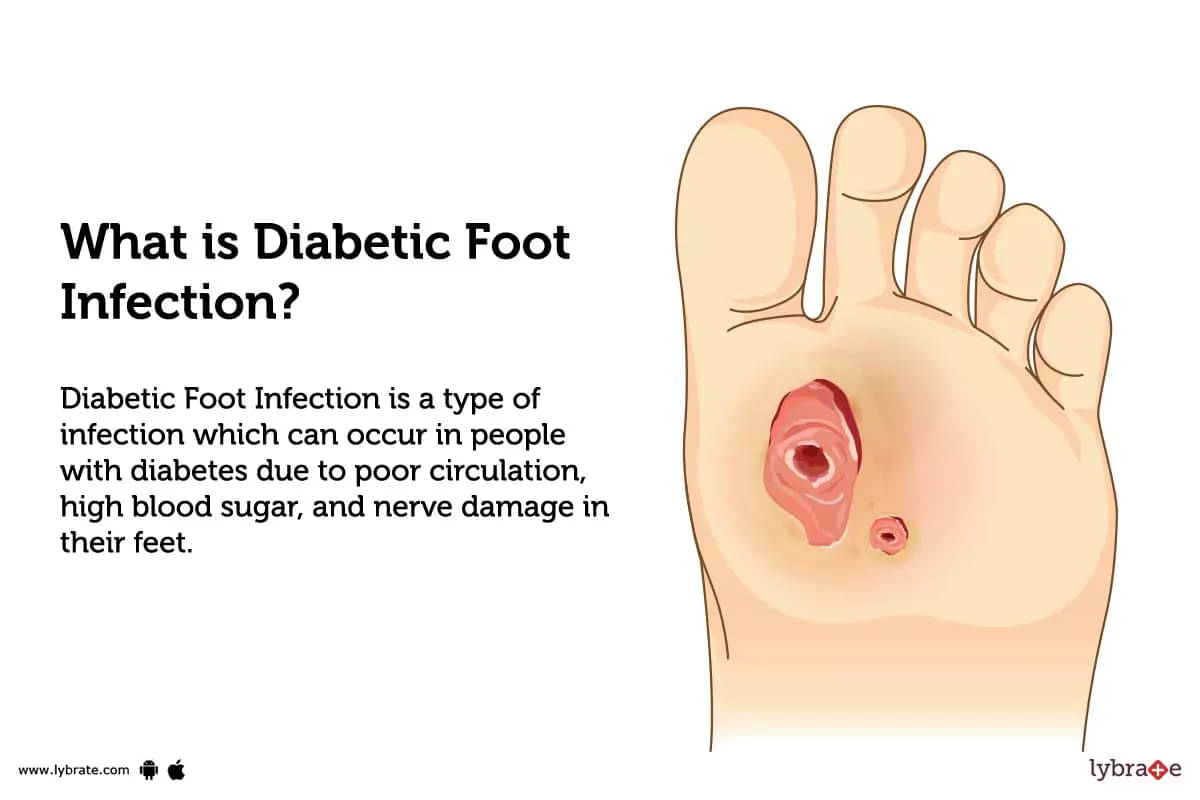
Diabetic Foot Infection: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Mar 14, 2023
Types of Diabetic Foot Infection
- Cellulitis: In this condition deeper layers of skin and the underlying tissue is infected, and is caused due to bacterial infection. It often appears as a red, swollen area which is hot in touch and tenderness is also seen.
- Osteomyelitis: It is a condition of bone infection occurring in patients of diabetes. It is caused by bacteria entering the bone through any break in the skin, and it can lead to pain, swelling, redness, and drainage from the affected area.
- Mycotic Toenail Infection: This is an infection of the nail bed or cuticle caused by fungi or yeast. Symptoms include discoloration of the nail, thickening of the nail plate, or pain in the toes.
- Fungal Skin Infections: These are infections caused by fungi or yeast that can appear as red patches on the skin that may be itchy or painful.
- Charcot Foot: This is a condition in which there is damage to bones and soft tissue due to repeated trauma from walking on an abnormally shaped foot due to nerve loss from diabetes.
What causes Diabetic Foot Infection?
- Diabetic foot infections (DFI) are caused mainly by high blood sugar levels that damage the nerves and circulation in feet, leading to open sores, dry skin or other issues.
- Poorly fitted footwear and not checking feet regularly can also lead to wounds which would allow bacteria to enter the body, resulting in an infection.
- People with diabetes are more likely to have foot infections as there is an increased risk of skin breakdown due to reduced blood circulation and lack of sensation in the feet.
- Higher amounts of sugar also provide nutrients which allow germs like bacteria or fungi to thrive, worsening an infection even further if not managed properly.
What are the symptoms of Diabetic Foot Infection?
How can you prevent Diabetic Foot Infection?
- Take a proper balanced diet and maintain a healthy weight.
- Keep feet clean and dry and check for cuts, blisters, sores, or changes in skin colour daily.
- To protect the feet from any kind of injury while doing exercise or walking do wear protective shoes.
- Protect feet from extreme temperatures with socks/ footwear.
- Avoid crossing legs for long periods; keep blood flowing to feet properly.
- Exercise regularly but avoid activities that might cause injury to the feet or ankles.
- Quit smoking; it increases risk of foot problems & slows circulation in the legs & feet which can worsen existing problems due to diabetes .
- Have regular diabetes check-ups, have regular foot exams with an endocrinologist/ podiatrist at least once a year .
- Check your blood glucose level regularly and monitor it closely under direction of doctor to minimize risk of infection in your feet due to Diabetes & its complications
Diabetic Foot Infection - Diagnosis and Tests
- Imaging test :The diagnosis of diabetic foot infection can be made through a physical exam and through imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, CT scan or an ultrasound. Blood tests may also be conducted to measure levels of markers that indicate infection and to identify any underlying causes such as diabetes.
- Wound/Ulcer Cultures :Samples from the wound/ulcer are taken and incubated in a laboratory to identify the type of infectious agent responsible for the infection.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Tests :This test measures the no. of WBCs in your blood, which can be indicative of an infection if found more than natural level.
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Test :This measure can detect inflammation caused by an infection
- Urine Analysis/Urinalysis:This test looks for bacteria or glucose in your urine, which could indicate a urinary tract or bladder infection respectively.
- Glucose Tolerance (GTT) Test :This test evaluates your body’s response to sugar, which may indicate diabetes if high levels are detected.
- HbA1c Test:A glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) test measures your average blood sugar level over a steady period and can help diagnose diabetes if high readings are present.
What are possible complications of Diabetic Foot Infection?
The possible complications of Diabetic Foot Infection include:
- Cellulitis:It is an infection of the deeper layers of the skin and underlying tissues
- Osteomyelitis:It is an infection of the bone
- Sepsis:It is a potentially life-threatening complication that occurs when an infection spreads throughout the body and causes organ failure
- Amputation:It may be necessary if the infection does not respond to treatment or if it has caused severe damage to the foot or leg
- Gangrene:It occurs when tissue dies due to lack of blood supply. This can lead to amputation in some cases.
Ayurvedic-Home Remedies for Diabetic Foot Infection?
- Apply clarified butter (ghee) mixed with rock salt powder on the affected area.
- Soak feet in warm water mixed with unrefined salt like Himalayan salt or sea salt for 15 minutes once a day.
- Replace the dressing dressings on heel regularly and keep them clean & dry as much as possible.
- Use herbs like Turmeric and Holy basil to make a paste and apply it on the affected part of your feet every day before going to bed
- Drink a mixture of 1 teaspoon pure ghee, 1 teaspoon honey, and 2-3 garlic cloves daily before going to bed for better results over time
- Take 2-3 teaspoons of Indian gooseberry (amla) juice diluted in half cup warm water daily .
What to eat in Diabetic Foot Infection?
- Eat a balanced diet of complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- Choose whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats for complex carbohydrates instead of simple sugars found in sweets and white breads.
- Include lean sources of protein such as skinless chicken breasts or fish, legumes and beans, low-fat dairy products, eggs, nuts and seeds.
- Make sure to include plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet to get necessary vitamins and minerals as well as dietary fibre that helps with digestion.
What not to eat in Diabetic Foot Infection?
- Foods high in sugar:Candy, cookies, cakes, pastries and other sweet treats should be avoided as they may cause spikes in blood glucose levels.
- Processed foods:Prepackaged meals, boxed foods and anything else loaded with preservatives and artificial ingredients should be avoided as they lack nutritional value.
- Trans fats:Margarine, store-bought pastries and fried foods contain trans fats that can increase inflammation throughout the body, so they should be eliminated from your diet completely.
- Refined carbohydrates:Avoid white breads and pasta as they are converted into sugar quickly after ingestion and can lead to unhealthy blood sugar levels.
- Red meat:Too much red meat can raise levels of arachidonic acid which increases inflammation in the body.
Diabetic Foot Infection Treatment
Treatment options for diabetic foot infections include:
- Surgery:In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove dead or infected tissue from the feet or ankles. This type of surgery may also involve drainage of any fluid that has collected in the area.
- Wound Care:Cleaning and dressing any open wounds on the feet is an important part of treating diabetic foot infections. It is important to keep wounds clean and dry, and change dressings regularly as directed by your doctor or healthcare provider.
- Debridement:Debridement is a procedure that involves removing dead or infected tissue from a wound in order to promote healing and reduce risk of infection spreading further into healthy tissue.
- Lifestyle Changes:Making lifestyle changes can help prevent the recurrence of diabetic foot infections, such as maintaining good control over blood sugar levels
- Open Wound Management:Use of wound dressings, debridement, antibiotics and other treatments depending on extent of the infection.
- Limb Amputation:Removal of all or part of a limb in worst cases to prevent spreading of the infection to other parts of the body.
- Revascularization:Reconstructing the patient's vascular system by creating alternate pathways for blood flow in order to improve healing and prevent infection spread.
- Osteomyelitis Treatment:Surgical debridement, flap coverage or bone grafting may be recommended in cases where there is severe bone damage by the infection.
Which doctor to consult for Diabetic Foot Infection?
- For a diabetic foot infection, it is important to see a medical doctor/physician who specializes in the treatment of diabetes.
- In particular, an endocrinologist or podiatrist should be consulted.
- An endocrinologist specializes in disorders related to hormones and metabolism which includes diabetes.
- A podiatrist specializes in treating conditions of the feet, including infections and ulcers caused by diabetes.
Which are the best medicines for Diabetic Foot Infection?
- Antibiotics: These drugs are used to treat bacterial infections that cause diabetic foot infections. Examples include penicillin, amoxicillin, cephalosporins, quinolones, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim)
- Anti-fungal drugs: These drugs are used to treat fungal infections such as athlete’s foot that can lead to diabetic foot infections. Examples include miconazole (Lotrimin AF), terbinafine (Lamisil AT), clotrimazole( Lotrimin AF), and nystatin (Mycostatin).
- Topical medications: These medications are applied directly to your skin or wound and can help with pain relief and prevent further infection. Examples include medications containing hydrocortisone, neomycin/polymyxin (Neosporin), bacitracin (Polysporin), and silver sulfadiazine (Silvadene).
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help relieve discomfort associated with diabetic foot infections.
- Wound dressing products: Certain gels, foams, hydrogels, ointments, creams, sprays and bandages may be applied directly on the wound in order to promote healing of the wound caused by a diabetic foot infection
How long does it take to recover from Diabetic Foot Infection?
Diabetic Foot Infection (DFI) is a common, serious and potentially life-threatening complication among patients with diabetes. Generally speaking, treatment for most DFIs may take anywhere from four to twelve weeks.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
- No, The results of treatment for diabetic foot infection can vary depending on the severity, location and type of infection.
- However, generally speaking, with the proper medical care – including antibiotics and medical attention to the area, in addition to controlling the diabetes, many people are
- able to manage or even eliminate their condition and obtain lasting outcomes.
- Therefore, while treatment can have long-lasting effects in most cases, it is important that diabetics receive regular care and attention to ensure that their infection does not return or worsen.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
After treatment of a diabetic foot infection, it is important to take measures to reduce the risk of recurrence and promote healing. These post-treatment guidelines include:
- Washing the foot with soap and warm water two times per day, wearing supportive footwear and clean socks, avoiding tight shoes or any form of pressure squeeze on the infected area, and keeping the foot dry after washing.
- Each day, inspect your feet for signs of infection such as redness, swelling or pain. If any are present, contact your doctor immediately as these may be signs that the infection is worsening and further treatment may be necessary
- Properly care for any open wounds or blisters on your feet to prevent infection from recurring due to loss of sensation caused by diabetes; use an antibiotic cream on wounds if necessary
- Increase physical activity levels gradually over time but do not suddenly increase energy expenditure; this can lead to further complications and stress on the feet
- Lastly, schedule regular visits with your podiatrist in order to keep a close eye on your diabetic foot health status and allow for early intervention should any complications arise due to poor management or stress caused by a sudden increase in activity levels
What is the cost of Diabetic Foot Infection treatments in India?
The charges of complete treatment of diabetic foot infections in India can vary widely from place to place and person to person depending on the severity of the infection and the type of treatment required.
Although the treatment charges can range from a few hundred to several thousand rupees.
What are side-effects of Diabetic Foot Infection treatments?
Diabetic Foot Infection - Conclusion
Diabetic Foot Infection is a serious complication of diabetes. It occurs when bacteria enter the foot through an open wound, and can lead to amputation if not treated properly. Treatment includes antibiotics to fight infection as well as debridement to remove dead tissue and promote healing.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Podiatrist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors