Cerebellum (Human Anatomy): Image, Function, Diseases, and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 14, 2023
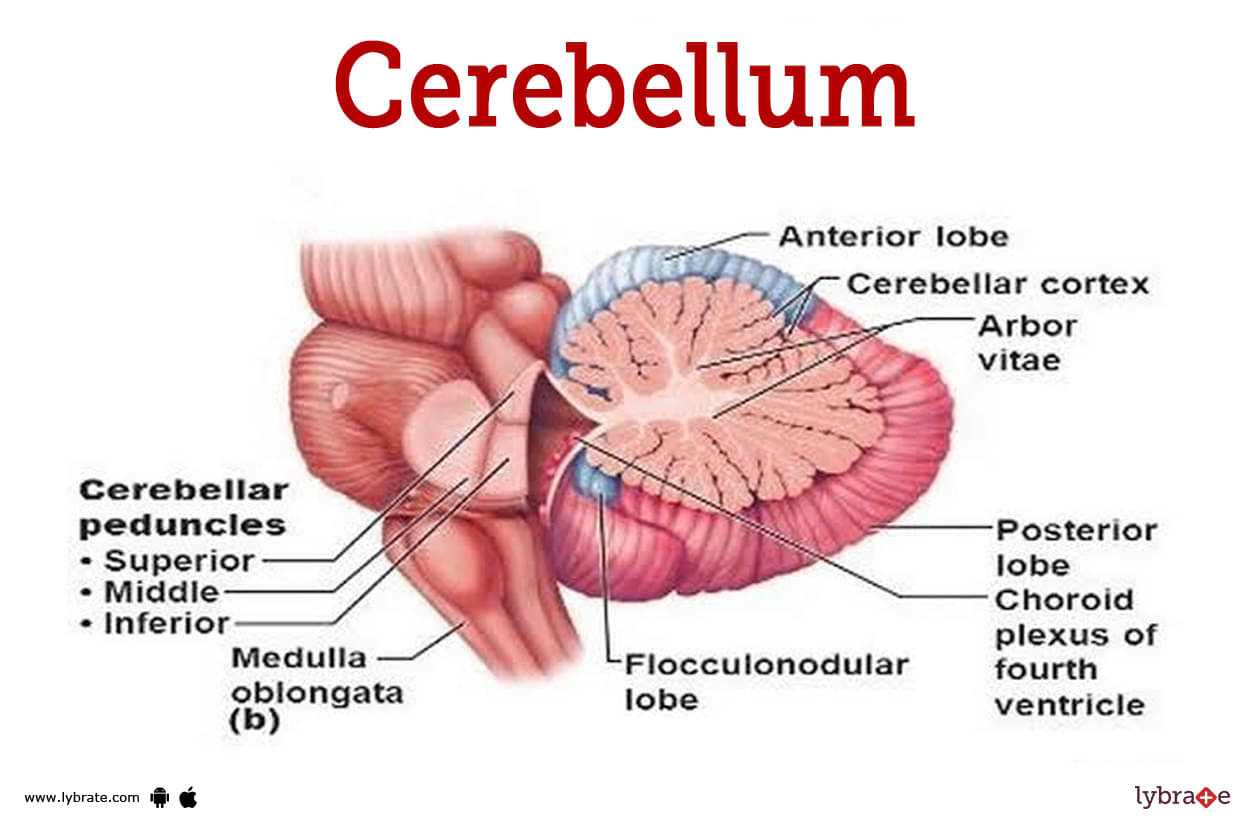
Cerebellum (or Little Brain) Image
It constitutes about 1/8th of the size of cerebrum (second largest part of brain) situated below occipital lobe connected with ventral brainstem by three peduncles, with the lateral halves, cerebellar hemispheres.
Cerebellum does not initiate but helps in maintaining proper posture, walking, running, voluntary movements as required during eating, dressing and writing. The cranial part of IV ventricle lies in pons Varolii. Drinking alcohol affects the cerebellum and it leads to uncoordinated movements of the body.
Its outer surface (cortex of gray matter) has a large number of gyri and sulci. Medullary solid part is filled with white matter called arbor vitae (tree of life). It acts as the executive of the cerebrum to run the initiated voluntary muscle actions.
Functions of Cerebellum
- The cerebellum plays an essential part in the coordination and regulation of the body's movements, which is particularly important while moving from one location to another.
- The cerebellum is a highly dense part of the brain that contributes to 80 percent of all neurons in the brain while only accounting for 10 percent of the total weight of the brain. It is involved in coordinating and contributing to higher levels of thinking as well as performing specific complex actions.
- The cerebellum is the part of the brain that is in charge of maintaining balance, as well as muscular coordination and muscle tone. Purkinje cells are specialised neurons that are located in the vermis region of the cerebellum. These cells have been described as having a flask-like form.
- Anatomically it consists of three parts have their own specific function and specific form of cells
- Archicerebellum (vestibulocerebellum): it helps in maintaining equilibrium and coordination of the eye movements head movements and neck movements and it is closely interconnected with the vestibular nuclei of the cerebellum.
- Midline vermis (paleocerebellum): it coordinates the trunk and the lower limb movements of the body also called as vermis helpful in maintaining the connection between the archicerebellum and neo cerebellum.
- Lateral hemispheres (neocerebellum): they are helpful in maintaining and coordinating the fast movements of the limbs and predominantly of the arms and the hands they are also responsible in coordinating the movement of the fingers.
Cerebellum Disorders
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: it is a rapidly progressive degenerative disorder in which abnormal isoform formation of cells and different regions of cerebellum occurs causing degeneration and necrosis of the cerebral network it is a very rare degenerative disorder which is fatal in nature
- Cerebellar Aneurysm: An aneurysm of the cerebellum arises when an artery in the cerebrum expands and takes on the form of a balloon as a consequence of internal pressure.
- Meningitis: It is the medical word for a disorder that develops when the layers of the brain or spinal cord become inflamed, most frequently as a result of an infection caused by meningitis. Symptoms include stiffness in the neck, discomfort in the neck area, headache, fever, and even lethargy.
- Traumatic Cerebellum Injury (TBI): It is an abbreviation for traumatic cerebellar injury, which refers to irreparable cerebellum damage caused by a traumatic accident. When schizophrenia is present, mental impairment, or mild personality changes (difficulty in analysing things), and mood changes may emerge.
- Dementia: Dementia is defined as a deterioration in cognitive ability caused by the loss or malfunctioning of nerve cells in the cerebellum, either directly or indirectly. Alcohol abuse (drinking of alcohol in an unhealthy way or in a quantity that exceeds the allowed range) and strokes are two probable causes of this illness, as other disorders such as cerebellar nerve degeneration.
- Cerebellum Abscess: A bacterial infection causes cerebellar abscess, which leads in the formation of a pocket in the region of the cerebellum affected by the abscess. In order to heal it, Antibiotics and surgical drainage of the afflicted area are required to treat the infection.
- Cerebellum Edema: Edema is the medical term for swelling in any region of the body, and cerebellum edema is the swelling of the brain tissue that occurs as a reaction to some damage or electrolyte imbalances. The region of cerebellum and the brain is called as hydrocephalus which also known as the feeling of fluid in the regions of the brain increasing the pressure of the cerebral vasculature.
- Multiple sclerosis (MS): it is a progressively increasing disease of the spinal cord and the brain and also affecting the peripheral nervous system of the body where there is a degenerative changes in the myelin sheath of the exons causing fatal redistribution of the neuronal pathways and also fluctuating neuronal degeneration. Open
- Dandy-Walker malformation: it is a rare congenital malformation of the cerebellum which involves degenerative deformation of the cerebellum and the 4th ventricle of the brain. During embryonic development when the 4th ventricle and the cerebral part isn't being developed there is a degenerative change in this process which causes this disease it causes partial paralysis and muscle fatigue and muscle stiffness of the lower limbs.
- Hereditary ataxias: it is a disorder in which a heterogeneous group of disorders is phenotypically characterize and it is usually associated with the atrophy of the cerebellum in this disorder there is decrease in the coordination of eye movements slurring of speech and impartial coordination of the hand movement is seen which increases through time.
- Alcoholic cerebellar degeneration: it is one of the most known type of acquired toxic ataxia in this disorder because of chronic alcoholism the degeneration of the cerebellum occurs and the people with thiamine deficiency are susceptible for this disorder.
- Medulloblastoma: it is the brain tumor of the cerebellum which could be a solid or partially solid mass formed in the cerebellum which primarily shows symptoms of occipital headache and in coordination between hand and leg movements and also slurring of speech and ataxia.
- Cystic astrocytoma: it is the congenital disorder of brain tumor occurring in 30% of the cases of glioblastoma and astrocytoma in which abnormal growth of cells in between the cerebellum occurs causing a solid or an impartial liquid mass information in cerebellum.
Cerebellum Tests
- Physical Examination: a physician can perform a specific physical examinations to check the coordination between hand and legs and also coordination of eye movements and the speech which includes checking of reflexes and also checking out the integrity of the joints and power of muscles and any sort of palpebral pain in the body
- CT Scan: Many X-rays of the patient are gathered during a computed tomography scan, often known as a CT scan, and these X-rays are then converted into comprehensive photographs of the patient's cerebellum with the help of a computer..
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging, sometimes known as an MRI scan, is an imaging technology that produces extremely detailed images of the cerebellum and other parts of the skull in order to provide a complete diagnosis. An MRI scanner operates by enclosing radio waves within a magnetic field.
- Angiography: A cerebellar angiography is a procedure that involves injecting 'a contrast agent' into the veins of a patient who is suspected of having a medical issue. This chemical then enters the cerebellum through the circulation. An X-ray of the patient's cerebellum is done to examine for the existence of any anomalies in the cerebellar arteries.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): MRA is an abbreviation for magnetic resonance angiography, which is a type of MRI scan that focuses on the arteries of the cerebellum. An MRA scan may reveal a blood clot or another probable cause of stroke.
- Lumbar Puncture: A lumbar puncture, sometimes known as a 'spinal tap,' is a treatment in which a needle is inserted into the area around the spinal nerves and fluid is extracted for analysis. A lumbar puncture is frequently performed when meningitis is suspected..
- Electroencephalogram Eeg: The electroencephalogram (EEG) is a technique for measuring electrical impulses in the cerebellum that includes inserting electrodes on the head. An EEG can help in the identification of seizures and other cerebellar disorders.
- Neurocognitive Testing: It is a term that refers to tests of a person's problem-solving ability, short-term memory, and a variety of other advanced cerebellar activities. Questionnaires are frequently used to test neurocognitive ability.
- Cerebellum Biopsy: A cerebellar biopsy is occasionally required to diagnose a cerebellum issue. This technique only necessitates a little piece of the patient's cerebellum.
Cerebellum Treatments
- Craniotomy: This operation is performed by a surgeon, who drills a hole through the side of the skull to release pressure within the skull. It is performed when there is some sort of infection causing excessive pressure in the brain and cerebellum
- Lumbar Drain: The lumbar region is drained when a drain is placed into the fluid that surrounds the spinal cord. This might reduce the amount of strain on the cerebellum and spinal cord.
- Radiation Therapy: If the cancer has spread to the cerebellum, radiation treatment may alleviate symptoms and halt disease progression.
Cerebellum Medicines
- Thrombolytics for cerebellum infarcts: If administered during the first few hours after the onset of symptoms, these treatments have the potential to reduce, and in some circumstances even cure, some types of strokes. During this operation, clot-busting drugs are injected directly into the patient's veins. In situations with apparent ischemia with noticeable deficits, this medication is given.
- Antiplatelet agents for thrombolysis of clots: Antiplatelet drugs are a type of therapy that can lower the risk of blood clot formation. Antiplatelet agents such as aspirin and clopidogrel are two medications (Plavix). As a result, there is a possible reduction in the likelihood of suffering a stroke.
- Cholinesterase inhibitors: These are a few medications that have shown some promise in improving patients' cognitive abilities, ranging from mild to severe Alzheimer's disease. They have no effect in preventing or delaying the progression of Alzheimer's disease.
- Levodopa for parkinson's disease: This medication is used to treat Parkinson's disease because of its ability to raise dopamine levels in the cerebellum and brain.
- Analgesics for migraine and headaches: Analgesics are medications used to relieve pain and reduce the amount of prostaglandins generated by the body. The drugs should be given no later than 48 hours after any cardiovascular event that produces discomfort at the time.
- Lipid-Lowering Agents for reducing cerebellum cholesterol: People who are at high risk of having cerebellar atrophy and thrombotic lesions that create plaques in brain arteries may benefit from taking statin drugs to decrease their cholesterol levels. These drugs include atorvastatin and rosuvastatin.
- Diuretics for maintaining cerebellum blood pressure: Diuretics such as Furosemide, Torsemide, Bumetanide, Hydrochlorothiazide, and Metolazone reduce the quantity of fluid transported through the system by increasing the amount of water ejected by urine and other ways, lowering the risk of any other cardiovascular event.
- Beta-Blockers for maintaining cerebellum blood pressure: Carvedilol, Bisoprolol, and Metoprolol succinate also reduce the pressure on the brain and cerebellum, which decreases the heart rate and aids in the prevention of a number of brain diseases such as infarcts and haemorrhages.
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACE Inhibitors) for maintaining blood pressure: Captopril, Enalapril, Lisinopril, Ramipril, and Trandolapril lessen the fluid load, making it simpler for the heart to maintain a steady stroke volume. They accomplish this by relaxing larger and smaller blood vessels.
- Angiotensin Receptor Blockers for maintaining cerebellum blood pressure: Valsartan and losartan cause a disruption in the metabolism of the angiotensin, which is in charge of controlling blood pressure and maintaining cardiac output. Some pharmaceutical salts are only used by highly skilled medical specialists.
- Aspirin as a blood thinner: It is the first drug that doctors use to prevent the formation of blood clots, lowering the risk of suffering a heart attack, aneurysm, or infarct.
- Warfarin as anticoagulant and Heparin as a thrombolytic: This class of drug inhibits the y-carboxylation of vitamin K-dependent coagulation components. It is beneficial in the treatment of stroke, haemorrhage, and cerebellar ischemia patients.
- Edaravone for cerebellum injury: The use of this drug slows the process of neurodegeneration and aids in the promotion of cerebellar development and vasculature.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What 3 things does the cerebellum control?
What is cerebrum function?
What are the 3 parts of the cerebellum?
What are some signs of cerebellar disease?
What happens if cerebellum is damaged?
What are the major diseases of the cerebellum?
How is cerebellar disease diagnosed?
Can cerebellum damage be treated?
What medications help the cerebellum?
Table of content
Find Neurosurgeon near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors