Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
About
Health Feed
Find Doctors
Capillaries (Human Anatomy): Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
Last Updated: Nov 28, 2022
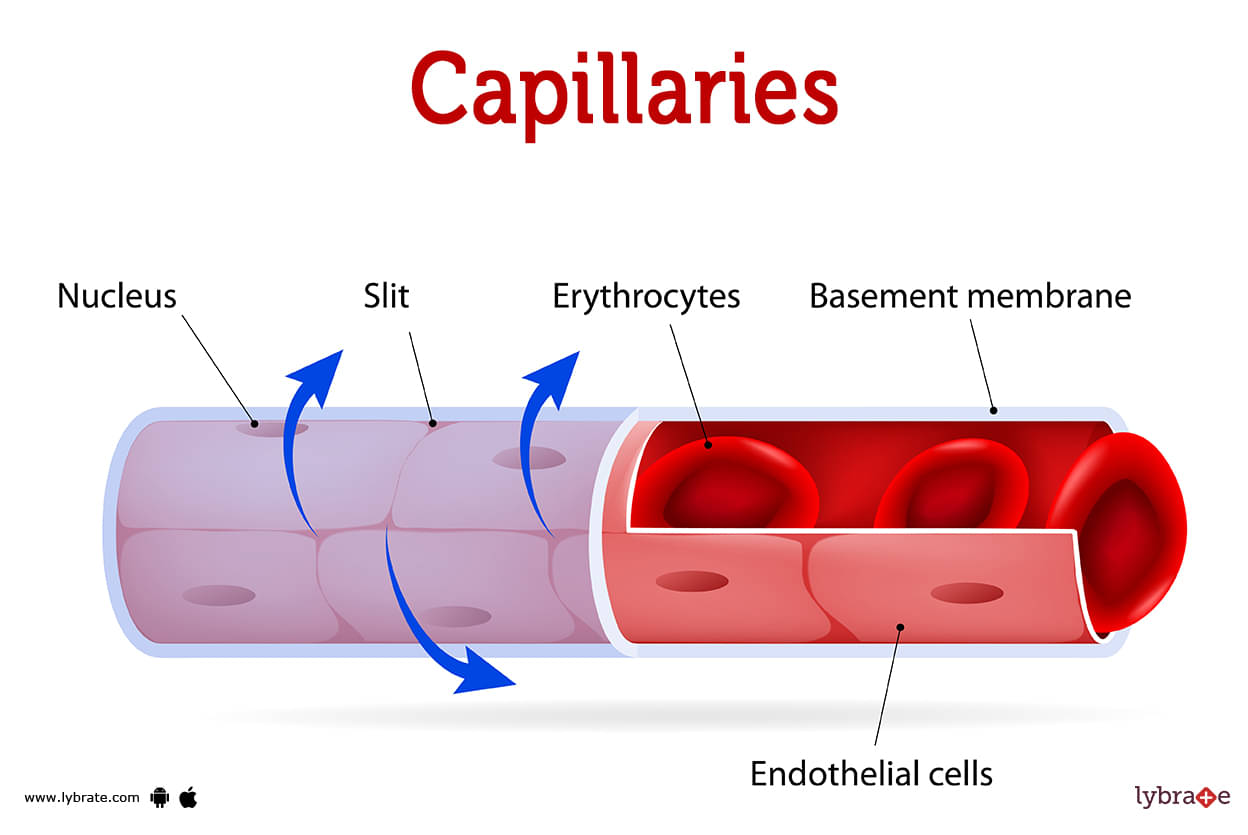
Capillaries Image
Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels in the body, connecting the tiniest arteries and veins. These tiny blood vessels are called 'microcirculation' because they move oxygen and nutrients to all of the body's cells and remove carbon dioxide so it can be released. Other parts of circulatory system are helpful in transporting blood to the capillaries some of which includes: Arteries,Viens and Capillaries.
Capillaries Functions
- Capillaries make it possible for gases, fluids, and nutrients to move through and exchange places in the body. Even though the arteries and arterioles carry these substances to the capillaries, the exchange happens in the capillaries.
- The capillaries take in carbon dioxide and waste products, which are then sent to the kidneys, liver, and lungs, in that order (for carbon dioxide emission).
- Healthy brain tissue is protected from harmful substances by the blood-brain barrier . A structure gets these molecules to the brain and keeps harmful things out at the same time.
- Hormones are sent to the right places in the body by the endocrine system. In order to create urine, the kidneys absorb water and sodium through the peritubular capillaries. With the help of the liver's ability to get rid of damaged RBCs and harmful substances.
- Lungs, which accomplish this by absorbing carbon dioxide and exhaling oxygen. The lymphatic system picks up fluid from the tissues and sends it to the lymph nodes. The small intestine moves nutrition from your digestive tract to the cells of your body.
- Inside capillaries, endothelial cells line the inside walls. They control how much oxygen, food, and other things get to the plant. Endothelial cells are surrounded by epithelial cells, which keep outside substances out.
- Most capillaries are only 8 to 10 micrometres wide (a micrometre is 0.001 mm). Since RBCs are so little, it stands to reason that they could squeeze through even the tiniest doorway. A capillary has two layers of cells .
- Capillaries come in three different shapes that let them do different things:
- Small openings (fenestrae) in continuous fenestrated capillaries allow for quick substance exchange . The kidneys, small intestine, and endocrine glands all contain this kind of capillary .
- In continuous, non fenestrated capillaries, only very tiny molecules can diffuse past the cell wall. The extracellular matrix of muscles contains this form of capillary, and it is also found in the neurological system.
- Certain chemicals are able to flow through the tiny fenestrae found in sinusoidal capillaries. You'll find this capillary type in your liver and spleen.
Capillaries Conditions and Disorders
- Systemic capillary leak syndrome: Unknown causes or treatments exist for the uncommon, perplexing condition known as systemic capillary leak syndrome (SCLS) . The capillary walls are corroded, and experts think it may be due to a chemical in the blood.
- Port wine stains: Dilation of blood vessels underneath the skin causes birthmarks with the appearance of port wine. The spreading of this disease gives the skin a pink or dark red appearance, hence the name. With time, they may thicken up and darken up.
- Petechiae: A petechiae is a tiny, red dot that appears on the skin after an injury. These flat, pinhead-sized bumps can be found in a wide range of red and purple tones and typically sit flush with the skin. Capillary rupture is the underlying cause of these skin discolorations. They won't magically turn white if you squeeze them.
- Arteriovenous malformation syndrome: Direct connections between arteries and veins, rather than capillaries, are what medical professionals call arteriovenous malformation syndrome (AVMS). Although these tangles can manifest themselves elsewhere in the body, the CNS is particularly prone to them.
- Microcephaly-capillary malformation syndrome: The syndrome of microcephaly and capillary malformation is a congenital condition that affects a tiny fraction of the population. Affected individuals experience a reduction in both head and brain size. In addition, the increased blood flow at the skin's surface caused by their dilated capillaries causes the affected area to appear pink or red.
- Capillary angiosarcoma: Capillary angiosarcoma (also known as endothelial cell carcinoma) is a cancer that can develop in the lining of blood vessels.
- Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is an inherited condition of the blood arteries that causes the formation of abnormal growths (telangiectases) which are vulnerable to bleeding. Other names for this illness include Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome.
- Macular degeneration: Central vision is lost as a result of macular degeneration . Dry macular degeneration is characterised by damage to the macula of the retina. Wet macular degeneration, in its simplest form, is characterised by the formation of leaking capillary tubes under the retina.
- Spider nevus: Often found on the face, neck, or chest, spider nevi are clusters of tiny blood capillaries that branch off from a larger vessel. This disorder goes by a number of different names, including spider telangiectasia and spider angioma.
- Strawberry birthmark: Most people refer to red birthmarks as strawberry nevi (hemangiomas). The collection of blood vessels immediately under the skin's surface is responsible for this pinkish-red hue. They are extremely common among newborns and toddlers.
- Vasculitis: Capillaritis is the initial stage of vasculitis, an inflammatory illness of the blood vessels. Rupture and obstruction are two examples of probable complications.
Capillaries Tests
- Capillary refill test: The circulation in the extremities can be quickly and easily measured by the capillary refill time (CRT). Detecting tissue dehydration and blood circulation can be accomplished with a simple test of the nail bed. The CRT checks how well the circulation system works in the extremities as they are located so far from the heart.
- Magnetic resonance angiography: MRAs, or magnetic resonance angiograms, are a subset of MRI that focus specifically on the blood vessels. When compared to a conventional angiogram, which merely requires putting a catheter into a blood vessel, magnetic resonance angiography is both more expensive and more uncomfortable.
- CT angiography: An injection of contrast dye and a CT scan are both used in the diagnostic process known as CT angiography to provide images of the blood vessels as well as other tissues in a particular body part. An IV line is inserted into your hand and arm to deliver the dye.
Capillaries Treatments
- Intravenous immunoglobulin infusions: these are helpful in treating subsequent instances of capillary leak syndrome.
- Laser therapy: By directing laser light at the blood supply beneath a single dilated capillary, a laser treatment called 'capillary elimination' can correct the condition. The laser's tremendous heat may cause capillary walls to burst. The capillary vessel will be eliminated by the lymphatic system along with other waste items.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is a medication therapy that uses potent chemicals to destroy the body's rapidly dividing cells. Chemotherapy is the main treatment because cancer cells proliferate and multiply a lot faster than other types of bodily cells. There are many different chemotherapy drugs available.
- Immunotherapy: Patients with cancer might benefit from immunotherapy, a form of treatment that activates the body's natural defences against illness. Your immune system aids your body's defences against infections and other diseases. White blood cells, lymph system organs, and tissues make up the immune system. Immunotherapy is a type of biological therapy, to use a medical phrase.
- Bone marrow transplantation: A medical technique called a bone marrow transplant involves injecting healthy donor cells into the bone marrow of the patient. The new cells come from either the recipient or a donor.
Capillaries Medicines
- Steroids for lowering capillary inflammation: Glucocorticoids are drugs that are used to treat malignancies that are immune-related, such basal cell carcinoma, which cause inflammation. Examples of drugs that are related to cortisone include prednisone, betamethasone, and dexamethasone.
- Analgesics for pain in Capillaries: The class of drugs known as analgesics, also referred to as painkillers, includes drugs including aspirin, acetaminophen, and ibuprofen. When there is a capillary perfusion and rupture condition, they are employed to treat pain.
- Statins for preventing capillary stenosis: Atorvastatin, Fluvastatin, Lovastatin, Pitavastatin, Pravastatin, Rosuvastatin, and Simvastatin are oral cholesterol-lowering drugs. By reducing cholesterol in the capillaries, statins have the ability to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, such as heart attacks and strokes, when chosen to be taken continuously and as directed by a professional.
- Antibiotics for infection in Capillaries: These are the drugs that stop the development of bacteria. Penicillin, ceftriaxone, and cephalosporins are common antibiotics.
- Supplements for promotion of growth at the time of rupture of Capillaries: Supplements are helpful if the body needs to expand and restore its arterio venous architecture. When there are issues with microcytic or macrocytic anaemia, the administration of iron, folic acid, ferrous sulphate, ferrous ascorbate, and zinc is useful in stimulating red cell growth.
- Antivirals for treating infection of Capillaries: as someone who has a severe viral infection brought on by rheumatic or herpes disease Some examples are aciclovir, valaciclovir, famciclovir, penciclovir, cidofovir, foscarnet, and immune response modulator.
How do I care for my capillaries?
- To safeguard your capillaries, improve your vascular health. maintaining an active way of life.
- lowering your caffeine and alcohol intake.
- maintaining a healthy weight
- If you smoke, you should give it up.
- Remaining compliant with chronic disease management and preventive care can help lower your risk.
- Diabetes, high levels of cholesterol, high blood pressure, stress, the rupturing of capillaries, enlarged blood vessels in the legs, numbness or tingling may be present on one side of your body, leg ache after light exercise vision abruptly changes are all potential danger signs and signs of capillary diseases.
Delhi
Mumbai
Chennai
Bangalore
Index
Table of content
Content Details
Written ByDrx Hina FirdousPhD (Pharmacology) Pursuing, M.Pharma (Pharmacology), B.Pharma - Certificate in Nutrition and Child CarePharmacology
Reviewed By
Find Vascular Surgeon near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously