaging with several contrasts can reveal infiltrative urinary bladder diseases.
- Urinalysis1: Protein within foods you eat breaks down, producing urea nitrogen. BUN levels should be within 7 and 20. As renal function decreases, so does the amount of BUN in the blood.
- Ureteroscopy: A small telescope called a ureteroscope is passed into the urethra and bladder, up the ureter, and to the place in which the stone is located during ureteroscopy, a technique to treat urinary bladder stones. The surgery typically takes one to three hours to finish and is usually done while the patient is under general anaesthesia.
- Urinary Bladder Biopsy: A urinary bladder biopsy is a process in which a tiny piece of urinary bladder tissue is surgically removed and studied under a microscope. You may use it to look for obstructions and structural flaws.
- Pressure Flow Study (Whittaker Test): In this the urinary bladder is punctured percutaneously and contrast is injected into the pelvis simultaneously intrapelvic pressure is measured if there is an abnormal rise in intra pelvic pressure it should be suggestive of pelvic ureteric junction obstruction.
Bladder Treatments
- Extra hydraulic lithotripsy: This procedure approach is electrohydraulic in nature, making enough pressure or crashing off renal stones; it is a gold standard method and a lesser invasive procedure for treating renal stones.
- Suprapubic cystolithotomy: It is a surgical procedure in which removal of bladder stone performed via lower abdominal incision and stones are removed manually instead of fragmentation
- Cystoscopy: It is a diagnostic as well as a therapeutic procedure in which a urologist diagnoses the problems occurring in the bladder and the urethra using a cystoscope probe inserted into the bladder consisting of a camera or an eyepiece.
- Exploratory laparotomy: It is the surgical procedure done for the lower abdominal organs including bladder urethra prostate kidneys etc. it involves removal of tumors cyst and Abscess along with stenosis and ischemic or necrotic lesions found in the lower abdominal organs
- Cystolithoplexy: It is a surgical procedure that is used to treat bladder stones which are hard deposit from minerals that are formed inside the bladder it is one of the most common techniques two trade adult bladder stools it is one of the most minimally invasive surgical procedure
- Urine cytology: It is the investigation performed for finding out various organisms present in the urine which could be result of our you don't need tract infection or being excreted out of the body after the infection has done it's part in the body
- Ureteroscopy: In this procedure a small scope is inserted into the bladder and your return and is used to diagnose a variety of urinary tract infections and any forms of lesions or cyst or Abscess or tumors present in the bladder or urethra.
- Laparoscopic stone surgery: By using laparoscopic ports instead of open surgical approach it is a minimally invasive procedure for the treatment of larger amount of stones
- Anderson hynes dismembered pyeloplasty: It is a newer conventional method of poor performing pile of plastic in which repositioning of the ureter in relation to the lower pole crossing vessels is done.
Bladder Medicines
- Broad Spectrum Antibiotics: Fluoro-quinolones (e.g.First-line therapy for acute, uncomplicated pyelonephritis is oral ciprofloxacin (500 mg twice daily for 7 days).
- Renal Specific antibiotics: Women who are pregnant and have urinary tract infections Antibiotics like nitrofurantoin, ampicillin, and the cephalosporins can be used with reasonable safety throughout the first trimester of pregnancy. Masculine urinary tract infections A fluoroquinolone or is advised for 7-14 days in treating a UTI in males with no evident complications.
- Diuretics: These medications are not only used to treat edema, but also other conditions that cause fluid retention, such as heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, cirrhosis, and high blood pressure. Diuretics such as aldactone, bumetanide, torsemide, hydrochlorothiazide, furosemide, and metolazone are used by a wide variety of doctors.
- Statins: These are known as lipid-lowering medicines with additional positive features for reducing the progression of CKD, such as decreasing oxidative stress and inflammation. Some of the examples of statins are rosuvastatin, atorvastatin etc
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACEIs): They belong to a class of drugs that inhibit the renin–angiotensin system and are believed to reduce proteinuria and albuminuria. Some of the drugs known to be found in market are Benazepril (Lotensin), Captopril (Capoten), Enalapril etc
- Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs): These are the drugs which decrease the functioning of angiotensin receptors decreasing the efficacy of RAAS mechanism. and improving the functioning of urinary bladders reducing inflammation. Some of the ARBs known to be used by expert physicians are andesartan (Atacand), eprosartan (Teveten), telmisartan, Losartan etc
- Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation, the anti-inflammatory mechanism of action of these drugs involves inhibiting the migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) to sites of cellular and tissue damage. Some of the important corticosteroids includes methylprednisolone
- Alkalyzers: For the treatment of hyperuricemia, hydronephrosis and pyelonephritis , and also in the case of renal stones alkalizer or alkalizing agents are used which increases the pH level of urinary bladders reducing the renal inflammation, some of the examples of alkalizing agents are sodium hydrogen carbonate, sodium citrate, magnesium hydrogen carbonate etc.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I know if my bladder has a problem?
You can feel the frequent urge to urinate if your bladder has a problem.
What causes bladder problems?
Causes of bladder problems are infection, ageing, diabetes, stones and nerve damage.
What are common bladder problems?
The most common bladder problems are infection in the urinary tract, urinary retention, incontinence and painful urination.
Are bladder problems serious?
Yes, bladder problems can lead to serious problems if left untreated.
How do I know my bladder is healthy?
You will not feel the frequent pain and urge to urinate if your bladder is healthy.
How do you cure bladder problems?
Bladder problems can be cured by making some lifestyle adjustments, performing bladder training, exercises and maintaining proper weight.
How can I clean my bladder?
You can clean your bladder by drinking enough water, doing exercises, urinating properly and taking a proper diet.
Delhi
Mumbai
Chennai
Bangalore
Index
Table of content
Content Details
Written ByDrx Hina FirdousPhD (Pharmacology) Pursuing, M.Pharma (Pharmacology), B.Pharma - Certificate in Nutrition and Child CarePharmacology
Reviewed By
Find Urologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously