Brain Aneurysm: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Feb 18, 2023
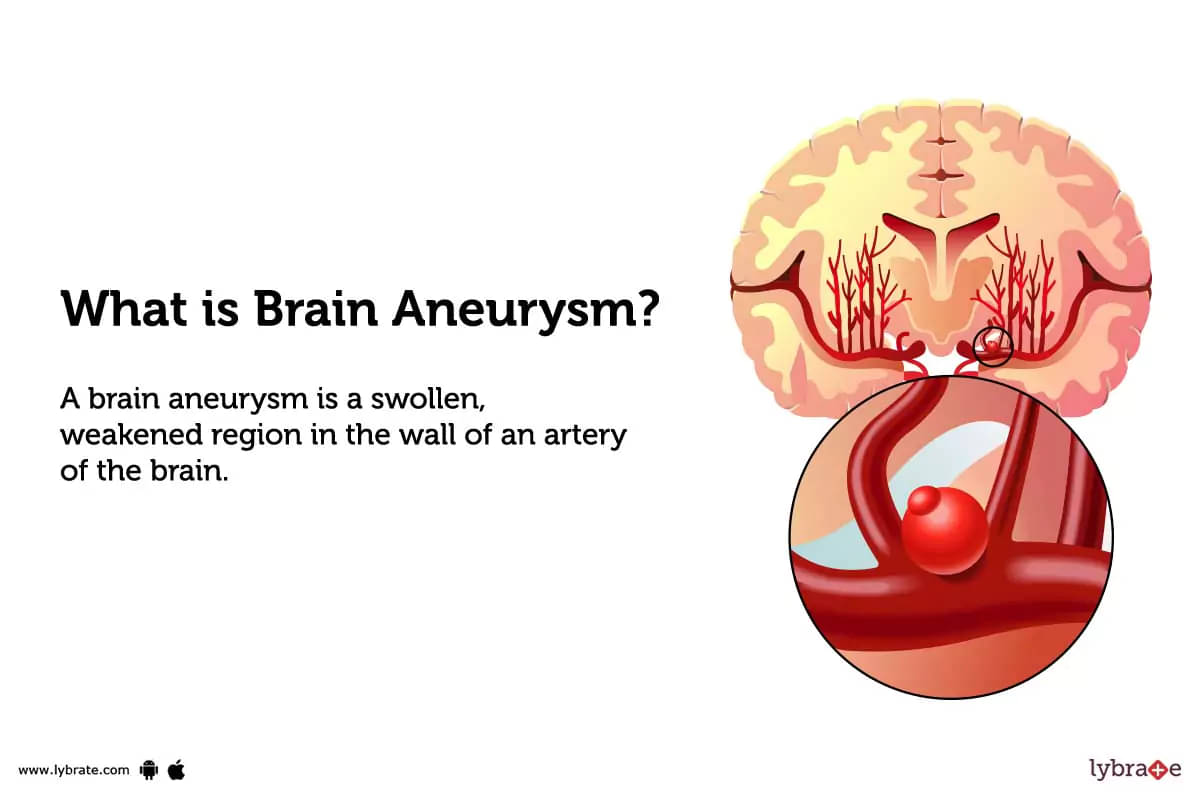
What is Brain Aneurysm?
A brain aneurysm is a swollen, weakened region in the wall of an artery of the brain. It has the potential to fill with blood and burst, causing brain to bleed (hemorrhagic stroke). Brain aneurysms can occur in any size artery within the brain and can range from very small to large. They are most commonly located at the junction where an artery branches.
Types of Brain Aneurysm
Aneurysms in the brain are classified into numerous categories based on their size, shape, and location.
- Saccular Aneurysms: Also known as 'berry' aneurysms, these are the most common type of brain aneurysm and are shaped like a small berry or a balloon on a stem. They usually form at branch points in arteries and account for about 80% of all intracranial aneurysms.
- Fusiform Aneurysms: These are less common than saccular aneurysms and occur when the entire circumference of a blood vessel is weakened and dilated.
- Giant Aneurysm: This type of aneurysm is larger than 25 mm in diameter and can cause serious complications due to its size. Giant aneurysms can rupture more easily than smaller ones and have higher rates of mortality after rupture due to their large size.
- Mycotic Aneurysm: This type of aneurysm is caused by infection from bacteria or fungi that enter the arterial wall through the bloodstream or directly from local infection sites such as dental abscesses or meningitis infections. Mycotic aneurysms are rare but can be life-threatening if left untreated.
What causes Brain Aneurysm?
Brain aneurysms are caused by a variety of factors, including:
- High blood pressure: High blood pressure can cause the walls of arteries in the brain to become weak and thin, leading to aneurysms.
- Genetics: Aneurysms can be inherited, or passed on through family members.
- Age: As people age, their arteries become more susceptible to damage and weakening, leading to aneurysm formation.
- Head injury or trauma: A head injury or trauma can cause damage to the arteries in the brain, leading to aneurysm formation.
- Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of developing an aneurysm due to its effects on blood vessels and circulation in the body.
What are the symptoms of Brain Aneurysm?
- Sudden terrible headache.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Blurred or double vision.
- Loss of feeling in the face or limbs.
- Convulsions and unconsciousness.
How can you prevent Brain Aneurysm?
- Quit Smoking: Quitting smoking may lessen the chance of developing a brain aneurysm, since smoking raises this risk.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise helps to reduce blood pressure and improve overall health, which can help prevent a brain aneurysm.
- Reduce Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol consumption has been linked to an increased risk of developing a brain aneurysm, so limiting alcohol intake is recommended.
- Avoid High Blood Pressure: High blood pressure is one of the main causes of a brain aneurysm, so it’s important to maintain healthy blood pressure levels by exercising regularly and eating healthy foods that are low in salt and fat.
Brain Aneurysm - Diagnosis and Tests
There are several tests that may be used to diagnose a brain aneurysm:
- Cerebral Angiography: This test uses X-ray images to provide detailed pictures of your blood vessels and other structures inside your skull. These pictures will help doctors evaluate any blockages or bulges in the arteries of your neck and head.
- Computerised Tomography Scan (CT): During this test, multiple X-rays are taken at different angles to create detailed images of the inside of your skull and other anatomical structures like the brain tissue and sinuses. It is often used to detect abnormal growths or tumours in this region that can indicate a possible aneurysm.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI scans use radiofrequency signals for creating images of the interior bones and soft tissues within the body including the neural pathways associated with aneurysms. Unlike CT scans, MRI scans do not use radiation which makes them popular for diagnosing potential aneurysms before they reach too dangerous levels where surgery may be necessary.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound machine uses high frequency sound waves that bounce off organs within the body allowing doctors to form detailed images which could help confirm if a person has an aneurysm or not.
What are possible complications of Brain Aneurysm?
- Subarachnoid haemorrhage: Bleeding between the brain and the tissue that covers it.
- Hydrocephalus: Accumulation of fluid in the brain, increasing the pressure within the skull as a result.
- Neurological deficits: Loss of physical or cognitive abilities due to damage to the brain tissue caused by aneurysm or its treatment.
- Rebleeding: Rupture of a previously treated aneurysm, leading to further bleeding and possible death.
- Vasospasm: Narrowing of blood vessels near an aneurysm, leading to decreased blood flow and oxygen supply to parts of the brain.
- Infection: Risk of infection following surgery or other treatments for aneurysms due to weakened immune system or use of antibiotics/steroids during treatment.
Home Remedies for Brain Aneurysm?
- Take a combination of Shatavari and Brahmi herbs. These herbs are known to work synergistically to improve neurological function, reduce inflammation and reduce the risk of aneurysm formation.
- Take frequent rests between extended periods of focus or effort. This will help in keeping your blood pressure levels regulated thus reducing the chances of aneurysm formation.
- Take a teaspoonful of Amla powder daily with warm water every morning as it is an amazing remedy for brain aneurysms and helps in curing them quickly.
- Consume plenty of herbal teas such as Gotu Kola tea, Ginkgo Biloba tea, Green tea, Lavender tea etc this helps in stimulating blood circulation and preventing the formation of aneurysms.
- Apply warm sesame oil on your forehead gently each day; this helps in enhancing circulation and healing any existing aneurysms naturally.
What to eat in Brain Aneurysm?
- Increase your consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables: A diet high in fresh produce may help lower your chance of having an aneurysm.
- Consume omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids are important for maintaining healthy blood vessels, which may help reduce the risk of aneurysm formation. Omega-3 fatty acids are found in foods including salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds.
- Get adequate amounts of protein: Eating adequate amounts of protein can help maintain healthy blood vessels and may reduce the risk of aneurysm formation. Fish, eggs, chicken, and lentils are all excellent sources of protein.
What not to eat in Brain Aneurysm?
- Avoid salty, processed, and fatty foods: Too much salt can raise blood pressure, which can put stress on brain aneurysms. Processed and fatty foods can also increase the risk of stroke or heart attack, which can lead to a brain aneurysm.
- Limit caffeine intake: Caffeine is a stimulant that increases heart rate and blood pressure, potentially putting extra stress on an aneurysm.
- Avoid alcohol: Drinking too much alcohol can also raise blood pressure and lead to other medical problems that may increase the risk of a brain aneurysm rupture.
Brain Aneurysm Treatment
- Initial treatment: Immediate medical attention is required for a brain aneurysm to reduce the risk of rupture and death. This might include blood pressure-regulating drugs, analgesics, and anticonvulsants to stop seizures.
- Surgical clipping: This is the most popular surgical procedure for treating brain aneurysms, and it includes placing a small metal clip to the aneurysm's base in order to stop blood flow and prevent it from rupturing.
- Flow diversion: This procedure involves placing a stent-like device at the base of the aneurysm to divert blood away from it and reduce pressure on its walls, thus preventing rupture.
- Endovascular treatments: In some cases, endovascular treatments may be used instead of surgery in order to seal off the aneurysm without opening up the skull. This involves threading a catheter through an artery in the groyne up into the brain in order to place a device that will stop blood flow into the aneurysm.
Which doctor to consult for Brain Aneurysm?
The best doctor to consult for a brain aneurysm is a neurologist, who specialises in the diagnosis and treatment of conditions affecting the nervous system.
Which are the best medicines for Brain Aneurysm?
- Blood Pressure Lowering Medications: These are typically used to treat high blood pressure and consist of beta blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and diuretics. These medications help lower overall blood pressure which reduces strain on weakened areas of certain vessels in the brain or neck — thereby reducing the chances of aneurysm rupture.
- Anticoagulants: These medicines thin out the blood and make it less likely that a clot will form around the aneurysm — which can reduce its chances of rupturing. Common anticoagulant drugs are warfarin, heparin and even aspirin in some cases.
- Corticosteroids: In some instances corticosteroid medications may be used on those with giant aneurysms that cannot be surgically treated due to their size or location in order to contain their growth and shrink them down over time, thus reducing the risk for rupture or further complications arising from pressure issues around it developing vessels due to growing size of the aneurysm itself..
- Calcium Channel Blockers: A type of medication called calcium channel blockers can also be administered where appropriate to reduce stress on both weakened areas as well as possible surrounding arteries that could have been damaged by increased stress levels around them due to a growing aneurysm nearby..
- Pain Medications: Opioids may also be used in some situations involving those who suffer from intense headaches due to bleeding occurring inside their head after experiencing a stroke stemming from someone’s ruptured brain aneurysms.
How long does it take to recover from Brain Aneurysm?
Generally, it can take several weeks to months to fully recover from a brain aneurysm. During this time, patients may experience physical and cognitive changes such as fatigue, headaches, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
Surgery and endovascular treatments, such as coiling and stenting, can be effective at stopping or slowing the growth of an aneurysm. In some cases, these treatments can even cause the aneurysm to shrink.
However, it is important to note that these treatments are not always permanent; in some cases, the aneurysm may continue to grow or even rupture again despite treatment.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- Generally, post-treatment care of the patient includes:
- Resting and recovering at home or in a health care facility as advised by the physician.
- To track improvement, schedule frequent follow-up sessions with the neurosurgeon.
- Compliance with prescribed medications, including pain medications and blood pressure medications.
- Regaining strength and better coordinating your body's movements via physical therapy.
- Wearing a helmet for six weeks following surgery to protect the head from injury.
- Follow up imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans for monitoring of any postoperative changes.
- Avoiding strenuous activities for several months until cleared by a physician.
What is the cost of Brain Aneurysm treatments in India?
Generally, treatments such as surgery and endovascular coiling can range from Rs. 50,000 to Rs. 3 lakhs or more. Other treatments such as embolization, radiosurgery and stent placement can range from Rs. 1 lakh - Rs. 5 lakhs or more. In addition, costs for hospital stay, post-operative care and medications can add up to the overall treatment cost.
What are side-effects of Brain Aneurysm treatments?
The side effects of brain aneurysm treatments vary depending on the type and severity of the aneurysm. Common side effects may include:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Neck pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Seizures or loss of consciousness (occasionally)
- Fatigue and confusion
- Visual changes, such as double vision, blurred vision or blindness in one eye (rarely)
- Speech problems.
- Difficulty with coordination and balance.
- Challenges swallowing.
Brain Aneurysm - Outlook/ Prognosis
In order to avoid problems like 'subarachnoid haemorrhage, hydrocephalus, neurological impairments,' which may take months or years to cure depending on how severe the condition is, you should visit a doctor in your area if you have any symptoms related to brain aneurysms.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Vascular Surgeon near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors