Plaque: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Jul 04, 2023
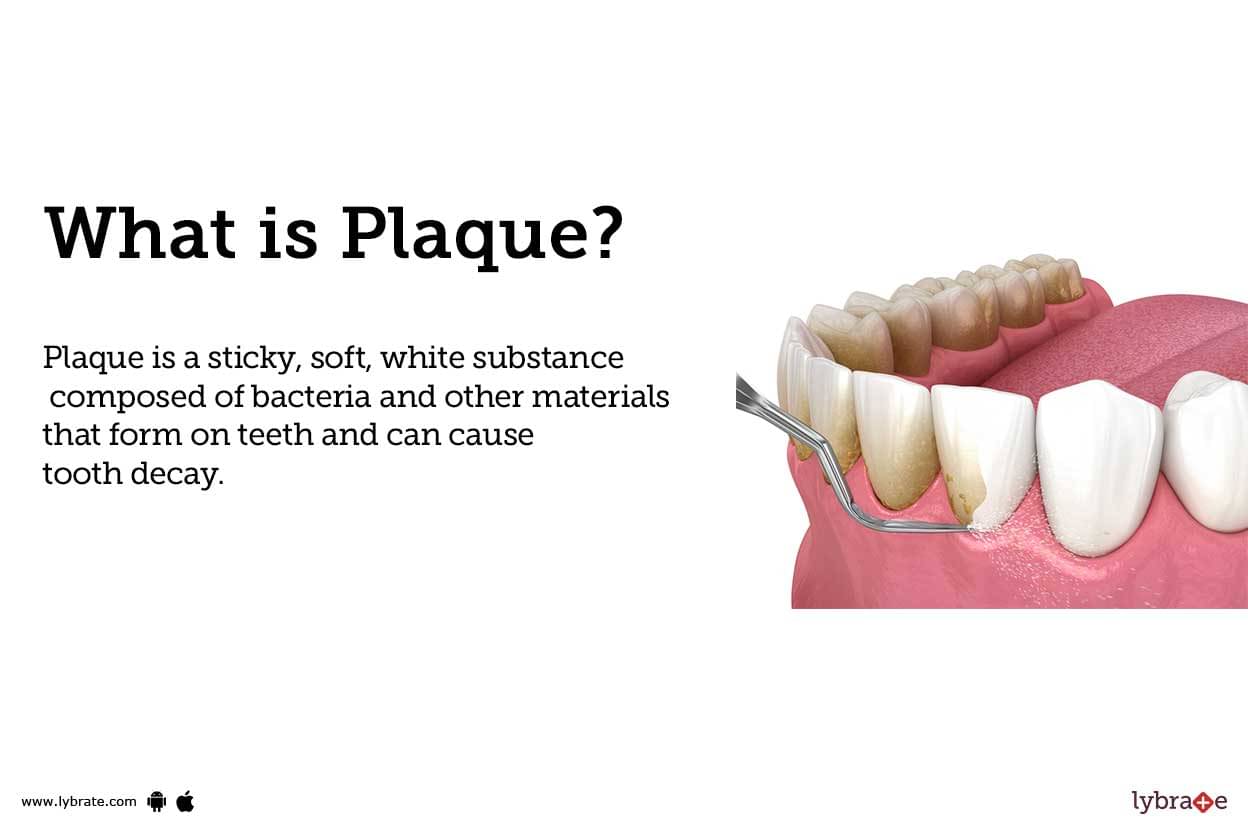
What is Plaque?
Plaque is a sticky, soft, white substance composed of bacteria and other materials that form on teeth and can cause tooth decay.
Types of Plaque
- Supragingival Plaque: This is the most common form of plaque that appears on top of the gums near the gum line. This type of plaque is usually caused by poor oral hygiene habits, such as not brushing or flossing enough or not using proper technique when brushing or flossing.
- Subgingival Plaque: This type of plaque lies below the gums near the roots of the teeth and in between them. It can be more difficult to remove than supragingival plaque because it can only be reached by either deep cleaning or scaling procedures performed by a dentist or hygienist.
- Calculus: Also known as dental tartar, this form of hardened plaque can only be removed with professional dental tools during a dental cleaning appointment with a dentist or hygienist.
- Soft Deposits: Soft deposits are made up primarily of food particles that have been left behind after eating meals and snacks throughout the day. These deposits are easily removed with regular brushing and flossing techniques but should be regularly monitored to ensure they do not harden into calculus over time if left untreated for too long.
What causes Plaque?
Plaque is an accumulation of bacteria, food particles, and saliva on teeth surfaces. If not removed on a regular basis, it produces a sticky film that may cause cavities and gum disease.
What are the symptoms of Plaque?
The following are the most prevalent plaque symptoms:
- Tooth decay: Plaque generates acid, which eats away at your tooth enamel, causing cavities.
- Gum disease: Inflammation of the gums, also known as gingivitis, may be brought on by plaque that has not been cleared properly. Gingivitis has the potential to develop into periodontitis, a more serious type of gum disease that may result in the loss of teeth if left untreated.
- Bad breath: Plaque and the bacteria it harbours can cause bad breath.
- Tooth sensitivity: Plaque that is allowed to build up on the teeth can lead to tooth sensitivity, as the enamel on the teeth becomes thin and worn away.
- Yellowing of the teeth: Plaque can cause the teeth to become yellow or discoloured.
How can you prevent Plaque?
Plaque can be prevented by:
- Practicing proper dental hygiene routines, such as brushing twice daily for two minutes with fluoride toothpaste and flossing everyday.
- Eating a balanced diet .
- Limiting sugary foods.
- Visiting the dentist regularly for professional cleanings, can also help to reduce plaque build-up.
Plaque - Diagnosis and Tests
There are several ways to diagnose dental plaque:
- Visual examination: A dental professional can look at your teeth and gums to see if there is any visible plaque build-up.
- Dental probe: A dental probe is a thin, pointed instrument that is used to gently scrape the surfaces of your teeth. The dental professional can then examine the probe for any plaque that may have been collected.
- X-rays: Dental X-rays can be used to identify plaque that may not be visible during a visual examination, such as plaque that has formed between the teeth or below the gum line.
- Disclosing tablets: These tablets, which can be purchased at a pharmacy, contain a dye that will temporarily stain any plaque that is present on your teeth. This might help you recognize regions of your mouth where your dental hygiene habit could be improved.
What are possible complications of Plaque?
- Plaque can lead to a range of complications, including gum disease, tooth decay, and tooth loss.
- It may also cause bad breath and a foul taste in the mouth.
- Plaque accumulation may cause gum inflammation (gingivitis), which can progress to infection if not treated appropriately.
- If left untreated, plaque buildup increases the risk of developing periodontal disease, which is an infection that damages the supporting structures (including gums, teeth, and bones) of the teeth.
- Plaque can lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems.
Home Remedies for Plaque?
- Oil Pulling: Oil pulling is an old Ayurvedic therapy that has been used to restore oral health for ages.Spitting out a spoonful of oil (coconut, sesame, or sunflower oil) after swishing it about in your mouth for 10-15 minutes. This aids in the reduction of germs in your mouth that produce plaque.
- Neem Leaves: Neem leaves are a powerful antibacterial and antifungal agent that can help reduce the bacteria in the mouth that cause plaque. You can chew on fresh neem leaves or make a paste from powdered neem leaves and water and apply it to your teeth and gums for 5 minutes before rinsing with warm water.
- Turmeric Paste: Turmeric has long been used in Ayurveda as an anti-inflammatory agent to help reduce inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup. To make this paste, mix 1 teaspoon of turmeric powder with enough water to create a thick paste, then massage it into your teeth and gums before rinsing with warm water.
- Fennel Seeds: Fennel seeds are known for their ability to fight off bad breath as well as plaque buildup due to their antibacterial properties. You can either chew on a few fennel seeds after meals or make a fennel tea by boiling 1 teaspoon of crushed fennel seeds in 2 cups of water for 10 minutes, strain and drink it after meals twice daily.
What to eat with a tooth Plaque?
You can try eating soft, non-sticky, and nutritious foods that are gentle on your teeth and gums. Some examples of such foods include:
- Cooked vegetables, such as steamed broccoli or mashed sweet potatoes
- Cooked grains, such as oatmeal or quinoa
- Soft fruits, such as bananas or avocados
- Scrambled eggs or tofu
- Tender meats, such as chicken or fish
- Dairy products, such as yoghourt or soft cheese
What not to eat in the dental Plaque?
You should avoid eating foods that are high in sugar, such as candy and soda, as these can contribute to the buildup of plaque on your teeth.
You should also limit your consumption of starchy foods such as white bread and potato chips.
Plaque Treatment
Treatment for Dental Plaque:
- Scaling: It cleans the plaque and tartar that have accumulated on the teeth's surfaces.
- Root planing: This helps to prevent germs from collecting at the roots of the teeth by smoothing them down.
- Brushing teeth regularly with a fluoride toothpaste: This helps to remove plaque from the surfaces of the teeth and can also help to prevent tooth decay.
- Flossing daily: A toothbrush cannot reach the spaces between the teeth and along the gumline where flossing enables the removal of plaque and food particles.
- Using mouthwash: Antimicrobial mouthwashes may aid in eradicating germs and reducing plaque.
Which doctor to consult for Plaque?
Plaque should be discussed with a doctor of dental medicine (DMD) or a doctor of dental surgery (DDS).
A dentist can diagnose and treat plaque buildup, as well as recommend lifestyle changes to help prevent it from forming in the future.
Which are the best medicines for Plaque?
To treat dental plaque, a variety of medications are used:
- Chlorhexidine: This mouthwash has antimicrobial properties that help destroy germs and prevent the development of plaque.
- Fluoride: Fluoride is a mineral that may help to improve tooth enamel and lower the risk of decay. It's a common ingredient in toothpaste and mouthwash.
- Triclosan: This is an antimicrobial agent that is sometimes added to toothpaste to help reduce plaque and prevent gum disease.
- Xylitol: This is a natural sweetener that has been demonstrated to minimise plaque accumulation on teeth. It is often present in sugar-free gum and other items.
- Zinc: According to certain studies, zinc may aid in the reduction of plaque buildup on teeth.
How long does it take to recover from Plaque?
Recovery from plaque can take anywhere from a few days up to several weeks, depending on the severity of the plaque build-up and the individual's response to treatment.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
The results of a treatment will depend on the specific treatment and the individual.
In general, some treatments may be permanent or result in long-term effects, while others may only provide short-term relief.
It is important to speak with your doctor to find out how long a specific treatment is expected to last and what steps you can take to maintain the results.
What is the cost of Plaque treatments in India?
Plaque treatment costs in India varies according to the extent of the issue and the kind of treatment needed.
Generally, treatments such as scaling and root planing may cost anywhere between ₹1,000 to ₹4,000.
Advanced treatments such as laser-assisted new attachment procedure (LANAP) may cost up to ₹50,000 per session.
Additional costs such as medications and X-rays may also be applicable.
What are the side-effects of Plaque treatments?
Plaque - Outlook / Prognosis
If you are suffering from any complications relating to dental plaque then you should consult a doctor nearby as they can cause complications like 'gum disease, tooth decay, and tooth loss'. Depending on the seriousness of the condition, the duration of the treatment process might be anywhere from a few months to several years.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Dentist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors