Epidural Hematoma: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Cost
Last Updated: Feb 18, 2023
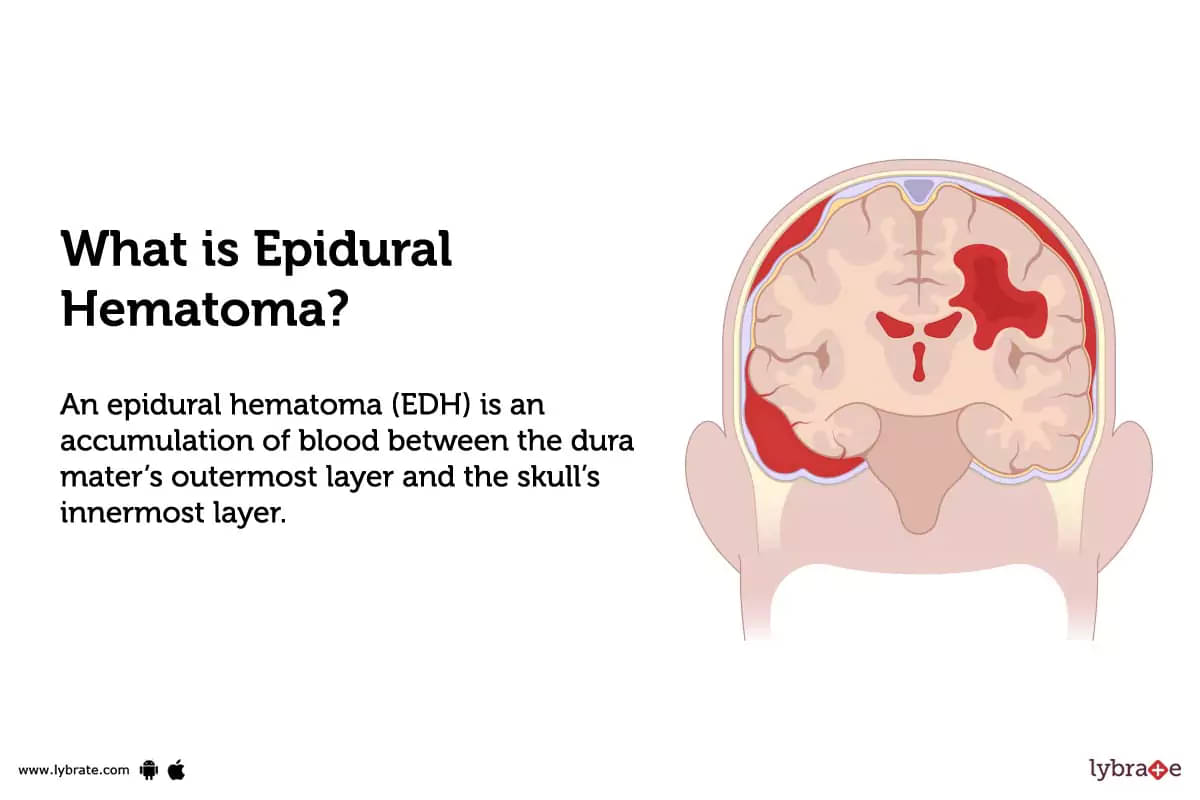
What is Epidural Hematoma?
An epidural hematoma (EDH) is an accumulation of blood between the dura mater's outermost layer and the skull's innermost layer.
Types of Epidural Hematoma
Epidural hematomas are classified into two categories; acute and chronic.
- Acute Epidural Hematoma:Acute epidural hematomas occur when a blow to the head causes bleeding between the skull and dura mater, which is the outermost layer of tissue covering the brain. This type of hematoma typically occurs when an object strikes the head with high velocity, such as a gunshot or a motor vehicle accident.
- Chronic Epidural Hematoma:Chronic epidural hematomas are more rare than acute epidural hematomas and usually develop slowly over time due to small tears in blood vessels in or around the skull.
What causes Epidural Hematoma?
- It is most commonly caused by a traumatic head injury, such as a car accident or fall, that tears a nearby artery.
- EDH can also be caused by bleeding disorders and certain surgeries.
- Also sometimes the cause of the condition can't be identified.
What are the symptoms of Epidural Hematoma?
- Severe headache that is sudden and worsens over time.
- Vomiting and nausea.
- Changed mental state, including confusion, sleepiness, and loss of consciousness.
- One-sided facial or bodily weakness or paralysis.
- Speech difficulties unequal pupils sizes.
- Seizures.
How can you prevent Epidural Hematoma?
- Wear a helmet while participating in contact sports or activities that involve a risk of head injury.
- Avoid activities like diving and skiing where the head is at risk of striking the ground or other objects.
- To reduce the danger of head injury while interacting with dangerous materials and machines, observe all applicable safety regulations.
- Seek immediate medical attention after suffering a blow to the head, even if symptoms are not severe or palpable at the time.
Epidural Hematoma - Diagnosis and Tests
- Ct scan: A head CT scan is the most frequent diagnostic procedure for epidural hematoma. Blood outside the brain's blood vessels may be detected by CT scan.
- Neurological examination: A neurological examination and Glasgow Coma Scale assessment to evaluate the patient's level of consciousness and neurological function.
- Blood test : Blood tests, such as a coagulation panel, may be ordered to check for any underlying bleeding disorders that may have contributed to the hematoma.
- X ray: A skull x-ray may be performed to check for any fractures in the skull that may have caused the hematoma.
- Angiography: Angiography, an imaging test that uses a contrast dye to visualize blood vessels, may be used to determine if there is any abnormal blood flow in the brain.
- Lumbar puncture: A lumbar puncture (spinal tap) may be performed to check for any blood in the cerebrospinal fluid, which can be an indication of an epidural hematoma.
What are possible complications of Epidural Hematoma?
- Intense headaches, stiffness of the neck, nausea and vomiting.
- Weakness or numbness in extremities.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Changes in vision or hearing.
- Seizures
- Coma or death.
Home Remedies for Epidural Hematoma?
- Drink water: To wash out toxins and avoid dehydration, consume a lot of water.
- Herbal supplements: Taking herbal supplements such as turmeric, ginger, ashwagandha, shatavari, and guggul to reduce inflammation.
- Balance diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to provide the body with essential nutrients for healing.
- Yoga: Practicing yoga and meditation to reduce stress levels which can aggravate symptoms of an epidural hematoma.
- Oil massage : Massaging the affected area with ayurvedic oils such as sesame oil and coconut oil to relieve pain and promote circulation in the area.
- Antioxidant: Taking antioxidant-rich foods such as berries, nuts, seeds, green tea etc., that help reduce inflammation in the body due to an epidural hematoma.
What to eat in Epidural Hematoma?
- Eating a balanced diet is important for people with epidural hematoma, as the body needs essential nutrients to help the brain heal and recover from injury.
- Whole grains, legumes, lean meats, fish, nuts, and seeds are all good examples of protein and fiber-rich foods to include into your daily diet.
- Low-fat dairy products may also be beneficial for providing calcium and other nutrients that can help support recovery from an epidural hematoma.
- It is also important to drink plenty of fluids to keep the body hydrated while it is healing from an epidural hematoma.
What not to eat in Epidural Hematoma?
- Steer clear of processed and fast foods, canned soups, cured meats, and sauces, since they are all rich in sodium.
- Be cautious with your alcohol consumption, since doing so may raise the risk of bleeding and strain on the brain.
- You should stay away from acidic or spicy meals since they might irritate your digestive tract.
- If a patient is taking anticoagulant medications, they should avoid leafy green vegetables or vitamin K-rich foods like kale and spinach.
- Avoid eating high-fat or fried foods which can be difficult to digest after a head injury and lead to nausea/vomiting.
- Avoid caffeine as it can interfere with sleep patterns which are important for recovery after a head injury.
Epidural Hematoma Treatment
- Emergency treatment: Immediate surgical evacuation of the hematoma and decompression of the brain tissue underneath it.
- Rehabilitation: Restoring physical and cognitive skills via physical, occupational, and speech therapy.
- Medication: Anticonvulsants to prevent seizures, antibiotics to treat infection, diuretics to reduce pressure in the brain, steroids to reduce swelling in the brain tissue, anti-anxiety medications and pain relievers for comfort.
- Burr hole evacuation: This is a surgical procedure to remove the pooled blood and relieve pressure on the brain caused by an epidural hematoma.
- Craniotomy: Craniotomy entails creating surgical incision in the skull and eliminating a portion of bone in order to access and expel the hematoma.
- Endoscopic surgery: This procedure uses a special instrument called an endoscope to visualize and evacuate the hematoma from within the skull.
- Stereotactic surgery: In this technique, a computer-generated image of the brain is used to guide small, precise instruments into place around the hematoma with minimal disruption of surrounding tissue
Which doctor to consult for Epidural Hematoma?
In most cases, a Neurosurgeon should be consulted for an EDH. This professional is qualified to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the neurological system, including the brain, spine, nerves, and muscles.
Which are the best medicines for Epidural Hematoma?
- Anti-coagulants: Anti-coagulant medications such as aspirin, clopidogrel, and warfarin can be prescribed to help prevent further bleeding in patients with epidural hematoma.
- Anticonvulsants: To prevent seizures, anticonvulsant medications may be prescribed to patients with epidural hematoma, such as phenytoin or levetiracetam.
- Steroids: Steroids can be used to reduce swelling around the brain caused by an epidural hematoma and help improve overall brain function.
- Diuretics: to reduce cerebral edema, or swelling of the brain.Bumetanide (Bumex) Ethacrynic acid (Edecrin) Furosemide (Lasix) Torsemide (Soaanz) are some examples
- Mannitol: a medication that can be used to reduce brain swelling by drawing water out of the brain and into the bloodstream.
- Nimodipine: a medication that can be used to improve blood flow to the brain and reduce the risk of ischemic injury.
How long does it take to recover from Epidural Hematoma?
- Recovery from EDH depends on several factors, such as the size and location of the hematoma, and how quickly treatment is received.
- Typically, individuals with small EDHs need between one to three weeks to heal.
- Larger EDHs may require ongoing physical therapy for up to six months or more in order to restore lost functioning.
Are the results of the treatment permanent?
- The results of treatment for epidural hematoma can vary depending on the severity of the injury and the promptness of medical intervention.
- In general, prompt surgical intervention can prevent permanent neurological damage and improve the chances of a full recovery.
- However, if the injury is severe and treatment is delayed, permanent neurological damage may occur.
What are post-treatment guidelines?
- After treatment for an epidural hematoma, the patient should be monitored closely for any signs of complications, such as infection, nerve damage, or increased intracranial pressure.
- Patients should also be advised to rest and avoid strenuous activity until their condition is fully resolved.
- They should also be monitored for any changes in neurologic function, such as headache or altered mental status.
- Additionally, follow-up imaging studies may be necessary to confirm that the hematoma has been successfully treated and to monitor for recurrence.
What is the cost of Epidural Hematoma treatments in India?
Most of the time, prices can be anywhere from a few thousand rupees to several lakhs.
What are side-effects of Epidural Hematoma treatments?
- Surgery: Potential risks include infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and anesthesia-related problems.
- Medication: Dizziness, headache, rash, nausea, vomiting, and changes in mental state are all possible adverse reactions.
- Physical Therapy: Possible side effects include muscle soreness or stiffness due to increased physical activity.
- Rehabilitation: Possible side effects include fatigue due to increased physical activity and difficulty with memory or concentration due to brain injury.
Epidural Hematoma - Outlook/ Prognosis
If you are suffering from any complications relating to Epidural Hematoma then you should consult a doctor nearby as they can cause complications like 'brain damage, permanent neurological deficits' in which treatment courses can range from a few months to years depending on the severity of the situation.
Table of content
15+ Years of Surgical Experience
All Insurances Accepted
EMI Facility Available at 0% Rate
Find Neurologist near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors