Carotid Artery (Human Anatomy): Picture, Definition, Conditions, & More
Last Updated: Feb 25, 2023
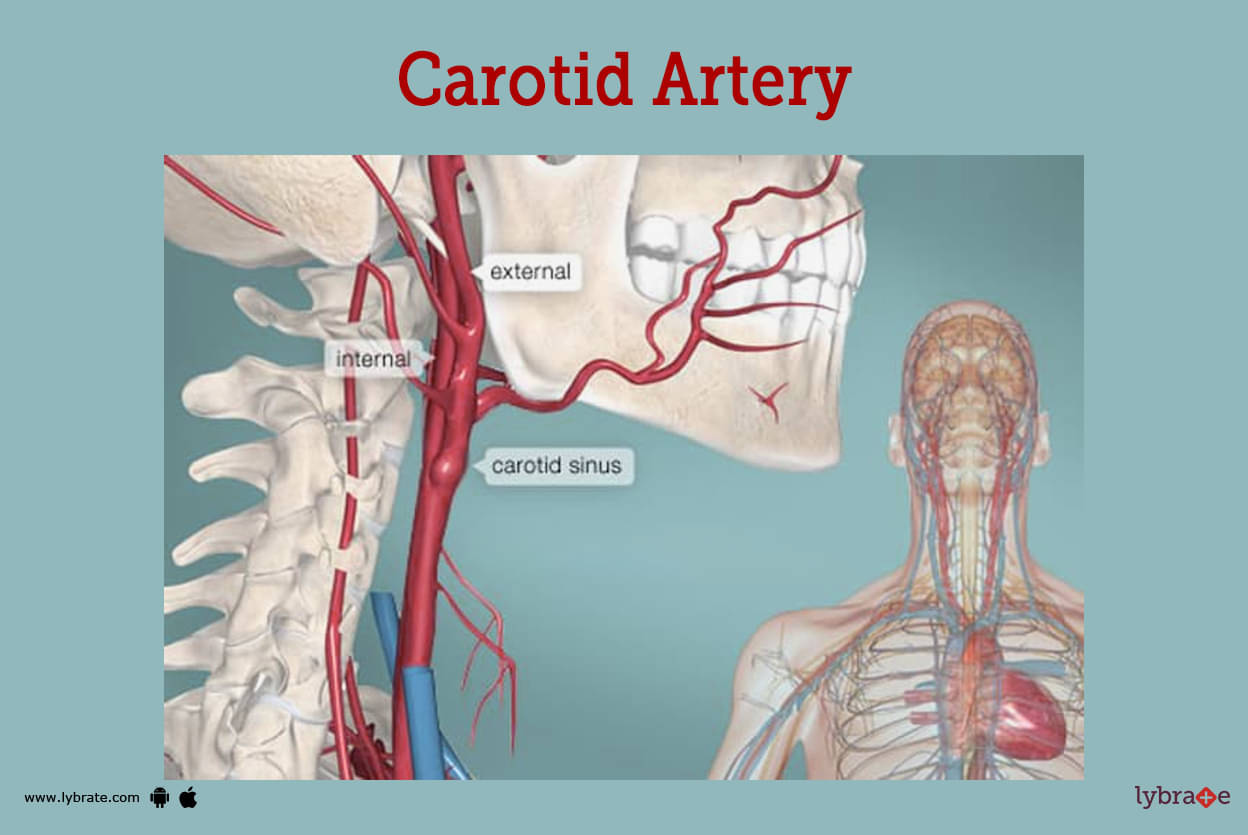
Carotid Artery Image
The carotid arteries are divided into two types: right and left. They are the main arteries of the head and neck, carrying blood to the brain, neck, and face. It is the origin of the right common carotid artery which is called as brachiocephalic trunk present just behind the sternocleidomastoid joint.
The left common carotid artery begins at the aortic arch, which is located in the upper part of the middle chest. It travels forward until it reaches the posterior aspect of the left sternoclavicular joint, at which point it enters the neck. There are no branches that come out of the internal carotid artery in the neck.
The external and internal carotid arteries are the only two terminal branches that arise from the common carotid artery. These arteries are situated on the sides of the neck on either side of the head. There are eight tributaries that originate from the external carotid artery.
- Superior Thyroid Artery
- Facial Artery.
- Posterior Auricular Artery.
- Maxillary Artery.
- Lingual Artery.
- Occipital Artery.
- Ascending Pharyngeal Artery
- Superficial Temporal Artery
Functions of Carotid Artery
The carotid artery is a large blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the brain and face. Its main functions are:
- Blood supply to the brain and other structures within the skull and eye sockets: The carotid artery carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the brain and other structures within the skull and eye sockets, providing vital nutrients and oxygen to the brain cells.
- Blood pressure regulation: The carotid artery plays a role in regulating blood pressure by sensing changes in blood pressure and sending signals to the brain to adjust heart rate and blood vessel size accordingly.
- Monitoring blood oxygen levels: The carotid artery has special receptors that monitor the oxygen levels in the blood and send signals to the brain to adjust breathing rate if necessary.
- Provide a Warning sign of disease: The carotid artery can be used as a warning sign of diseases such as atherosclerosis, which is the build-up of plaque in the artery, this can lead to a stroke if a piece of plaque breaks off and blocks the blood flow to the brain.
Overall, the carotid artery is a vital blood vessel that plays an important role in supplying oxygen and nutrients to our brain, regulating blood pressure, and monitoring blood oxygen levels. It is also a warning sign for some serious diseases like atherosclerosis.
Carotid Artery Conditions
- Carotid artery vasculitis: Inflammation of the carotid artery, which can be brought on by either a disorder that affects the immune system or an infection. This medical disorder is referred to as vasculitis of the carotid artery.
- Stroke: A stroke may be brought on by a sudden blood clot that forms in the carotid artery, which can prevent blood from flowing to the brain. It is possible for pieces of cholesterol plaque that have formed in the carotid artery to break off and go into the brain, which would then result in a stroke. This is something that might take place at any point in the life of the patient.
- Carotid artery stenosis: Stenosis of the carotid artery is a narrowing of the carotid artery, which is typically caused by the deposition of cholesterol plaque, which is also known as atherosclerosis. Stenosis of the carotid artery is associated with an increased risk of stroke. In the majority of instances, signs and symptoms won't become apparent until the disease has moved to a more advanced stage.
- Carotid artery aneurysm: When there is a weak spot in the carotid artery, which causes a portion of the artery to expand out like a balloon with each beat of the heart, aneurysm of the carotid artery can occur. This condition is also known as a carotid artery dissection. Aneurysms carry the risk of rupturing, which, in the event that it does take place, could result in a stroke or major bleeding.
- Carotid artery embolism: An embolus is a piece of cholesterol plaque that has broken away from the carotid artery wall and travelled all the way to the brain, where it has caused a stroke in the patient. This can happen if the cholesterol plaque breaks apart. This medical ailment is referred to as an embolism of the carotid artery.
- Carotid artery atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis of the carotid artery is characterised by the slow accumulation of cholesterol plaque in the wall of the carotid artery over the course of several decades. At some point throughout the progression of atherosclerosis, this process will take place. Plaque that has accumulated in the carotid artery has the potential to eventually produce stenosis, commonly known as a narrowing of the artery, which can lead to a stroke if left untreated.
- Amaurosis fugax: One eye is affected by the type of temporary blindness known as amaurosis fugax. The most common cause of this condition is an embolus, which is a piece of cholesterol plaque that becomes detached from the carotid artery wall and travels through the bloodstream. It is possible for the embolus to become trapped in an artery that provides blood to the eye, which would then restrict blood from flowing to the eye.
- Temporal arteritis: This particular kind of vasculitis is known as temporal arteritis, and it manifests itself clinically as inflammation of the branches of the carotid artery. This illness is brought on by a disorder that affects the immune system. A high temperature, a severe headache that is localised to one side of the head, and pain in the jaw that is exacerbated by chewing are some of the symptoms.
- Carotid hypersensitivity syndrome: Carotid hypersensitivity syndrome is a condition in which putting pressure on the carotid sinus of some individuals might cause them to pass out due to a sudden drop in their blood pressure. Carotid hypersensitivity syndrome is a condition that can be caused by a genetic predisposition. It is possible for symptoms to manifest themselves when shaving or when wearing a shirt collar that is excessively snug.
- Carotid Artery Blockage: Carotid artery blockage is a condition that occurs when fatty deposits known as plaques obstruct the blood vessels that supply blood to your brain and head. This condition is also known as atherosclerosis (carotid arteries). Your risk of having a stroke, which is a medical emergency that occurs when there is a disruption in the blood supply to the brain or when the blood supply to the brain is significantly reduced, will increase as a result of the blockage. When there is a temporary blockage in the blood flow to the brain or when there is a considerable reduction in the blood supply to the brain, this can cause a stroke.
- Peripheral arterial occlusion: It is a condition of the carotid artery in which the carotid artery becomes narrowed, resulting in a reduction in the amount of blood that flows to the limbs. This condition is known as carotid artery stenosis.The development of peripheral vascular disease as a result of this process is caused by the accumulation of fatty deposits and calcium in the arterial walls. The technique is directly responsible for bringing forth this situation.
- Raynaud's phenomenon: A medical condition in which certain parts of the body, when exposed to certain temperatures, experience a tingling or numbing sensation in those parts of the body. Raynaud's phenomenon is characterised by a reduction in the amount of blood that is able to reach the affected area as a consequence of an excessive constriction of the branches of the carotid artery that supply blood to the skin in response to cold temperatures.
- Carotid artery Aneurysm: A bulge in one of the arteries that supplies blood to your brain and other structures in the immediate area is known as an aneurysm of the carotid artery. Atherosclerosis is one of the most prevalent causes of cardiovascular disease and can occur for a number of different reasons. Some people don't experience any symptoms at all, while others may have facial swelling, hoarseness, or a lump in their neck that they can feel throbbing. However, there are some people who don't have any symptoms at all.
Carotid Artery Tests
- Carotid artery ultrasound: The carotid artery is scanned by placing a probe on the patient's skin and then viewing the reflected sound waves on a screen. Carotid infarction, blood flow, and the presence of necrosis or stenosis can all be evaluated using this test.
- Carotid duplex ultrasound: It is the gold standard for detecting any kind of stenosis or necrosis and also the obstruction of the carotid artery by any nodule or epithelial protrusion, and it is used to scan the flow of blood in the carotid artery. Carotid artery angiography, known as an angiogram: In this specific sort of investigation a contrast is injected into the carotid artery by a trained cardiologist and image is formed through X-rays of that part it is a better method to find stenosis and aneurysm of the carotid artery.
- Computed tomographic angiography (CT-A scan): During the course of a CT scan, numerous x-ray pictures are obtained. These pictures are collected with the assistance of a computer in order to get more detailed views of the arteries. It is performed to scan the arteries in order to determine whether or not there is any narrowing or other abnormalities present in the arteries, and it has a lower risk than traditional angiography.
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA scan): An MRI scanner combines a powerful magnet with a computer to produce pictures of the structures found within the human body that are very detailed. The MRA (magnetic resonance angiography) setting on an MRI scanner is what provides the clearest views of the arteries possible.
- Carotid sinus massage: A doctor or a specialised physician will massage the patient's neck directly over the carotid sinus in an environment that is safer and more controlled. This type of maneuver is a tried-and-true method for diagnosing disorders of the carotid sinus as well as abnormal heart rhythms.
Carotid Artery Treatments
- Pre op embolization: An embolization of the carotid artery is performed prior to vascular graft repair or any other kind of graft repair in order to prevent the overflow and loss of blood during the time of surgery. This is a preventive procedure that is done in order to have a successful outcome from the surgery.
- Carotid artery replacement: it is a process in which after endardectomy of carotid artery vascular graft is placed after which a stent can also be placed to prevent further embolism and obstruction.
- Sclerotherapy: It is a minimally invasive process in which anti-sclerotic solutions are used to treat embolization of the branches of the carotid artery. It is a gold standard approach for stroke and carotid artery surgery.Carotid artery bypass grafting: it is a surgery done after carotid artery bifurcation stenosis in this a bypass is produced which shifts the flow of blood from carotid artery bifurcation to the graft of bypass.
- Carotid endarterectomy: a surgical procedure that widens the carotid artery when cholesterol plaque has produced a narrowing, also known as stenosis. A vascular surgeon will make an incision in the carotid artery, remove any plaque that is present, and then stitch the artery back together.
- Dacron graft repair: The most popular and reliable approach for the replacement of a blood artery that supplies blood to the carotid arteries is to use a Dacron aortic transplant. Patients who underwent surgery to have tubular Dacron grafts inserted continue to have normal functioning aortic valves 15 years after the procedure. The majority of these patients' aortic valves function normally.
- Vascular graft repair: The stent graft ensures that the carotid artery, both above and below the aneurysm, is completely closed up. Because the graft is stronger than the weaker artery, blood may flow through it without any problems.
- Carotid artery stenting: A wire is threaded through an artery in the leg all the way up to the carotid artery, where it is connected to a thin wire tube, also known as a stent. The stent is then stretched inside a constriction in the carotid artery. Individuals diagnosed with carotid artery stenosis who are not good candidates for endarterectomy may nevertheless be candidates for carotid artery stenting.Carotid artery medicines
- Statins for preventing carotid artery stenosis: these are Cholesterol lowering medicines taken orally like atorvastatin fluvastatin, lovastatin , pitavastatin ,pravastatin, rosuvastatin , simvastatin When taken consistently and as directed by a specialist, statins have the potential to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes.Aspirin for preventing embolism of carotid artery: It contains analgesic and pain-relieving characteristics, as well as antipyretic(fever-reducing) properties and it also interferes with the process that causes blood to clot. If taken on a regular basis, it may reduce the risk of both heart attacks and strokes.
- Clopidogrel (Plavix) for preventing thrombosis of carotid artery: It disrupts the process through which the blood clots. It is routinely administered to patients who have recently had a heart attack or stroke in order to reduce the risk of having a similar incident in the future.
- Ca Channel Blocker acts as a Hypertension Blocker: It is known for reducing blood pressure, which prevents embolism and damage to the carotid artery. It also prevents angina and is helpful in decreasing symptoms of Raynaud's phenomenon. Some of the commonly used calcium channel blockers are Amlodipine, Nicardipine, Nifedipine, Nimodipine, etc.
- Hydralazine for reducing hypertension: The antihypertensive effects of hydralazine come from its ability to promote arteriolar vasodilation, which lowers blood pressure. It is helpful in decreasing the pressure from the carotid arteryNitrovasodilator for visual dilation of arteries: It is acting as a vasodilator, which assists in lowering hypertension and relieving pressure on the carotid artery. Some examples of similar medications are nitroglycerine and isosorbide mono- and di-nitrate.
- Glycosides for carotid arterial contractility: Digoxin, an inhibitor of Na'/K' ATPase, causes a rise in the calcium and contractility of the heart muscle, as well as an increase in vagal tone.
- Ranolazine for carotid arterial hemorrhage: The medication ranolazine, which is used for chest discomfort, inhibits late Na current. This lowers diastolic wall tension and the amount of oxygen the heart needs to function.corticosteroids for treating vasculitis of arteries: Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as prednisone or methylprednisolone, are frequently utilised in the treatment of vasculitis, a condition that impacts the arteries.
- Thrombolytics for thromboembolism of arteries: It is administered intravenously as a powerful 'clot-busting' drug in order to break a blood clot and forestall a heart attack or stroke from developing as a direct result of the clot's presence in the body.
- Cilostazol and pentoxifylline for reducing stroke volume: They make the arteries in the lower extremities more receptive to the passage of blood by making them more permeable. Patients who suffer from peripheral vascular disease may discover that the discomfort they feel when walking is alleviated when they take these drugs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the warning signs of clogged carotid arteries?
What do they do if your carotid artery is blocked?
Can you live with a 70% blocked carotid artery?
How can I check my carotid artery at home?
How can I naturally unblock my carotid artery?
Does your neck hurt when your carotid artery is blocked?
How do you clear a blocked carotid artery without surgery?
Table of content
Find Vascular Surgeon near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors