Digestive System (Human Anatomy): Image, Function, Diseases, and Treatments
Last Updated: Mar 17, 2023
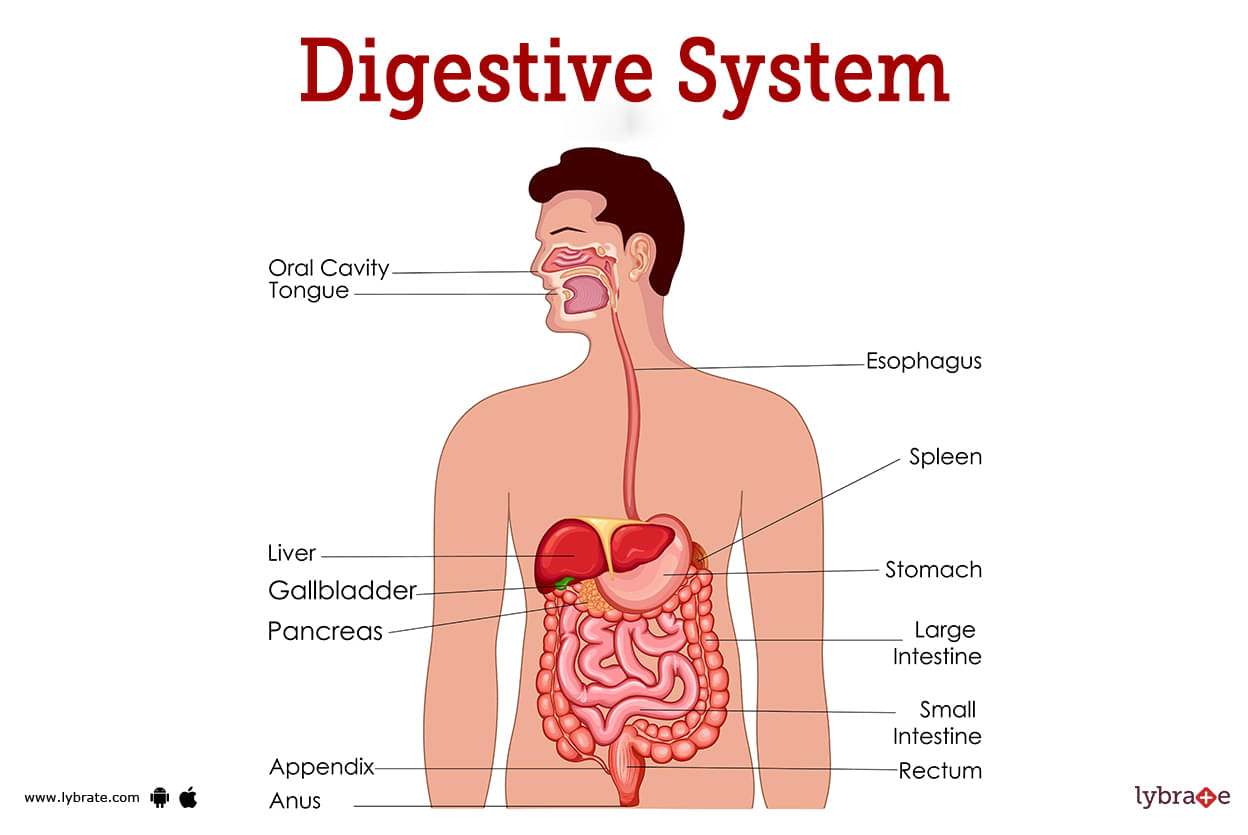
Digestive System Image
The gastrointestinal tract and its supporting organs make up what we call the digestive system. Digestive processes entail breaking down food into smaller and smaller pieces so that it may be absorbed and used by the body.
It is via the digestive system that nutrients are delivered to the body's tissues and organs. The system processes food, obtains its nutrients, and turns them into usable forms of energy. The major organs of digestion are:
- Esophagus: a tube-shaped organ located between the throat and the chest that carries food from the mouth to the stomach. The area's muscles help move food down into the stomach.
- Stomach: A huge digestive organ that stores and breaks down food using a variety of acids and enzymes. Between two and eight hours, the food here will be safe to eat.
- Liver: This organ generates bile, which aids in the digestion of protein, carbs, and fats, and also filters pollutants from the blood.
- Gallbladder: The bile generated by the liver is stored in this sac-like organ until it is needed.
- Pancreas: Insulin, a hormone secreted by this gland, is essential for the body to metabolise sugar.
- Small intestine: The small intestine is the first part of the digestive tract to take food from the stomach and begin breaking it down while absorbing most of the nutrients from the meal.
- Large Intestine: There are billions of beneficial bacteria packed within this organ, and they are responsible for breaking down food into waste and absorbing necessary fluids and minerals.
- Rectum: This little region at the very end of the big intestine serves as a holding pen for waste.
- Anus: This is the external opening of the rectum, through which feces are expelled.
A number of things, including as food, stress, disease, and others, can upset the delicate balance required for the proper functioning of this network of organs and the fluids that surround them.
Digestive System Functions
The stomach produces digestive acids and enzymes to break down the food we ingest. The digestive and absorptive processes result in the formation of stomach folds known as rugae. A regular peristaltic action bends the stomach, which aids digestion towards the end of the stomach and the opening to the small intestine, where the pyloric sphincter is located.
The small intestine or gut can be up to 20 feet in length and an inch in diameter. The digestive system's primary function is to process the food and liquids we ingest into useable nutrients and water.
The small intestine is divided into three sections by their respective border tissues: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum. The jejunum is responsible for virtually all of the digestive system's absorption.
The large intestine, also called the large gut, measures around 5 feet in length and 3 inches in diameter. This is accomplished by drawing moisture from both digested and undigested garbage.
Despite the fact that absorption at this stage is much lower than in the small intestine, some absorption still occurs. The rest is converted into faeces, which is then sent to the rectum and stays there until a signal for the desire to defecate is received.
Digestive System Conditions
- Diarrhea: Loose, watery, and occurring more than three times daily faeces go by this appellation. Mild infections of the colon or small intestine are the most common cause of diarrhoea.
- Constipation: It happens when you have trouble pooping or going to the restroom as frequently as you should. Stomach waste is not passed regularly through the large intestine (colon) because to irregular bowel movements.
- Acid reflux: Chronic inflammation of the larynx (patient presents with pain throat, moderate hoarseness, recurrent throat cleaning tendency, and chronic cough) and Posterior glottic stenosis have both been associated to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), in addition to the more familiar heartburn and regurgitation.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): it is a gastrointestinal (GI) illness characterised by altered bowel habits and persistent stomach discomfort. These include alterations to the microbiota, altered immunological function, aberrant motility, and hypersensitivity to the gastrointestinal tract.
- Celiac disease: The inability of the small intestine to properly absorb nutrients is what is meant by the term 'gluten sensitivity.' Gluten is mainly made up of protein, which the body has trouble breaking down. Abdominal discomfort and loss of appetite are two of the symptoms.
- Hepatitis: The liver becomes inflamed due to this condition. Hepatitis can be caused by excessive or chronic alcohol consumption, toxic substances, the immune system, or certain drugs.
- Crohn’s disease: Diseases of the colon and intestines that cause inflammation are known as Crohn's and ulcerative colitis, respectively. A headache, nausea, and/or stomach discomfort are the most often reported symptoms.
- Cirrhosis of the liver: Several diseases and conditions, such as chronic drinking and hepatitis, can lead to cirrhosis, a late or severe stage of liver scarring (fibrosis). Cirrhosis treatment intensity and duration are influenced by the underlying cause of the condition. Liver transplantation is an option if the liver has failed.
- Cancers: Various cancers, including colorectal, stomachal, intestinal, pancreatic, and liver cancers
Digestive System Test
- Physical Examination: Listening with a stethoscope, palpation, and percussion are all helpful diagnostic tools for determining the nature of a variety of abdominal disorders.
- Upper Endoscopy (Esophagogastroduodenoscopy or EGD): It is one of the diagnostic procedures that involves seeing and examining the upper portion of the digestive system (up to the duodenum) by inserting an endoscope (a flexible tube with a camera at one end) via the mouth. This is done in order to perform the operation.
- Lower Endoscopy (Colonoscopy Or Sigmoidoscopy): During this procedure, the endoscope is sent into the nasopharynx and into the colon in its entirety. It allows the mucosal lining of the lower gastrointestinal system to be seen and examined in more detail. It assists in the diagnosis of issues such as rectal bleeding, cancer, and other conditions.
- Abdominal X-ray: An X-ray of the abdomen can be used to visualise and investigate medical conditions, such as intestinal perforation or blockage, that are located in the abdominal cavity.
- Computed Tomography (CT Scan): An x-ray machine and a computer work together in a CT scanner to create pictures of the internal organs and structures of the abdomen. This technique aids in the detection of abdominal diseases including appendicitis and cancer.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI Scan): The term refers to a type of medical imaging technology. Computer-generated radio waves in a magnetic field are used to create high-resolution images of internal organs in the abdomen (liver, gallbladder, pancreas, etc.).
- Abdominal Ultrasound: Using this method, which does not involve any cutting or invasive surgery, doctors can examine anything that happens to be located in the belly. Abdominal structures like the gallbladder, kidneys, and liver can be seen and potential issues detected via transmission and reflection of the ultrasound waves.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): It's a form of testing that helps doctors figure out what's wrong with organs in the belly, such the gallbladder, liver, and pancreas, and then figure out how to fix it.
Digestive System Treatment
- Abdominal Surgery: Conditions including cholecystitis, appendicitis, colon or stomach cancer, and similar emergencies necessitate surgical intervention.
- Pyloromyotomy: Surgery for hypertrophic pyloric stenosis entails making a lengthy incision from the anterior pyloric wall down to the submucosa.
- Sengstaken-Blakemore (SB) Tube: Surgical procedures can be performed using either minimally invasive techniques (such as laparoscopic or keyhole surgery, in which a camera is inserted into a succession of tiny incisions) or the more traditional, open approach (in which a major incision is made to access the target area).
- Endoscopy: The instruments on an endoscope can be used to treat a variety of conditions, including cancer and bleeding in the rectal area.
- Ascitic Tapping: Patients who suffer from cirrhosis and severe liver disease are typically candidates for the procedure known as paracentesis. When acute ascites, a swelling in the belly brought on by liver failure, creates discomfort, this operation, in which a needle is inserted under the skin and used to extract fluid from the abdomen, can be performed.
- Gastric Ligation: a surgical procedure that involves either the closure of the arteries that are bleeding or the wedge resection of the stomach that contains the arteriole.
- Gastropexy: The surgical repair of an esophageal hiatal hernia is typically an option for patients who have been diagnosed with a severe case of the condition. a procedure that involves first detorsion of the stomach, then its subsequent fixation.
- Flatus Tube: It is used to reduce the amount of gas that has built up in the stomach as a result of a variety of illnesses and acid production.Colonoscopic Detorsion: It is a therapeutic method for easing the volvulus production in the stomach, and its purpose is to reduce the symptoms of the condition.
- Endoscopic Banding Or Injection Sclerotherapy: The procedure known as endoscopic sclerotherapy (EST) involves injecting a sclerosant directly into a varicose vein in order to produce thrombosis and ultimately obliterate the vein.
- Balloon Tamponade: This tamponade balloon catheter has two lumens, allowing saline to be injected into the balloon while also draining blood from the liver. These days, balloon tamponade is rarely utilised to halt variceal bleeding.
- TIPSS(Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Stent Shunting): Under imaging guidance, a connection is made between the portal vein and the hepatic vein in a surgery known as transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS).
- Open Cholecystectomy: A gallbladder removal through an abdominal incision is referred to as an open gallbladder removal. This type of surgery removes the gallbladder.
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is also known as 'minimally invasive cholecystectomy' since it only requires making four very small incisions in the abdominal wall and use a camera to execute the procedure.
- Lobectomy: surgery in which whole or part of the liver is removed. It's a frequent treatment for cancer.
Digestive System Medicines
- Analgesics for pain in Digestive System: Medications like aspirin, ibuprofen, diclofenac sodium and acetaminophen are examples of analgesics that can alleviate some of the pain associated with gastrointestinal inflammation. Paracetamol and naproxen are two further examples of analgesics.
- Antibiotics for infection in Digestive System: bacterial illnesses of the parts of the gut are treated with antibiotics. Staining Gram-positive bacteria: Vancomycin resistance with Gram-negative bacteria: Ceftriaxone, in conjunction with either azithromycin or doxycycline, if Gram stain does not appear to be exposing Vancomycin Ceftriaxone.
- Nutritional supplements for reducing pain in Digestive System: When dealing with microcytic or macrocytic anaemia, it is recommended to provide iron, folic acid, ferrous sulphate, Paris ascorbate, and zinc to stimulate red cell growth. It's also helpful for treating sideroblastic anaemia.
- Supplements for promotion of growth at the time of fracture of Digestive System: Nutritional supplements, such glucosamine and chondroitin, are prescribed by doctors to relieve joint discomfort and speed recovery. To ensure healthy bone development and metabolism, vitamin D and calcium supplements are prescribed based on age and nutritional needs.
- Antivirals for treating infection of Digestive System: Although these drugs are powerful against bacterial and fungal lung infections, they have no impact on the virus that causes bronchitis. Included in this group of medicines are amantadine, ribavirin, acyclovir, ganciclovir, and foscarnet.
- Chemotherapeutic medicines for Digestive System: While liver cancer is ultimately fatal, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are effective therapies. The liver may be surgically removed or transplanted if the condition is life-threatening.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the 5 diseases of the digestive system?
How can I improve my digestive system?
What is the fastest way to cure digestive problems?
What are the 5 ways that you can improve your digestion?
What is the cause of digestion?
What symptoms affect the digestive system?
Can digestive disorders be cured?
Table of content
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors