Colitis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Mar 09, 2023
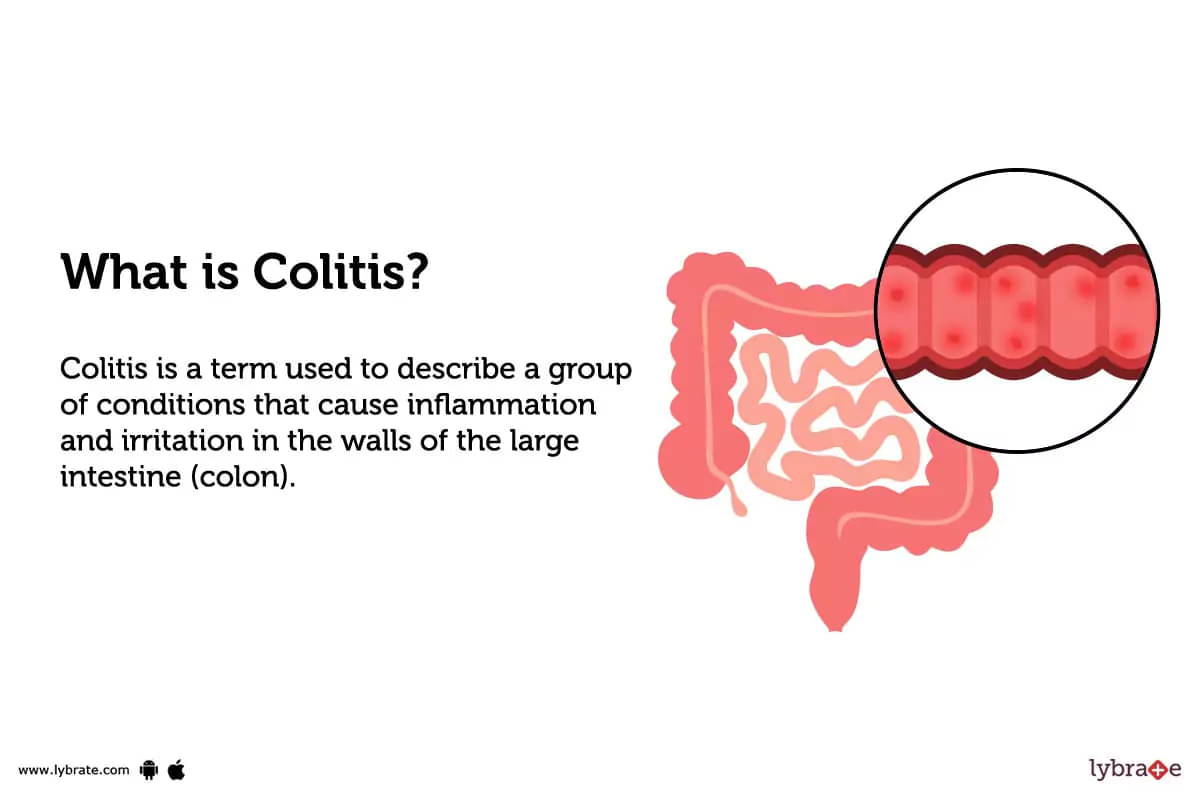
What is Colitis?
Types of Colitis
Colitis has many different types. The most common types are:-
- Ulcerative Colitis: This type of colitis is caused by an abnormal response of the immune system that leads to inflammation in the lining of the large intestine and rectum.
- Infectious Colitis: This type of colitis is caused by certain infectious organisms, such as certain bacteria (like E. coli) or parasites that invade and damage the tissues in the colon wall, leading to inflammation and other symptoms like abdominal cramps, fever and bloody diarrhoea which could become very severe in some cases.
- Microscopic Colitis: Microscopic colitis includes two types which are Collagenous Colitis and Lymphocytic Colitis is characterised by inflammation cells seen only under microscope during examination of a sample from large intestine taken during endoscopy.
- Ischemic Colitis: Ischemic colitis happens when there's impaired blood supply to the large intestine due to some medical conditions or surgical procedures.
- Toxic Megacolon: Toxic megacolon is considered a serious complication which occurs when the colon becomes greatly distended because its nerves & muscle have become paralyzed due to certain drugs (like opiates & corticosteroids) infections or inflammatory diseases.
What causes Colitis?
- The cause of colitis is unknown, but it is believed to be associated with genetics, abnormal immune responses and environmental triggers such as certain foods or stress.
- In certain situations, certain bacteria and viruses could also play a role.
- People with Crohn's disease, a type of IBD, also have an increased risk of colitis.
What are the symptoms of Colitis?
- Abdominal pain and cramping: People with colitis often have abdominal pain, cramping, and discomfort in the abdomen.
- Diarrhoea: Colitis often manifests itself with the symptom of diarrhoea.
- Blood in stools: This might include visible streaks of blood or even darker coloured stools that may appear tarry or black.
- Fatigue: Constant fatigue can be associated with colitis because of poor nutrient absorption from chronic inflammation.
- Weight loss: Malnutrition due to nutrient malabsorption may lead to sudden or gradual weight loss in people with colitis depending on severity level of inflammation.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature can indicate an infection is present and should trigger an evaluation by a doctor to identify the cause if this symptom persists.
How can you prevent Colitis?
- Have a nutritious diet that is rich in fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Sugar, junk food, and processed foods should be avoided at all costs.
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Maintain a consistent exercise routine of at least half an hour every day, five days per week.
- Get enough sleep (7-8 hours) to reduce stress levels & allow the body time to rest and heal naturally.
- Reduce your stress by learning how to manage it better, meditating or practising Yoga/mindfulness exercises daily.
- Don’t smoke or use drugs that increase risk factors, such as alcohol consumption, caffeine intake, and heavy consumption of red meat products & fried foods.
Colitis - Diagnosis and Tests
- Physical Exam:The first step in diagnosing colitis is to have a medical professional do a physical examination on the patient. It is possible that your doctor may examine your skin, belly, rectum, and the rest of your body for any indications of inflammation or other abnormalities.
- Blood Tests:For diagnosing colitis, blood testing may be helpful in detecting anaemia as well as signs of infection in the patient. In addition, tests such as a complete blood count, assessment of liver function, and measurement of C-reactive protein may be performed.
- Stool Sample:Your doctor may request a stool sample to test for traces of blood in your stools, an indication that you may have colitis or another condition affecting the intestines.
- Imaging Tests:X-ray, CT scan or MRI scans can be used to check for any changes or abnormalities in the form and functioning of the gastrointestinal tract that point towards a colonic disease underlying colitis symptoms such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease.
- Colonoscopy:This is an intrusive examination done under general anaesthesia where a long tube with a mini camera is inserted into the rectum and guided through the colon so that it can be examined closely for any damage or inflammation along the walls caused by IBD like colitis.
What are possible complications of Colitis?
- Dehydration:Without proper hydration, the inflammation that accompanies colitis can become severe and cause irreversible damage to the body.
- Malnutrition:Loss of appetite and difficulty in absorbing nutrients can lead to malnutrition.
- Toxic Megacolon:Extreme swelling of the colon with bloating and cramping may be seen with very severe cases of colitis, which can lead to a life-threatening condition called toxic megacolon.
- Fistulas or Abscesses:In some cases, fistulas or abscesses may develop when tissues around an area of colitis become infected, leading to inflammation and further complications that require treatment.
- Spread Infection:Left untreated, it is possible for infection to spread throughout the body leading to more serious issues such as Sepsis or Ulcerative Colitis Arthritis (UCA).
Home Remedies for Colitis
- Drink buttermilk mixed with 1 tsp fenugreek powder and some cumin powder.
- Consume a teaspoon of coriander seed powder with buttermilk twice daily.
- Prepare a paste of 1 tablespoon of ginger powder and honey and consume it twice a day.
- Take jaggery roasted in castor oil one teaspoon every morning on an empty stomach
- Drink warm water with 2 to 3 teaspoons of fresh amla juice every day.
- Drink peppermint tea with lemon to reduce inflammation and pain symptoms.
What to eat in Colitis?
- Eating a balanced, anti-inflammatory diet is important for people with colitis. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are examples of foods rich in fibre that should be consumed since they are simple to digest and contain vital nutrients.
- Consuming meals low in cholesterol and saturated fat may also help lessen the inflammation linked to colitis.
- Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce symptoms of colitis. For this reason, it is advised to consume fish two to three times every week.
- Fermented foods like yoghurt and kefir contain probiotics which may help reduce inflammation associated with colitis as well as improve gut health overall.
What not to eat in Colitis?
- Avoid fried and greasy foods, as these can aggravate symptoms.
- Avoid spicy meals since they might cause irritation and inflammation in the intestines.
- Cut back on dairy products as they may be difficult to digest.
- Minimise your consumption of processed meals like cookies, chips. These may cause inflammation in some people with colitis.
- Avoid alcohol and caffeine ,which can stimulate gut contractions and worsen symptoms if you are sensitive to either substance.
Colitis Treatment
- Medications:Medication is often used as part of colitis treatment to decrease inflammation and manage symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes:Lifestyle changes such as avoiding certain foods, drinking ample amounts of fluids, eating a balanced diet, and taking probiotics may also help manage symptoms.
- Resection:This procedure involves removing the diseased colon or a segment of the large intestine in order to reduce inflammation, pressure, and pain in that area.
- Colectomy:A colectomy may be performed to remove the entire colon and rectum when colitis is seen as a long-term condition or risk factor for cancer.
- Ileostomy:An ileostomy is an option when there is significant destruction of both small and large intestines that requires removal of most of these structures; this procedure creates an opening on the abdomen through which bodily waste can be eliminated away from the body into a pouching system placed around it.
- Stricturoplasty:This type of surgery will repair any narrowed areas of your intestine in order to improve your overall flow through the digestive tract, allowing more food and nutrients to pass through easily with less pain or difficulty caused by blockages due to inflammation or scarring from colitis-related tissue damage.
- Laparoscopic Surgery for Colitis:This method uses smaller incisions than traditional abdominal surgery, making recovery times quicker without compromising surgical outcomes by using specialised instruments during procedures instead of open exploration with hands inside cavities like those made in conventional surgeries .
Which doctor to consult for Colitis?
Patients suffering from colitis should consult a gastroenterologist. A gastroenterologist is a doctor who deals with the diagnosis and treatment of disorders and illnesses of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Which are the best medicines for Colitis?
- Anti-inflammatory medications:This type of medication helps to reduce inflammation in the lining of the digestive tract and can be used to treat acute attacks of colitis. Examples include mesalamine, sulfasalazine, and balsalazide.
- Corticosteroids:These powerful anti-inflammatory drugs are used to treat more severe cases of colitis that do not respond to other medications.
- Immunosuppressants:These medicines may be used to treat instances of chronic colitis that have not responded to long term therapy. Azathioprine, cyclosporine, and tacrolimus are a few examples.
- Antibiotics:These drugs are sometimes used to kill bacteria in the intestines that may be contributing to a flare-up of symptoms in people with ulcerative colitis or infectious colitis caused by a bacterial infection.
- Biologic Agents:Biologics work by targeting specific parts of the immune system to inhibit inflammation associated with colitis. Examples include infliximab (Remicade) and adalimumab (Humira).
How long does it take to recover from Colitis?
The time it takes to recover from colitis can vary significantly based on a range of factors, such as the type and severity of the condition, the age and overall health of the individual, and the treatments they undergo.
Generally, less severe cases may resolve with proper lifestyle changes and medical treatment in a matter of weeks or months. More serious cases may require more intensive treatments, which may lead to longer recovery periods of several months or even years.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
Although the results of treatment for colitis can be substantial and long-lasting, it is not possible to guarantee permanent results.
While some patients may no longer experience symptoms after successful treatment, others may need ongoing monitoring by a healthcare professional in order to better manage the condition.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- Monitor diet:Follow any dietary instructions provided by the doctor, including avoiding spicy and high-fat foods and adding more fibre-rich foods.
- Get rest:Take it easy and avoid strenuous physical activity for at least one week after the procedure, as well as ensuring adequate rest each night.
- Follow medications:Take all of your prescription medicines exactly as your doctor tells you to.
- Avoid smoking:Do not smoke cigarettes or use other tobacco products, as these can delay healing or worsen existing symptoms.
- Call doctor with problems:If any new symptoms develop or pain increases, contact the doctor immediately as this could mean an infection is developing that needs medical attention right away.
What is the cost of Colitis treatments in India?
Generally, medication and lifestyle modifications may cost between ₹500-3000 per month. Depending on the technique, surgery might cost anywhere from 50,000 to over a lakh. Additionally, colonoscopy costs in the range of ₹15000 to ₹25000. Gastroenterologists may also charge consultation fees ranging from ₹200–2000 depending on their experience and reputation.
What are side-effects of Colitis treatments?
- Abdominal pain and cramping:Treatment of colitis can cause abdominal pain and cramping, which is often experienced as a side-effect of medication.
- Diarrhoea:When the body adapts to the new routine, a diet change may cause diarrhoea.
- Anaemia:Inflammation of the intestinal wall caused by colitis can lead to anaemia, due to a lack of nutrients absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract.
- Nausea and vomiting:Medications for colitis may cause nausea and vomiting, primarily due to disruption of nutrient absorption by the intestines.
- Weight loss:Chronic inflammation from colitis can lead to weight loss as digestive function is impaired or disrupted.
Colitis - Outlook/ Prognosis
If you have any colitis issues, you should see a doctor right away since they may cause 'malnutrition, toxic megacolon, fistulas, or abscesses,' and treatment courses can vary from a few months to years depending on the extent of the problem.
References
- Colitis- Medline Plus, Medical Encyclopedia, NIH, U.S. National Library of Medicine [Internet]. medlineplus.gov 2019 [Cited 23 July 2019]. Available from:
- Ischemic colitis- Mayo Clinic [Internet]. mayoclinic.org [Cited 23 July 2019]. Available from:
- Ulcerative colitis- Mayo Clinic [Internet]. mayoclinic.org [Cited 23 July 2019]. Available from:
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find General Physician near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors