Bronchi (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Dec 05, 2022
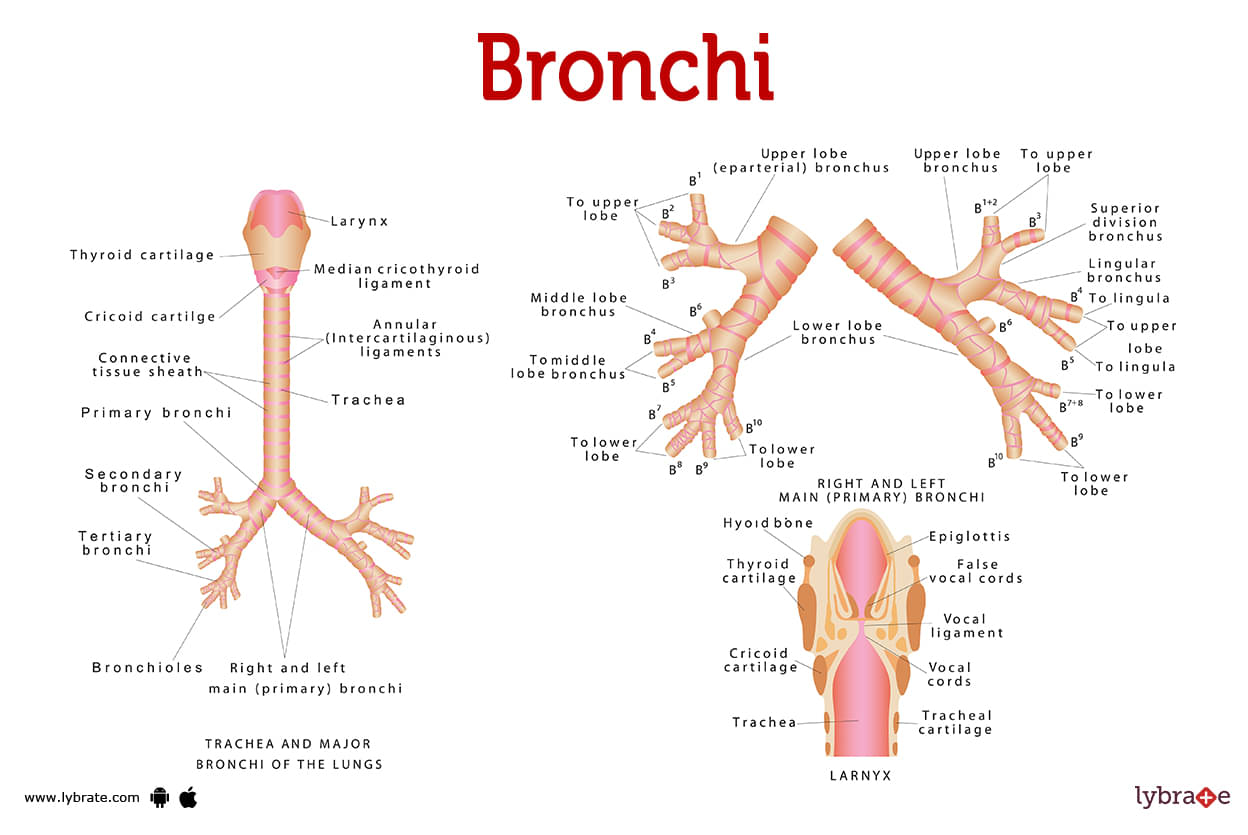
Bronchi Image
The bronchi are two big tubes that connect your windpipe to your lungs. Each lung has a left and right major bronchus. These tubes branch out from the major bronchi into segments that resemble tree branches. Asthma and bronchitis are just two of the many respiratory conditions that can affect your bronchi.They're in your chest.The plural version of bronchus is bronchi. The left bronchus transports air to the left lung. The right bronchus transports air to the right lung. Your bronchi are an important component of your respiratory system. Your lungs enlarge and your bronchi distribute air throughout your lung as you breathe.
What is the tracheobronchial tree?
The tracheobronchial tree connects the nasal cavity to the bronchi and lungs and the exchange of gases(oxygen and carbon dioxide) occur there. Your tracheobronchial tree consists of:
- Your neck is the beginning of your trachea.
- Bronchi: which is in between and important part of trachea.
- Your bronchioles are the lowest part of your bronchi.
What are the parts of the bronchi?
Your bronchi have two main (or primary, or first) parts:
- Your right lung's right main bronchus is a small, wide airway. A long, skinny passageway into your left lung is called the left main bronchus.
- The right and left major bronchi are the bronchial branches that are the widest.Your bronchi then split into progressively smaller branches, beginning with:
The lobar bronchi, which enter one of the lobes of your lungs. the lobes' segmental bronchi, which go across each segment. The smallest parts of your bronchi are called bronchioles.
What do the bronchi look like?
The trachea serves as the tree's trunk in your tracheobronchial tree, while the bronchi serve as its branches. Both right and left major bronchi divide into smaller pieces as they move deeper into your lungs. Like this, tree branches split off and get smaller and smaller until they reach the leaves.
Where are the bronchi located?
- There are bronchi in both of your lungs.
- The left and right main bronchi in the upper part of your lungs are referred to as primary (first) bronchi.
- Also known as lobar bronchi, secondary bronchi are located close to the centre of your lungs.
- Segmental bronchi,also referred to as tertiary (third) bronchi, have been situated at the periphery of your lungs right before the bronchioles.
What is gas exchange?
Oxygen gets into your bloodstream as you breath. As you exhale, carbon dioxide is released. The process is known as a gas exchange.You have around 480 million alveoli to perform this critical function.
Bronchi Functions
The bronchi are the tubes that bring and take away air from your lungs. The bronchi also serve as a filter, clearing the air you breathe of dust and other impurities. Mucus-producing cells line your airways. Your airways will stay wet thanks to the mucus.
Additionally, it serves to shield the lungs from invading bacteria, viruses, fungus, and other particles by capturing them. Tiny hairlike structures called cilia border the bronchi. The cilia assist transport mucus (phlegm) and pollutants out of your lungs. Whenever you cough or swallow, the mucus and the particles it contains are expelled from your body or moved into your digestive system.
How do your bronchi work with your respiratory system?
As part of the respiratory system, the bronchi are essential to proper breathing. To put it simply, each time you take a breath:
- From your mouth, air goes to your trachea.
- Your trachea splits into two tubes called bronchi, one on each side.
- The bronchi transport air to the lungs.
- The air is transported to the tiny sacs called alveoli in your lungs by bronchioles at the end of the bronchi.The alveoli are responsible for gas exchange in your body.
Bronchi Conditions and Disorders
- Asthma: Inflammation of the airways that is chronic and makes it difficult to breathe.
- bronchiectasis: when mucus is brought up through coughing as a result of the bronchi becoming wider and scarred.
- Bronchitis: Inflammation or infection in your bronchi that lasts for a short time (acute) or for a long time (chronic)
- Bronchiolitis: A lung infection caused by a virus that affects the bronchioles.
- Pneumonia: A severe infection of the lungs that, in most cases, develops after an initial bout with the common cold or the influenza.
- Tuberculosis: An infection that is brought on by the bacterium that causes tuberculosis.
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: A condition that affects a baby's breathing and occurs as a result of their lungs not developing as they should.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): a collective term for a range of respiratory issues brought on by lung inflammation. These diseases include bronchitis and emphysema.
- Cystic fibrosis: a hereditary disorder in which the body secretes unusually thick and sticky mucus
- Exercise-induced asthma: Exercise-induced asthma develops when someone's airways become more susceptible to constriction as a result of greater exertion.
Bronchi Tests
- Bronchoscopy: the insertion of a short, flexible tube with a camera inside your bronchi to acquire a better understanding of what is occurring there.
- Bronchoscopy with endobronchial ultrasound: Introducing a small, flexible tube equipped with a camera into your bronchi in order to get a better look of what's going on within.
- Bronchoscopy with Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL): A process that involves the use of a specific liquid to remove mucus and other debris from your bronchi by means of suction.
- CT scans: The use of X-rays and specialised computers gives medical professionals the ability to view the lungs from a variety of perspectives.
- Endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS): a kind of bronchoscopy which can be utilised to find inflammation or cancer.
- Exhaled nitric oxide test: The level of inflammation in your bronchi can be determined by your doctor by measuring the amount of nitric oxide you exhale.
- Spirometry: Keeping a log of how much air you can hold in your lungs as well as how forcefully you can exhale that air is an important part of lung capacity training.
Bronchi Treatments
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: A course that teaches you how to lead a healthier lifestyle and makes it easier for you to improve your breathing.
- Thoracotomy: It is an operation that takes place in the thorax region of the chest. Done in order to treat several potentially life-threatening conditions of the lungs, which can be identified through a lung biopsy..
- Video-assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS): This refers to a variety of procedures performed on the chest wall to treat a variety of lung conditions. This endoscopy is performed beforehand to ensure a good vision.
- Open thoracotomy: When the patient does not want to undergo chemotherapy or radiation therapy but has a significant amount of cancer or another infection in their lungs.
- Keyhole thoracotomy: An incision is made just below the breastbone during this type of surgery that is considered minimally invasive. Without having to go through the chest wall, medical professionals are now able to see and treat the entirety of the lung.
- Thoracentesis: A medical procedure in which a doctor uses a needle and syringe to extract fluid, pus, or other material from the lungs of a patient.
- Pneumonectomy: The complete removal of one or both lungs using surgical means.
- Chest Tube (Thoracostomy): An incision is made in the patient's chest wall for the purpose of performing this procedure, during which any excess fluid in the chest wall is drained.
Bronchi Medicines
- Steroids for reducing inflammation of Bronchi: Budesonide is a corticosteroid medication that is prescribed to patients suffering from asthma as well as other lung conditions. In addition to its use in the treatment of asthma and other lung conditions, the corticosteroid medication mometasone furoate is also available. One of the most common corticosteroid medications utilised in the treatment of COPD is fluticasone propionate.
- Analgesics for pain in Bronchi: Ibuprofen is an NSAID used to treat pain ailments such as headaches, muscle pains, and others. Piroxicam is an NSAID used to treat knee, hip, and arm pain.
- Antibiotics for infection in Bronchi: Antibiotics like amoxicillin can be used to treat a broad variety of illnesses, including those caused by bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Amoxicillin coupled with another antibiotic known as clavulanate potassium. Also referred to simply as 'amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium.' Cefuroxime axetil is a type of cephalosporin antibiotic that is utilised in the treatment of a wide range of illnesses, one of which being bronchitis.
- Antivirals for treating infection of Bronchi: Zidovudine is used to treat HIV as well as a variety of other infections. HIV infection as well as a number of other infections are treated with atazanavir. Lamivudine is additionally utilised in the treatment of hepatitis B.
- Chemotherapeutic medicines for Bronchi: Cisplatin is a medication that is used in the chemotherapeutic treatment of a wide variety of malignancies. Axitinib as well as other types of cancer drugs Pemetrexed is effective against a wide variety of malignancies, including cancer.
How common are conditions that affect the respiratory system?
Some respiratory diseases are among the most common illnesses in the world. Approximately:
- The number of persons with asthma is 334 million.
- COPD affects 65 million people worldwide.
- Tuberculosis is an insidious lung infection that affects 10.4 million people worldwide.
How can I keep my bronchi healthy?
The bronchi, lungs, and rest of your respiratory system will thank you if you do these things to maintain their health:
- Get and stay at a healthy weight for your age, body type, and gender.
- Avoid being around smoke.
- You should keep your house clean and change the air filters often.
- If you spend a lot of time around dust, allergens, or chemical fumes, wear protective gear like a face mask.
- Maintaining good oral and hand hygiene, avoiding crowds during flu season, getting an annual flu shot, and asking your doctor if a pneumonia vaccine is appropriate for you are all ways to prevent respiratory infections.
When should I contact my physician for bronchi conditions?
If you start to have difficulties breathing, you should contact health care services or go to the local emergency room. Here are some warning signals of breathing difficulties:
- Around or inside of your mouth, you can be bluish, grey, or pale. Retractions of the chest occur when the chest seems to sink in with each breath.
- Breathing more quickly for no apparent reason. Grunting. nasal flare without a rise in body temperature, sweating
- Wheezing (a tight whistling sound while breathing out) (a tight whistling sound while breathing out).
Table of content
Find General Physician near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors